Economic Consequences of International Monetary Regulation Changes
Navigating the Economic Landscape: International Changes in Monetary Regulations
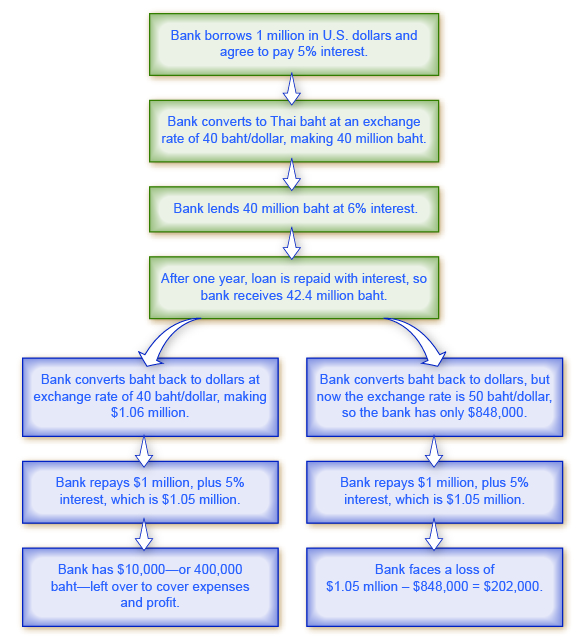
The intricate dance of global economics is continually influenced by a multitude of factors. One such pivotal element is the constant evolution of monetary regulations on the international stage. In this article, we delve into the economic consequences of these changes and their far-reaching impacts.
The Ripple Effect on Global Trade and Commerce
Changes in international monetary regulations have a profound impact on global trade and commerce. Alterations in exchange rates, trade agreements, and currency valuations can lead to shifts in the competitive landscape. Exporters and importers must adapt to these changes, affecting supply chains and ultimately influencing the cost of goods and services worldwide.
Investor Sentiment and Financial Markets
Investors are particularly sensitive to changes in monetary regulations as they directly affect financial markets. Currency fluctuations and adjustments in interest rates can significantly impact investment strategies and portfolio performances. The uncertainty stemming from regulatory changes often leads to shifts in investor sentiment, influencing market trends and volatility.
Currency Valuations and Exchange Rate Risks
One of the direct consequences of international monetary changes is the fluctuation in currency valuations. Exchange rates become more volatile, introducing new dimensions of risk for businesses engaged in international transactions. Companies must carefully manage and hedge against these risks to maintain stability in their financial operations.
Inflationary Pressures and Central Bank Policies
Changes in monetary regulations can have direct implications on inflationary pressures within countries. Central banks often adjust interest rates and money supply to achieve economic stability. However, the effectiveness of these policies can vary, leading to challenges in managing inflation and its cascading effects on consumer purchasing power and overall economic health.
Global Financial Stability and Systemic Risks
The interconnectedness of the global financial system means that changes in monetary regulations can introduce systemic risks. Events in one part of the world can quickly transmit shockwaves across borders, affecting financial institutions and markets. Policymakers must carefully balance the need for regulatory adjustments with the potential destabilizing effects on the broader financial ecosystem.
Impacts on Developing Economies and Emerging Markets
Developing economies and emerging markets are often more susceptible to the consequences of international changes in monetary regulations. These regions may face challenges in maintaining economic stability, attracting investments, and managing debt levels. The resulting disparities in economic conditions can exacerbate global inequalities.
Trade Balances and Current Account Deficits
International monetary changes can influence a country’s trade balance and current account deficits. Fluctuations in exchange rates impact the competitiveness of exports and imports, affecting the overall balance of trade. Persistent current account deficits can lead to economic imbalances and vulnerability to external shocks.
Technological Innovations in Financial Services
The landscape of financial services is evolving rapidly, and international monetary changes play a role in shaping this transformation. Innovations such as digital currencies and blockchain technology are gaining prominence, challenging traditional banking systems and providing new avenues for cross-border transactions. These advancements bring both opportunities and challenges for the global economic system.
Looking Ahead: Adaptation and Collaboration
As the world grapples with the economic consequences of international changes in monetary regulations, adaptation and collaboration are key. Policymakers, businesses, and investors must remain vigilant, fostering an environment that supports economic resilience and sustainability. The ability to navigate the complexities of the global economic landscape will be crucial for ensuring a stable and prosperous future.
For a more comprehensive understanding of the economic consequences of international changes in monetary regulations, explore this detailed study here. The study provides insights into case analyses and potential strategies to navigate the evolving global economic landscape in the wake of regulatory shifts.
Global Integration Impact: Economic Dynamics Unveiled

Unveiling the Economic Dynamics: Effects of Global Economic Integration
In an era marked by increased interconnectedness, the effects of global economic integration extend far beyond borders, shaping the economic landscape in profound ways. From trade and investment to cultural exchange, the impact of global integration on economies is multifaceted, presenting both opportunities and challenges.
Trade Liberalization and Economic Growth
One of the primary drivers of global economic integration is trade liberalization. Reduced trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, foster increased international trade. This surge in cross-border commerce contributes to economic growth as nations gain access to new markets, diverse products, and a broader consumer base. The reciprocal nature of trade agreements creates a symbiotic relationship, fueling economic expansion.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Flows: A Catalyst for Development
Global economic integration attracts substantial Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows. Companies seek opportunities beyond their domestic markets, establishing operations and investing in foreign countries. This influx of investment acts as a catalyst for economic development, driving innovation, creating jobs, and fostering technology transfer. However, managing the balance between attracting investment and protecting national interests becomes a key challenge for governments.
Supply Chain Interdependence: Efficiency vs. Vulnerability
The integration of global supply chains is a hallmark of economic globalization. While this interconnectedness enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness, it also introduces vulnerabilities. Disruptions in one part of the world can have cascading effects on production and distribution globally. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the fragility of highly interdependent supply chains, prompting a reevaluation of resilience and risk management strategies.
Technological Transfer and Innovation Acceleration
Global economic integration facilitates the transfer of technology and accelerates innovation. Companies operating in diverse markets bring unique perspectives and technological advancements to different regions. This cross-pollination of ideas contributes to global progress and the diffusion of cutting-edge technologies. However, managing the ethical dimensions of technology transfer and ensuring fair competition remain critical considerations.
Cultural Exchange and Market Diversity
Beyond the economic realm, global integration fosters cultural exchange. Consumers gain access to a diverse array of products and services from around the world, enriching their cultural experiences. This diversity in the marketplace encourages innovation and competition, as companies strive to meet the preferences and demands of a global consumer base. Cultural exchange becomes a natural byproduct of economic interconnectedness.
Income Inequality and Social Disparities
While global economic integration generates wealth and opportunities, it also contributes to income inequality and social disparities. The benefits of integration are not evenly distributed, and certain segments of society may face job displacement or wage stagnation. Addressing the social implications of economic integration requires thoughtful policies that promote inclusivity, education, and social safety nets.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainability Challenges
The intensification of global economic activities has environmental ramifications. Increased production and transportation contribute to carbon emissions, deforestation, and resource depletion. Achieving sustainable development amidst global integration necessitates a focus on environmentally responsible practices, renewable energy sources, and international cooperation to address shared environmental challenges.
Financial Market Dynamics: Risks and Opportunities
Financial markets are highly influenced by global economic integration. While integration provides opportunities for diversification and investment, it also exposes markets to contagion risks. Economic events in one part of the world can quickly impact financial markets globally. Effective risk management, international regulatory cooperation, and financial resilience become imperative in navigating the dynamics of integrated financial systems.
Policy Coordination and Governance Challenges
Managing the effects of global economic integration requires effective policy coordination and governance at both national and international levels. Nations must strike a balance between reaping the benefits of integration and safeguarding their domestic interests. Issues such as tax avoidance, regulatory arbitrage, and intellectual property rights necessitate collaborative efforts to establish fair and equitable global economic governance.
Shaping a Balanced Future: Navigating Global Integration
In conclusion, the economic effects of global economic integration are far-reaching and complex. Striking a balance between the opportunities and challenges requires proactive policies, ethical considerations, and a commitment to sustainable development. Navigating the evolving landscape of global integration necessitates adaptability, cooperation, and a shared vision for a more inclusive and balanced economic future.
Explore more about the Economic Effects of Global Economic Integration and the intricate dynamics shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Fallout: Natural Disasters’ Impact

Global Economic Fallout: Unraveling the Impact of Natural Disasters
Natural disasters wield substantial influence over the global economy, triggering a cascade of effects that extend far beyond immediate destruction. This article delves into the intricate dynamics of how natural disasters leave an indelible mark on the world economy, examining the challenges faced, strategies for resilience, and the imperative for collective action.
Immediate Economic Disruptions: The Unavoidable Shockwaves
When natural disasters strike, the immediate economic disruptions are profound. Physical infrastructure damage, disrupted supply chains, and the halt in production all contribute to a sudden and substantial economic shock. The costs associated with rebuilding, coupled with the loss of productivity, set the stage for a challenging recovery period.
Supply Chain Disruptions: The Ripple Effect Across Industries
Natural disasters disrupt global supply chains, affecting industries far beyond the epicenter. Interruptions in the production of critical components can paralyze industries worldwide. The interconnected nature of modern supply chains means that a single disruption can have a ripple effect, impacting manufacturing, distribution, and ultimately, the global economy.
Impact on Global Trade: A Stifled Flow of Goods and Services
Natural disasters impede global trade, affecting the movement of goods and services across borders. Ports may be damaged, transportation networks disrupted, and logistics infrastructure compromised. This hinders the smooth flow of international trade, leading to a decline in both imports and exports, further exacerbating the economic fallout.
Insurance Costs and Financial Burdens: A Strain on Economies
The financial burden of natural disasters extends to insurance costs, with affected businesses and individuals filing claims for damages. The cumulative effect on insurance industries can lead to higher premiums globally. Governments, facing increased financial burdens, must allocate resources for reconstruction efforts, diverting funds from other essential areas such as education and healthcare.
Human Capital and Labor Market Challenges: A Social-Economic Conundrum
Natural disasters create significant challenges in the labor market. Displaced workers, damaged infrastructure, and disrupted education systems contribute to a temporary but impactful decline in human capital. The loss of skilled labor and workforce productivity compounds the economic strain, posing long-term challenges to the affected regions and reverberating globally.
Investor Confidence and Financial Markets: The Oscillating Pendulum
Natural disasters shake investor confidence, leading to fluctuations in financial markets. Stock markets may experience downturns, currency values may fluctuate, and investor sentiment becomes increasingly cautious. The uncertainties associated with the aftermath of natural disasters contribute to a volatile economic environment on a global scale.
Long-Term Economic Implications: The Lingering Shadows
While the immediate impact of natural disasters is palpable, the long-term economic implications are equally significant. Regions struggling with reconstruction may experience a prolonged economic downturn. Disruptions in education and healthcare can lead to a less skilled and less healthy workforce, impacting productivity for years to come.
Strategies for Economic Resilience: Navigating the Aftermath
To build economic resilience in the face of natural disasters, nations must adopt strategic measures. Investing in robust infrastructure that can withstand disasters, implementing effective early warning systems, and developing comprehensive disaster recovery plans are essential. Global collaboration in sharing best practices and resources is pivotal for a collective response to these challenges.
Technology and Innovation: Paving the Path to Resilience
Technology and innovation play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of natural disasters. Advanced early warning systems, data analytics for risk assessment, and innovations in construction and infrastructure contribute to minimizing damage. The integration of technology fosters adaptive strategies that enhance resilience and recovery efforts.
The Imperative for Collective Action: A Global Responsibility
Natural disasters underscore the need for collective action on a global scale. Nations, international organizations, and businesses must collaborate to build resilient infrastructures, share knowledge and resources, and develop sustainable practices. Collective efforts are essential to not only mitigate the impact of natural disasters but also to build a more resilient and interconnected global economy.
A Call to Action: Nurturing a Resilient Global Economy
In conclusion, the impact of natural disasters on the global economy is a multifaceted challenge that demands proactive and collaborative solutions. From immediate disruptions to long-term economic implications, the fallout requires strategic planning, innovation, and a commitment to global resilience. As we navigate an era of increasing climate-related events, nurturing a resilient global economy becomes a shared responsibility for the well-being of current and future generations.
To explore more about the Impact of natural disasters on the global economy, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Global Housing Policy Shifts: Economic Ramifications

Introduction:
The global landscape of housing policies is undergoing transformative changes, with profound implications for the world economy. This article explores the economic ramifications of shifts in housing policies, delving into how these changes impact nations, businesses, and individuals.
Housing Market Dynamics:
Changes in housing policies reverberate through the housing market, influencing supply, demand, and pricing dynamics. Policies that encourage affordable housing can stimulate economic activities by making homeownership more accessible. Conversely, shifts that limit housing options may pose challenges for both the real estate industry and aspiring homeowners, affecting economic aspects of housing transactions.
Investments and Economic Growth:
Housing policies play a crucial role in shaping investment patterns and overall economic growth. Policies that incentivize real estate investments can contribute to economic expansion by driving construction activities, creating jobs, and fostering a vibrant housing market. However, policies that create uncertainty or impose restrictions may dampen investor confidence, potentially impacting economic growth.
Social and Economic Equity:
Housing policies are instrumental in addressing social and economic equity. Policies that promote fair housing practices and provide affordable housing options contribute to a more equitable society. Ensuring access to housing for diverse socioeconomic groups is not only a social imperative but also a factor influencing economic stability and inclusivity.
Mortgage Markets and Financial Stability:
The health of mortgage markets is closely tied to housing policies. Changes in policies related to lending practices and mortgage regulations influence financial stability. Policies that strike a balance between facilitating homeownership and preventing excessive risk-taking contribute to a robust and stable financial system, fostering economic resilience.
Urban Development and Infrastructure:
Housing policies intersect with urban development and infrastructure planning. Policies that prioritize sustainable and well-planned urban growth can enhance economic development by creating efficient living spaces, reducing commuting times, and improving overall infrastructure. Smart housing policies align with broader urban development goals, contributing to economic efficiency and quality of life.
Housing Affordability and Consumer Spending:
Affordable housing is linked to consumer spending patterns. Policies that address housing affordability positively impact disposable income, allowing individuals to allocate resources to other areas of the economy. On the contrary, housing policies that lead to inflated prices may constrain consumer spending, affecting the overall economic landscape.
Rental Market Dynamics and Flexibility:
Policies governing the rental market also play a role in economic outcomes. Rental policies that strike a balance between tenant protections and landlord incentives contribute to a stable rental market. A well-regulated rental sector provides housing flexibility, which is essential for a dynamic and adaptable workforce, ultimately influencing economic productivity.
Government Expenditure and Social Programs:
Changes in housing policies influence government expenditure, particularly in social programs related to housing. Policies that prioritize social housing programs may lead to increased public spending. Balancing these expenditures with broader economic considerations is essential to ensure the effectiveness of social programs while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
International Real Estate Investments:
Global economic implications extend to international real estate investments. Changes in housing policies in one country can influence the decisions of international investors. Policies that create a favorable environment for real estate investments may attract foreign capital, contributing to economic growth and cross-border economic interactions.
For more insights into the global economic implications of changes in housing policies, visit Global economic implications of changes in housing policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the global economic implications of changes in housing policies are multifaceted, influencing various facets of economies worldwide. Striking a balance between promoting housing affordability, encouraging investment, and ensuring social equity is crucial for fostering resilient and inclusive economic growth. As nations navigate these policy shifts, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities become essential in shaping a housing landscape that supports both economic prosperity and societal well-being.
Social Media SEO Unleashed: Boosting Visibility and Engagement

Navigating the Social Media Landscape with SEO
In the dynamic realm of digital marketing, the integration of SEO strategies for social media is paramount. This article explores the symbiotic relationship between SEO and social media, offering insights into optimizing your social media presence for enhanced visibility and engagement.
Understanding the Intersection of SEO and Social Media
While SEO traditionally focuses on search engine rankings, its principles extend seamlessly into the realm of social media. The synergy between SEO and social media lies in the ability to leverage optimized content to boost visibility across diverse platforms.
Crafting SEO-Optimized Social Media Profiles
The foundation of effective social media SEO begins with optimized profiles. Ensure that your social media profiles are complete, accurate, and aligned with your brand. Utilize relevant keywords in your bio and description to enhance discoverability and convey your brand message effectively.
Leveraging Keywords in Social Media Content
Keywords are the backbone of SEO, and their strategic use extends to social media. Integrate relevant keywords into your social media posts, captions, and hashtags. This not only improves the searchability of your content within each platform but also aligns with search engine algorithms.
Encouraging Social Sharing and Backlinks
Social sharing is a powerful signal for search engines. Encourage your audience to share your social media content by creating shareable and engaging posts. Additionally, the backlinks generated from shared content contribute to your website’s authority, positively impacting SEO.
Optimizing Multimedia for Social and Search
Multimedia elements, including images and videos, play a crucial role in social media engagement. Optimize your multimedia content by adding descriptive alt text, captions, and relevant keywords. This not only enhances accessibility but also contributes to better search engine visibility.
Strategically Using Hashtags for Discoverability
Hashtags are a prominent feature across various social media platforms. Strategically use hashtags relevant to your content and industry. Research popular and trending hashtags to maximize your content’s discoverability and engagement within the social media landscape.
Promoting User Engagement for Algorithmic Favor
Social media algorithms prioritize content with higher engagement. Foster user interaction by responding to comments, asking questions, and running polls. Increased engagement not only boosts your content’s visibility on social media but also positively influences search engine rankings.
Integrating Social Proof into Your SEO Strategy
Social proof, such as positive reviews, testimonials, and user-generated content, can significantly impact your online reputation and SEO. Encourage satisfied customers to share their experiences on social media, contributing to a positive brand image and influencing search engine perception.
Analyzing Social Media Insights for Optimization
Regularly analyze social media insights to understand the performance of your content. Identify high-performing posts, audience demographics, and engagement metrics. Use these insights to refine your content strategy, aligning it with both social media trends and SEO goals.
Staying Current with Social Media and SEO Trends
The landscape of social media and SEO is dynamic, with trends evolving rapidly. Stay informed about the latest updates and features on social media platforms. Align your strategy with emerging trends to maintain a competitive edge and ensure your brand remains visible and engaging.
Elevating Your Social Media Presence with SEO Strategies
To delve deeper into the world of SEO for social media and implement effective strategies, visit SEO for social media. Navigate the intersection of SEO and social media, optimize your content for increased visibility, and position your brand for success in the evolving digital landscape.
Boosting Shopify SEO: Strategies for E-Commerce Success

Unveiling the Secrets: SEO for Shopify Stores
E-commerce success hinges on effective online visibility, and mastering SEO for Shopify stores is paramount. In this guide, we’ll explore essential strategies to boost your Shopify store’s search engine optimization.
Crafting SEO-Optimized Product Descriptions
The heart of any e-commerce store lies in its products, and optimizing product descriptions is key to attracting search engine attention. Use relevant keywords naturally in your product descriptions to enhance search engine visibility. A well-crafted product description not only informs potential buyers but also appeals to search algorithms.
Harnessing the Power of Shopify SEO Apps
Shopify offers a range of SEO apps designed to simplify and enhance your optimization efforts. Explore apps that assist in keyword research, on-page SEO, and analytics. By integrating these tools into your Shopify store, you can streamline your SEO tasks and gain valuable insights into your website’s performance.
Strategic Use of Shopify Tags
Tags in Shopify serve as valuable metadata, helping search engines categorize and understand your content. Implement strategic tagging for products, blog posts, and pages. This enhances the organization of your site and contributes to improved search engine rankings.
Optimizing Product Images for SEO
In the world of e-commerce, visuals matter. Optimize your product images for SEO by using descriptive filenames and alt text. Search engines consider image information, and a well-optimized image can contribute to higher rankings. Additionally, fast-loading images improve user experience, further benefiting SEO.
Building a User-Friendly Navigation Structure
A seamless navigation structure is crucial for both users and search engines. Organize your products into logical categories and create a clear menu structure. This not only enhances user experience but also aids search engine crawlers in efficiently indexing your Shopify store.
Leveraging Customer Reviews for SEO
Customer reviews are a powerful tool for e-commerce SEO. Encourage customers to leave reviews for your products. User-generated content adds valuable keywords and builds trust with potential buyers. Search engines often favor pages with authentic customer reviews, boosting your store’s credibility.
Implementing Schema Markup on Shopify
Enhance the visibility of your Shopify store in search results by implementing schema markup. This structured data provides additional information to search engines, improving the way your content is displayed. Utilize schema markup for products, reviews, and other relevant information on your site.
Prioritizing Mobile Optimization
With a growing number of users shopping on mobile devices, mobile optimization is non-negotiable. Ensure that your Shopify store has a responsive design that adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes. Mobile-friendly websites receive preferential treatment in search engine algorithms.
Streamlining Checkout for Improved SEO
A smooth and efficient checkout process not only improves user experience but can also positively impact SEO. Reduce cart abandonment rates by simplifying the checkout process. The faster users can complete their purchases, the more likely they are to convert, contributing to improved SEO metrics.
SEO for Shopify Stores: A Continuous Journey
SEO for Shopify stores is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regularly audit your website, monitor analytics, and stay informed about industry trends. Evolve your SEO strategies as your store grows and as search engine algorithms evolve.
To delve deeper into the world of SEO for Shopify stores, explore effective strategies and tools at SEO for Shopify stores. Elevate your e-commerce store’s online visibility and set the stage for long-term success in the competitive digital landscape.
World Energy Regulation Shifts: Economic Transformations

Introduction:
The world is undergoing transformative changes in energy regulations, and these shifts have far-reaching economic implications. This article explores the profound impact of changes in energy regulations on the global economy, examining how policies shape energy markets, influence investments, and contribute to broader economic trends.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
One of the primary drivers of changes in energy regulations is the global shift towards renewable energy sources. Policies promoting the use of clean and sustainable energy, such as solar and wind power, contribute to the growth of the renewable energy sector. This revolution not only addresses environmental concerns but also stimulates economic activity by creating jobs and fostering innovation in the renewable energy industry.
Investments in Clean Technologies:
Changes in energy regulations often lead to increased investments in clean technologies. Governments worldwide are incentivizing businesses to adopt energy-efficient practices and invest in green technologies. This trend not only aligns with environmental goals but also stimulates economic growth by driving innovation and creating new markets for clean and sustainable technologies.
Energy Independence and Security:
Strategic changes in energy regulations are aimed at achieving energy independence and security. Policies that diversify energy sources, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and enhance energy efficiency contribute to a more secure and resilient energy infrastructure. This, in turn, has positive economic implications by reducing vulnerabilities to energy supply disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Job Creation in the Energy Sector:
The transition to cleaner energy sources creates job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. Policies supporting the growth of clean energy industries lead to job creation in areas such as solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and green construction. The economic impact extends beyond energy production, positively influencing employment rates and local economies.
Impact on Traditional Energy Industries:
While there is a push towards cleaner energy, changes in regulations also impact traditional energy industries. Policies aimed at reducing reliance on fossil fuels may pose challenges for industries like coal and oil. Governments must navigate a delicate balance between promoting clean energy and managing the economic transition for regions heavily dependent on traditional energy sources.
Smart Grids and Technological Innovation:
Advancements in energy regulations often involve the integration of smart grids and innovative technologies. Policies supporting the development of smart grids enhance energy efficiency, enable better management of energy resources, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. These technological innovations contribute to economic efficiency and the modernization of energy infrastructure.
Global Cooperation in Energy Transition:
Energy regulations are increasingly becoming a focal point of global cooperation. International agreements and collaborations aim to address climate change by transitioning to sustainable energy systems. This cooperation not only has environmental benefits but also fosters economic collaboration between nations, creating opportunities for joint investments and technology exchange.
Consumer Empowerment and Energy Choices:
Changes in energy regulations empower consumers to make sustainable energy choices. Policies that promote consumer access to clean energy options, such as rooftop solar panels or community-based renewable projects, contribute to a decentralized energy landscape. This empowerment enhances economic resilience and supports the growth of local and community-driven energy initiatives.
Economic Challenges and Transition Costs:
While the shift towards cleaner energy is promising, there are economic challenges associated with the transition. Changes in energy regulations may entail upfront costs for businesses and industries adapting to new standards. Governments must carefully manage these challenges to ensure a smooth and economically viable transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Innovation Hubs and Economic Hubs:
Cities and regions that embrace changes in energy regulations become innovation hubs and economic centers. Policies that encourage the development of clean energy technologies attract businesses, research institutions, and skilled professionals. These hubs drive economic growth, creating a ripple effect that extends beyond the energy sector to various industries and services.
For more insights into the world economic impact of changes in energy regulations, visit World economic impact of changes in energy regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, changes in energy regulations are reshaping the global economic landscape. The transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources presents significant opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation. As nations navigate this energy transition, it is crucial to implement policies that balance environmental stewardship with economic considerations, fostering a resilient and prosperous global economy.







