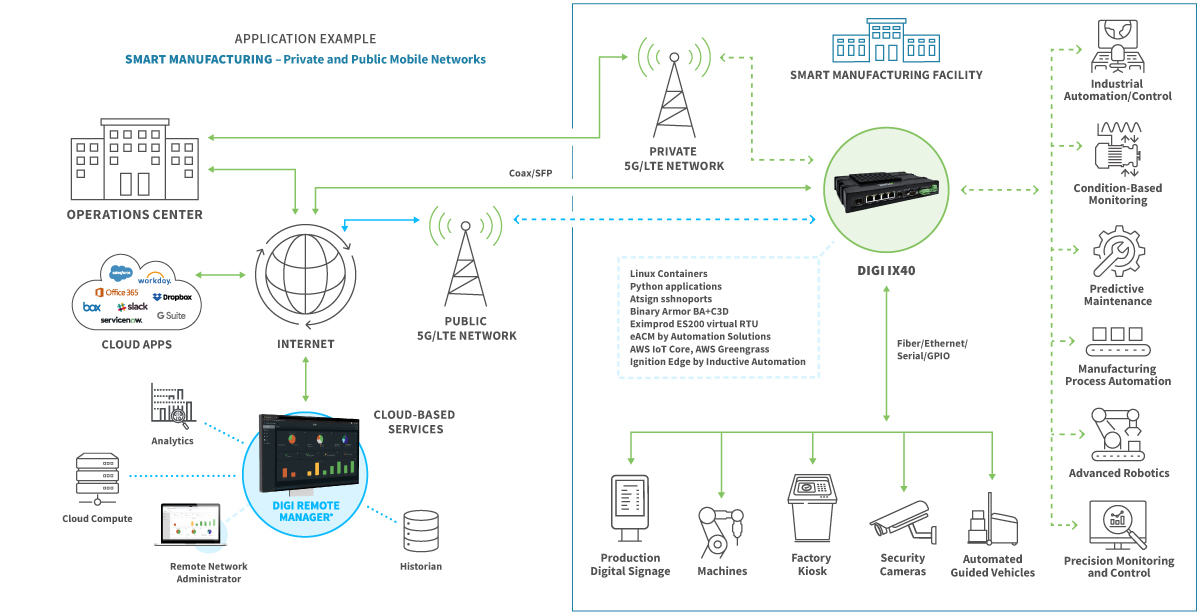
What is a Smart Factory?
Imagine a manufacturing facility where machines talk to each other, predict their own maintenance needs, and adapt to changing demands in real-time. That’s the essence of a smart factory. It leverages cutting-edge technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), big data analytics, and cloud computing to optimize every aspect of the manufacturing process, from design and production to delivery and beyond. These interconnected systems create a flexible, responsive, and highly efficient production environment.
Key Technologies Powering Smart Factories
The transformation to a smart factory isn’t possible without several key technological pillars. IoT devices embedded in machinery and throughout the production line collect vast amounts of data on performance, efficiency, and potential issues. AI and ML algorithms then analyze this data to identify patterns, predict failures, and optimize production parameters. Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure to store and process this massive dataset, allowing for real-time analysis and decision-making. Robotics and automation play a crucial role in executing tasks with precision and speed, further enhancing efficiency. Finally, advanced cybersecurity measures are essential to protect the sensitive data and connected systems within the smart factory.

Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most significant benefits of smart factories is the dramatic increase in efficiency and productivity. By automating repetitive tasks and optimizing resource allocation, manufacturers can reduce waste, minimize downtime, and accelerate production cycles. Real-time data analysis allows for immediate identification and resolution of bottlenecks, preventing costly delays. Predictive maintenance, based on AI analysis of machine data, helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, ensuring continuous operation and maximizing uptime. The overall result is a significant boost in output and a reduction in production costs.
Improved Product Quality and Consistency
Smart factories are not just about speed and efficiency; they also play a vital role in improving product quality and consistency. By monitoring every stage of the manufacturing process with precision, these factories can identify and correct deviations from the desired specifications in real-time. This ensures that every product meets the highest quality standards, minimizing defects and improving customer satisfaction. Moreover, the data collected throughout the process provides valuable feedback for continuous improvement, enabling manufacturers to refine their processes and produce even higher-quality products over time.
Greater Flexibility and Adaptability
In today’s dynamic market, the ability to adapt quickly to changing demands is paramount. Smart factories excel in this area, thanks to their flexible and adaptable nature. They can easily adjust production schedules and reconfigure their operations to meet fluctuating customer orders or respond to unforeseen circumstances. This agility allows manufacturers to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market, ensuring they can quickly adapt to new trends and customer preferences. This enhanced flexibility also enables manufacturers to quickly introduce new products or adapt existing ones to meet evolving needs.
Enhanced Supply Chain Management
Smart factories extend their benefits beyond the factory floor. They facilitate enhanced supply chain management by providing real-time visibility into the entire supply chain. Through data integration and sophisticated analytics, manufacturers gain insights into inventory levels, supplier performance, and potential disruptions. This allows them to optimize logistics, reduce lead times, and ensure a smoother, more efficient supply chain. Predictive analytics can help anticipate potential supply chain issues, allowing manufacturers to proactively mitigate risks and prevent disruptions.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Factories
While the potential benefits of smart factories are immense, the transition to a smart factory isn’t without challenges. The initial investment in new technologies and infrastructure can be substantial. Integrating various systems and ensuring seamless data flow can be complex and require significant expertise. Furthermore, cybersecurity risks need to be carefully considered and addressed to protect sensitive data and prevent disruptions. Finally, the workforce requires training and upskilling to effectively manage and utilize the new technologies.
The Future of Manufacturing: A Collaborative Ecosystem
The future of manufacturing is not just about individual smart factories; it’s about the creation of a collaborative ecosystem. Smart factories will increasingly interact with each other, sharing data and insights to optimize entire supply chains. This collaborative approach will lead to further efficiency gains, enhanced innovation, and a more resilient and sustainable manufacturing sector. The journey towards a fully realized smart factory ecosystem will be evolutionary, but the potential rewards are substantial, promising a future of more efficient, responsive, and sustainable manufacturing. Click here to learn about smart factories in Industry 4.0.