Japan’s April 2025 Interest Rate Decision What it Means
The Context: A Balancing Act for the BOJ
Japan’s economy, in April 2025, will likely be navigating a complex landscape. Global economic uncertainty, potential inflationary pressures, and the ongoing recovery from the pandemic will all be significant factors influencing the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) decision on interest rates. The BOJ will be carefully weighing the need to stimulate growth against the risk of fueling inflation, a delicate balancing act that requires a nuanced understanding of the domestic and international economic climate. The strength of the Yen, export performance, and domestic consumption will all play a key role in shaping the BOJ’s assessment.
Inflationary Pressures and the BOJ’s Target
Inflation will be a paramount concern. While Japan has historically struggled with deflation, the global rise in energy and commodity prices could push inflation above the BOJ’s target of 2%. The BOJ will be analyzing the persistence and breadth of inflation, differentiating between temporary supply-side shocks and more entrenched demand-pull inflation. If inflation proves to be more persistent than anticipated, the pressure to adjust interest rates upwards will mount, even if it risks slowing economic growth.

Global Economic Uncertainty and its Impact
The global economic outlook will heavily influence the BOJ’s decision. A global recession, for example, could significantly impact Japanese exports and dampen domestic demand, potentially necessitating a continuation of low interest rates or even further monetary easing. Conversely, a strong global recovery might embolden the BOJ to normalize its monetary policy more aggressively. Geopolitical factors, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine and its impact on energy prices, will also play a significant role.
Domestic Economic Indicators: A Key Consideration
The BOJ will closely monitor key domestic economic indicators to gauge the health of the Japanese economy. These include GDP growth, employment rates, consumer spending, and business investment. Stronger-than-expected economic performance might lead to a more hawkish stance on interest rates, whereas weaker-than-expected data could necessitate a more accommodative approach. The interplay between these indicators and global economic conditions will be crucial in the decision-making process.
Potential Scenarios and Their Implications
Several scenarios are possible. The BOJ might maintain its current ultra-low interest rate policy if inflation remains subdued and global economic uncertainty persists. Alternatively, a gradual increase in interest rates might be implemented if inflation proves more persistent and the domestic economy shows resilience. A more aggressive rate hike is less likely, given Japan’s history of deflation and the government’s focus on economic growth. Each scenario has distinct implications for various sectors of the economy, including businesses, consumers, and the financial markets.
The Yen and its Influence on the Decision
The value of the Yen is another key factor. A weaker Yen can boost exports but also increases the cost of imported goods, potentially contributing to inflation. The BOJ will need to consider the impact of its interest rate decision on the Yen’s exchange rate. A significant appreciation of the Yen might necessitate maintaining a lower interest rate to support export competitiveness, while a weakening Yen might allow for a more hawkish approach, although the latter carries the risk of imported inflation.
Political Considerations and Public Opinion
While the BOJ strives for independence, political considerations and public opinion cannot be entirely disregarded. The Japanese government’s economic policies and public sentiment towards inflation and economic growth will inevitably influence the BOJ’s approach. A government pushing for rapid economic growth might encourage a more accommodative monetary policy, while concerns about inflation among the public might push the BOJ towards a more cautious approach.
Long-Term Implications and Market Reactions
The April 2025 interest rate decision will have significant long-term implications for the Japanese economy and its financial markets. A shift towards higher interest rates could attract foreign investment and strengthen the Yen, but it also carries risks of slowing economic growth. Conversely, maintaining ultra-low interest rates could support economic growth in the short term but might contribute to asset bubbles and further weaken the Yen. Market reactions will be swift and significant, with potential implications for bond yields, stock prices, and the currency exchange rate. Please click here for information about the Bank of Japan’s interest rate policy in April 2025.
Japan’s Interest Rates 2025 Outlook & Economic Impact
Japan’s Current Monetary Policy Stance
As of late 2023, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) continues to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy, characterized by negative interest rates on some commercial bank reserves and a commitment to yield curve control (YCC). This means the BOJ actively intervenes in the bond market to keep the 10-year government bond yield around zero. This policy, implemented to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation, has been a cornerstone of Japan’s economic strategy for years. However, the effectiveness and long-term sustainability of this approach remain a subject of ongoing debate, both domestically and internationally.
Global Inflationary Pressures and Their Impact on Japan
The global inflationary environment presents a significant challenge to the BOJ’s current policy. While Japan has experienced relatively subdued inflation compared to other developed nations, rising import costs due to global energy prices and supply chain disruptions are putting upward pressure on prices. This inflationary pressure, while currently moderate, could force a recalibration of the BOJ’s approach in the coming years. The balance between supporting economic growth and controlling inflation will be a key consideration for policymakers.
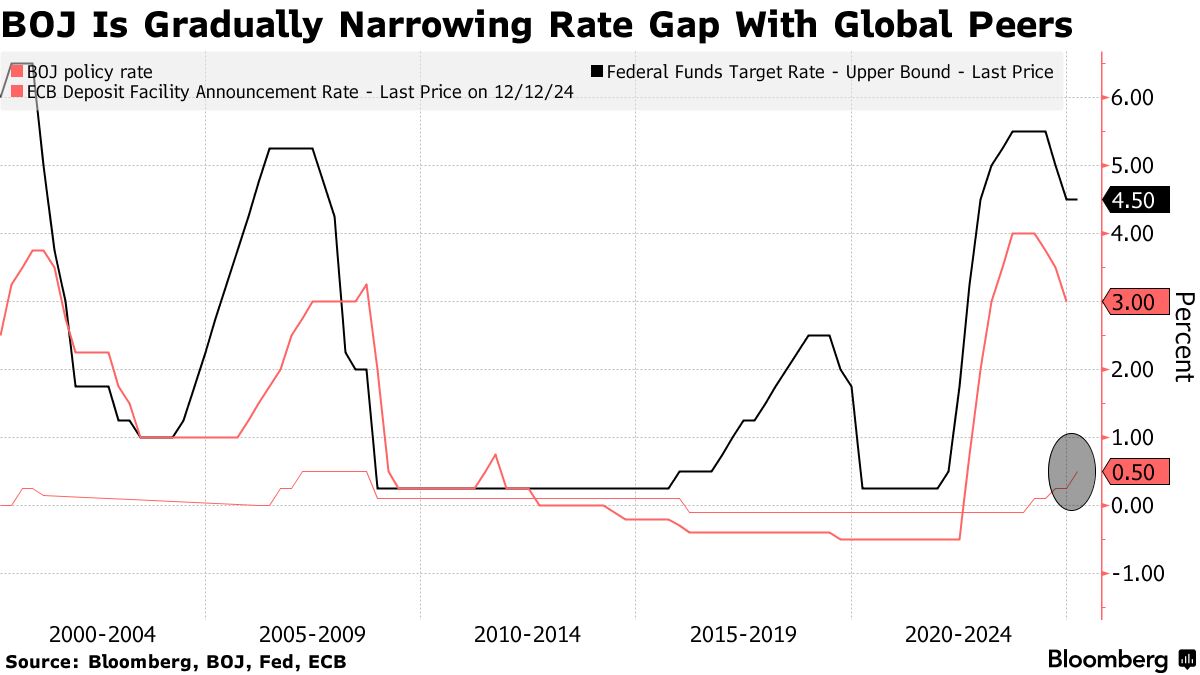
Potential Shifts in BOJ Policy in 2025
Predicting the BOJ’s actions in 2025 is inherently uncertain, but several scenarios are possible. One possibility is a gradual exit from YCC, potentially involving a slow and controlled increase in long-term interest rates. This approach would aim to minimize market disruption while allowing the BOJ to respond to evolving economic conditions. Another scenario might involve a more abrupt shift, driven by unexpectedly high inflation or a significant change in global economic dynamics. A complete abandonment of negative interest rates is also a possibility, though the timing and execution remain highly debated.
The Yen’s Volatility and its Influence on Interest Rates
The value of the Japanese yen plays a crucial role in shaping the BOJ’s policy decisions. A weakening yen can exacerbate inflationary pressures by increasing import costs, making it more difficult for the BOJ to maintain its ultra-loose stance. Conversely, a strengthening yen could provide some breathing room, allowing for a more gradual adjustment of monetary policy. The yen’s volatility will be a key factor influencing the BOJ’s strategy in the lead-up to and throughout 2025.
Economic Growth Projections for Japan in 2025
Japan’s economic growth outlook for 2025 is subject to considerable uncertainty. Factors such as global economic conditions, domestic consumption patterns, and the success of government structural reform initiatives will all play a role. While sustained, albeit moderate, growth is anticipated by many economists, the pace of expansion remains a key unknown. This uncertainty further complicates the BOJ’s task in balancing growth and inflation management.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Businesses and Consumers
Any changes to interest rates in Japan will have significant consequences for businesses and consumers. Higher interest rates could increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially slowing investment and economic growth. Consumers might also face higher mortgage rates and reduced borrowing capacity. Conversely, lower interest rates, while stimulating borrowing and investment, could potentially fuel inflation if not carefully managed. The impact will depend heavily on the magnitude and speed of any interest rate adjustments.
The Role of Government Fiscal Policy
The BOJ’s monetary policy decisions are intertwined with the government’s fiscal policies. Fiscal stimulus measures can support economic growth, potentially reducing the need for aggressive monetary tightening. However, excessive government spending could lead to higher inflation and complicate the BOJ’s efforts to control price increases. The coordination between monetary and fiscal policies will be crucial in navigating the economic challenges of 2025.
Risks and Uncertainties for the Japanese Economy
The outlook for Japan’s economy in 2025 is fraught with uncertainties. Geopolitical risks, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and tensions in the Taiwan Strait, could disrupt global supply chains and trigger further inflationary pressures. Domestic factors such as an aging population and shrinking workforce also present challenges to long-term economic growth. The BOJ will need to carefully consider these risks when formulating its monetary policy strategy.
Potential for Unexpected Events and Their Impact
The economic landscape is inherently unpredictable, and unexpected events could significantly impact Japan’s interest rates and economic performance in 2025. Sudden shifts in global commodity prices, unforeseen geopolitical developments, or unexpected changes in domestic political dynamics could all necessitate rapid adjustments in BOJ policy. The ability of the BOJ to adapt to these unforeseen circumstances will be a critical determinant of Japan’s economic success in the coming years. Learn more about the Bank of Japan’s interest rate policy in 2025 here: [link to tankionlineaz.com]


