Japan’s April 2025 Interest Rate Decision What it Means
The Context: A Balancing Act for the BOJ
Japan’s economy, in April 2025, will likely be navigating a complex landscape. Global economic uncertainty, potential inflationary pressures, and the ongoing recovery from the pandemic will all be significant factors influencing the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) decision on interest rates. The BOJ will be carefully weighing the need to stimulate growth against the risk of fueling inflation, a delicate balancing act that requires a nuanced understanding of the domestic and international economic climate. The strength of the Yen, export performance, and domestic consumption will all play a key role in shaping the BOJ’s assessment.
Inflationary Pressures and the BOJ’s Target
Inflation will be a paramount concern. While Japan has historically struggled with deflation, the global rise in energy and commodity prices could push inflation above the BOJ’s target of 2%. The BOJ will be analyzing the persistence and breadth of inflation, differentiating between temporary supply-side shocks and more entrenched demand-pull inflation. If inflation proves to be more persistent than anticipated, the pressure to adjust interest rates upwards will mount, even if it risks slowing economic growth.

Global Economic Uncertainty and its Impact
The global economic outlook will heavily influence the BOJ’s decision. A global recession, for example, could significantly impact Japanese exports and dampen domestic demand, potentially necessitating a continuation of low interest rates or even further monetary easing. Conversely, a strong global recovery might embolden the BOJ to normalize its monetary policy more aggressively. Geopolitical factors, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine and its impact on energy prices, will also play a significant role.
Domestic Economic Indicators: A Key Consideration
The BOJ will closely monitor key domestic economic indicators to gauge the health of the Japanese economy. These include GDP growth, employment rates, consumer spending, and business investment. Stronger-than-expected economic performance might lead to a more hawkish stance on interest rates, whereas weaker-than-expected data could necessitate a more accommodative approach. The interplay between these indicators and global economic conditions will be crucial in the decision-making process.
Potential Scenarios and Their Implications
Several scenarios are possible. The BOJ might maintain its current ultra-low interest rate policy if inflation remains subdued and global economic uncertainty persists. Alternatively, a gradual increase in interest rates might be implemented if inflation proves more persistent and the domestic economy shows resilience. A more aggressive rate hike is less likely, given Japan’s history of deflation and the government’s focus on economic growth. Each scenario has distinct implications for various sectors of the economy, including businesses, consumers, and the financial markets.
The Yen and its Influence on the Decision
The value of the Yen is another key factor. A weaker Yen can boost exports but also increases the cost of imported goods, potentially contributing to inflation. The BOJ will need to consider the impact of its interest rate decision on the Yen’s exchange rate. A significant appreciation of the Yen might necessitate maintaining a lower interest rate to support export competitiveness, while a weakening Yen might allow for a more hawkish approach, although the latter carries the risk of imported inflation.
Political Considerations and Public Opinion
While the BOJ strives for independence, political considerations and public opinion cannot be entirely disregarded. The Japanese government’s economic policies and public sentiment towards inflation and economic growth will inevitably influence the BOJ’s approach. A government pushing for rapid economic growth might encourage a more accommodative monetary policy, while concerns about inflation among the public might push the BOJ towards a more cautious approach.
Long-Term Implications and Market Reactions
The April 2025 interest rate decision will have significant long-term implications for the Japanese economy and its financial markets. A shift towards higher interest rates could attract foreign investment and strengthen the Yen, but it also carries risks of slowing economic growth. Conversely, maintaining ultra-low interest rates could support economic growth in the short term but might contribute to asset bubbles and further weaken the Yen. Market reactions will be swift and significant, with potential implications for bond yields, stock prices, and the currency exchange rate. Please click here for information about the Bank of Japan’s interest rate policy in April 2025.
Japan’s Interest Rates 2025 Outlook & Economic Impact
Japan’s Current Monetary Policy Stance
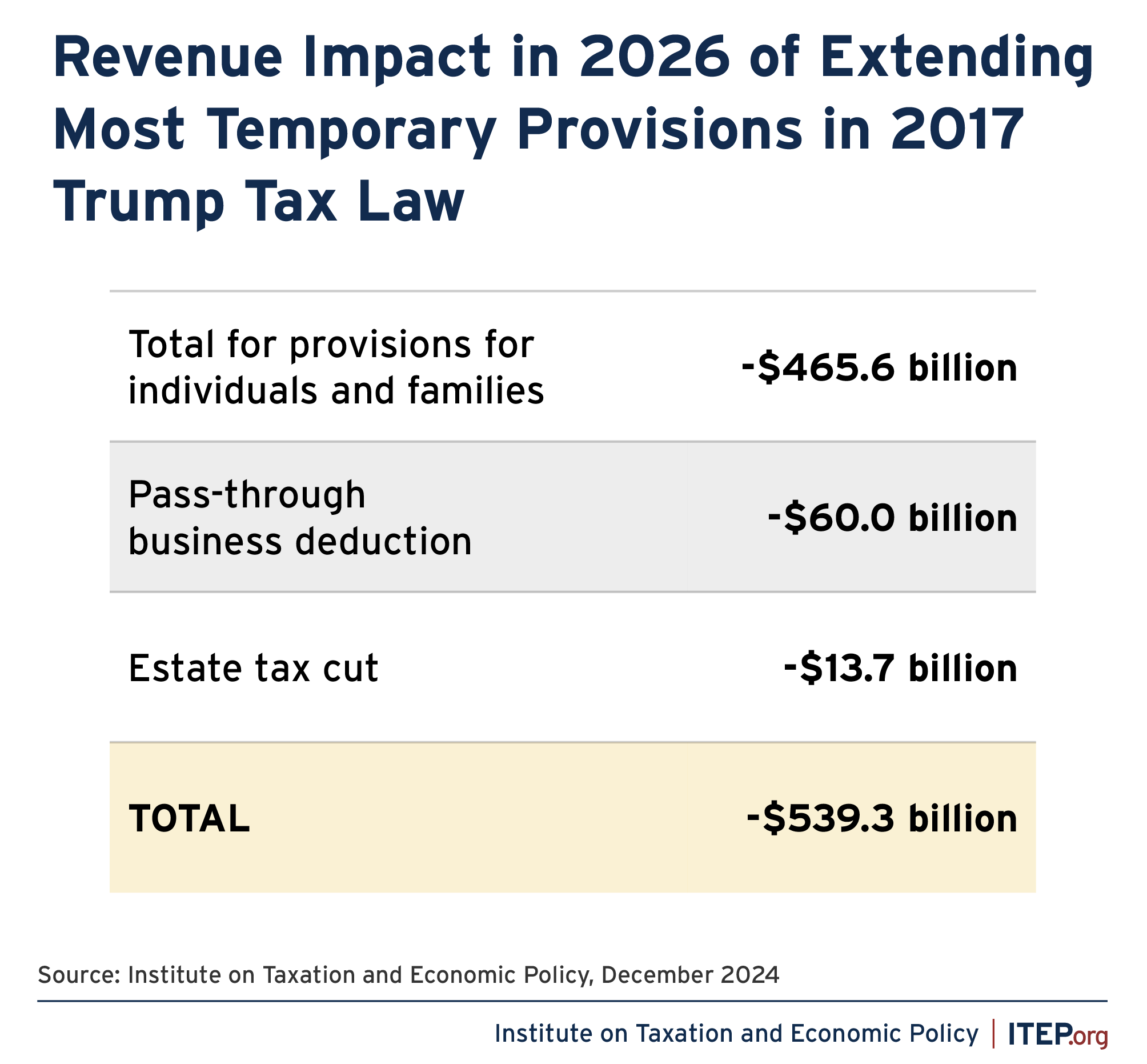
As of late 2023, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) continues to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy, characterized by negative interest rates on some commercial bank reserves and a commitment to yield curve control (YCC). This means the BOJ actively intervenes in the bond market to keep the 10-year government bond yield around zero. This policy, implemented to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation, has been a cornerstone of Japan’s economic strategy for years. However, the effectiveness and long-term sustainability of this approach remain a subject of ongoing debate, both domestically and internationally.
Global Inflationary Pressures and Their Impact on Japan
The global inflationary environment presents a significant challenge to the BOJ’s current policy. While Japan has experienced relatively subdued inflation compared to other developed nations, rising import costs due to global energy prices and supply chain disruptions are putting upward pressure on prices. This inflationary pressure, while currently moderate, could force a recalibration of the BOJ’s approach in the coming years. The balance between supporting economic growth and controlling inflation will be a key consideration for policymakers.
Potential Shifts in BOJ Policy in 2025
Predicting the BOJ’s actions in 2025 is inherently uncertain, but several scenarios are possible. One possibility is a gradual exit from YCC, potentially involving a slow and controlled increase in long-term interest rates. This approach would aim to minimize market disruption while allowing the BOJ to respond to evolving economic conditions. Another scenario might involve a more abrupt shift, driven by unexpectedly high inflation or a significant change in global economic dynamics. A complete abandonment of negative interest rates is also a possibility, though the timing and execution remain highly debated.
The Yen’s Volatility and its Influence on Interest Rates
The value of the Japanese yen plays a crucial role in shaping the BOJ’s policy decisions. A weakening yen can exacerbate inflationary pressures by increasing import costs, making it more difficult for the BOJ to maintain its ultra-loose stance. Conversely, a strengthening yen could provide some breathing room, allowing for a more gradual adjustment of monetary policy. The yen’s volatility will be a key factor influencing the BOJ’s strategy in the lead-up to and throughout 2025.
Economic Growth Projections for Japan in 2025
Japan’s economic growth outlook for 2025 is subject to considerable uncertainty. Factors such as global economic conditions, domestic consumption patterns, and the success of government structural reform initiatives will all play a role. While sustained, albeit moderate, growth is anticipated by many economists, the pace of expansion remains a key unknown. This uncertainty further complicates the BOJ’s task in balancing growth and inflation management.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Businesses and Consumers
Any changes to interest rates in Japan will have significant consequences for businesses and consumers. Higher interest rates could increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially slowing investment and economic growth. Consumers might also face higher mortgage rates and reduced borrowing capacity. Conversely, lower interest rates, while stimulating borrowing and investment, could potentially fuel inflation if not carefully managed. The impact will depend heavily on the magnitude and speed of any interest rate adjustments.
The Role of Government Fiscal Policy
The BOJ’s monetary policy decisions are intertwined with the government’s fiscal policies. Fiscal stimulus measures can support economic growth, potentially reducing the need for aggressive monetary tightening. However, excessive government spending could lead to higher inflation and complicate the BOJ’s efforts to control price increases. The coordination between monetary and fiscal policies will be crucial in navigating the economic challenges of 2025.
Risks and Uncertainties for the Japanese Economy
The outlook for Japan’s economy in 2025 is fraught with uncertainties. Geopolitical risks, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and tensions in the Taiwan Strait, could disrupt global supply chains and trigger further inflationary pressures. Domestic factors such as an aging population and shrinking workforce also present challenges to long-term economic growth. The BOJ will need to carefully consider these risks when formulating its monetary policy strategy.
Potential for Unexpected Events and Their Impact
The economic landscape is inherently unpredictable, and unexpected events could significantly impact Japan’s interest rates and economic performance in 2025. Sudden shifts in global commodity prices, unforeseen geopolitical developments, or unexpected changes in domestic political dynamics could all necessitate rapid adjustments in BOJ policy. The ability of the BOJ to adapt to these unforeseen circumstances will be a critical determinant of Japan’s economic success in the coming years. Learn more about the Bank of Japan’s interest rate policy in 2025 here: [link to tankionlineaz.com]
Trump’s 2025 Interest Rate Plan What You Need to Know
Understanding the Uncertainty Surrounding a Potential Trump 2025 Interest Rate Plan
Predicting Donald Trump’s economic policies, particularly regarding interest rates, is a challenging task. His past actions and statements offer clues, but his approach tends to be unpredictable and often driven by immediate political considerations. Any proposed plan for 2025 would depend heavily on the economic climate at the time and the composition of the Federal Reserve Board, which operates independently from the executive branch. We can, however, analyze potential scenarios based on his previous actions and rhetoric.
Trump’s Past Approach to Interest Rates
During his first term, Trump often publicly criticized the Federal Reserve’s decisions to raise interest rates. He viewed these increases as hindering economic growth, favoring lower rates to stimulate the economy and bolster the stock market. This pressure, though ultimately unsuccessful in dictating specific policy, highlights his preference for lower borrowing costs. However, the actual impact of his pressure is debatable, with economists pointing to other factors influencing the economy’s performance during his presidency.

Potential Scenarios for a 2025 Interest Rate Plan
If re-elected in 2024, several scenarios could unfold regarding interest rates in 2025. One possibility is a continuation of the low-rate environment, potentially aiming for even lower rates to further stimulate economic growth. This might be appealing in a post-pandemic economy still struggling to fully recover, but it also carries risks, such as increased inflation. Conversely, a more cautious approach might prioritize inflation control, potentially leading to rate hikes, even if it dampens short-term economic expansion. The exact course would depend on numerous interacting factors.
The Role of the Federal Reserve
It’s crucial to remember that the Federal Reserve (the Fed) maintains its independence in setting interest rates. While a President can influence the Fed’s choices through appointments to the Board of Governors and through public statements, the Fed is designed to act autonomously to manage monetary policy. Therefore, any “Trump plan” would face the reality of the Fed’s own economic forecasts and assessments, which may or may not align with the administration’s political goals.
The Impact of Inflation on Interest Rate Decisions
Inflation will likely be a dominant factor influencing interest rate decisions in 2025, regardless of who is President. High inflation generally necessitates higher interest rates to cool down the economy. If inflation remains elevated, the Fed would likely prioritize bringing it under control, even if it means slowing economic growth. Conversely, if inflation moderates, a lower-rate environment could become more politically and economically feasible.
The Influence of Global Economic Conditions
The global economic landscape will also significantly shape interest rate policy. Global economic shocks, geopolitical instability, and international trade relations all play a role. A global recession, for instance, could push the Fed (and potentially a Trump administration) toward lower rates to stimulate the US economy. Conversely, strong global growth might allow for higher rates without significant economic disruption. The interconnectedness of the global economy makes predicting this aspect particularly complex.
The Political Implications of Interest Rate Decisions
Interest rates have profound political implications. Lower rates are generally popular in the short term, as they boost consumer spending and investment. However, sustained low rates can lead to inflation and longer-term economic instability. Higher rates, while potentially necessary to curb inflation, often face political criticism as they can slow economic growth and impact borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. A Trump administration would need to navigate this political tightrope carefully.
Potential for Unconventional Monetary Policy
It’s not entirely outside the realm of possibility that a Trump administration might advocate for or even influence the adoption of unconventional monetary policies. These policies, used in the past in response to severe economic crises, involve measures beyond the traditional manipulation of interest rates. This could involve quantitative easing (QE) programs or other unconventional measures, but these carry their own risks and have to be carefully considered by the Fed.
The Importance of Considering Multiple Factors
Predicting interest rate policy in 2025 requires considering multiple interacting factors: the economic climate, inflation levels, global economic conditions, the Fed’s independence, and the President’s policy preferences. While Trump’s past pronouncements give us some hints, any prediction remains highly speculative, and a multitude of unforeseen events could alter the course of events dramatically.
Analyzing the Long-Term Economic Outlook
Ultimately, a successful economic strategy necessitates a long-term perspective that balances short-term goals with sustainable growth. While a specific interest rate policy for 2025 remains elusive, analyzing the interplay of these economic factors provides a more nuanced understanding of the possible scenarios and their potential consequences. A thorough economic assessment, incorporating various data points and projections, is crucial for sound policy-making. Click here to learn about Trump’s interest rate policy in 2025.
Fed’s 2025 Rate Hike Impact on Your Wallet
The Looming Shadow of Higher Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) decisions on interest rates significantly impact the everyday lives of Americans. While predicting the future is impossible, we can look at potential scenarios for 2025, considering the Fed’s ongoing battle with inflation and the possibility of further rate hikes. Even small adjustments can ripple through the economy, affecting your savings accounts, loans, and overall financial well-being. The uncertainty itself can cause stress, making financial planning that much harder.
How Higher Rates Affect Your Savings Accounts
If the Fed raises interest rates in 2025, your savings accounts could see a modest boost. Banks typically increase the interest they pay on savings and money market accounts to remain competitive and reflect the higher cost of borrowing. This means your money could earn a bit more, although the increase might not be dramatic enough to offset inflation. The key here is to compare rates offered by different banks and credit unions to maximize your returns. Don’t be afraid to switch institutions if you find a better deal.
The Impact on Credit Card Debt
Higher interest rates usually translate to higher credit card interest rates. If you carry a balance on your credit cards, you’ll be paying more in interest charges. This can significantly impact your monthly budget, leaving less money available for other expenses. The best approach is to aggressively pay down your credit card debt as quickly as possible. Consider strategies like the debt snowball or avalanche methods to tackle high-interest debt efficiently.
Mortgages and Home Equity Loans: A Double-Edged Sword
For those considering buying a home in 2025 or refinancing their existing mortgage, higher interest rates mean higher monthly payments. This makes homeownership less accessible for some, while for others, it potentially reduces the value of their existing property. However, if you already own your home and have a fixed-rate mortgage, your monthly payments won’t change, even if the Fed raises rates. Home equity loans, however, are usually tied to the prevailing interest rates, meaning you’ll likely pay more if the rates increase.
Auto Loans and Other Consumer Loans
Similar to mortgages, borrowing money for a car or other large purchases will become more expensive if the Fed increases rates. Auto loan rates typically track the Fed’s actions, so expect higher monthly payments if you’re planning to purchase a vehicle in 2025. This applies to other consumer loans as well, including personal loans and student loans (although student loan interest rates often have different regulatory mechanisms). Shop around for the best rates and consider pre-approval to secure better terms.
Investing in a Rising Rate Environment
Higher interest rates can impact investment returns. While it’s never wise to panic-sell, understanding how different asset classes react to rising rates is crucial. Bonds, for example, often lose value when interest rates rise. Conversely, some investors might find opportunities in sectors less sensitive to interest rate changes, or even invest in higher-yielding fixed-income securities. It’s always best to consult a qualified financial advisor to craft a strategy tailored to your individual circumstances and risk tolerance.
Budgeting and Financial Planning in Uncertain Times
The best defense against the uncertainties of fluctuating interest rates is a well-crafted budget and a proactive approach to financial planning. Track your income and expenses, identify areas where you can cut back, and build an emergency fund to cushion against unexpected expenses. Regularly review your financial goals and adjust your strategies as needed. Consider consulting a financial advisor to gain personalized insights and build a resilient financial plan that withstands economic fluctuations.
Understanding the Fed’s Actions and Their Ripple Effects
The Fed’s actions aren’t random; they aim to manage inflation and maintain economic stability. Understanding the reasoning behind rate hikes—and the potential consequences—is critical for making informed financial decisions. Following economic news and staying aware of the Fed’s announcements can help you anticipate potential changes and adjust your financial strategies accordingly. Remember that even small rate changes can have significant long-term effects, underlining the importance of careful financial planning. Please click here to learn about US interest rate policy in 2025.
Global Economic Resilience: Responding to Public Health Challenges
Navigating Challenges: Global Economic Resilience in Public Health Crisis
In the face of unprecedented public health challenges, the global community is compelled to respond with resilience and agility. The interplay between the health and economic sectors becomes a critical focal point, requiring coordinated efforts, innovative solutions, and adaptive strategies to safeguard both public well-being and economic stability.
Economic Impact of Public Health Crises: A Dual Challenge
Public health crises, such as pandemics, exert profound economic impacts that reverberate across industries and nations. The dual challenge of mitigating the spread of diseases and stabilizing economies becomes apparent. The economic repercussions manifest in disrupted supply chains, decreased consumer spending, and financial market volatility, posing a complex challenge that demands multifaceted solutions.
Fiscal Stimulus Measures: Bolstering Economic Resilience
Governments worldwide deploy fiscal stimulus measures to counteract the economic fallout of public health crises. These measures include financial aid packages, tax relief, and infrastructure spending aimed at supporting businesses, individuals, and sectors heavily affected by disruptions. Fiscal stimulus becomes a key tool in stabilizing economies, fostering recovery, and preventing long-term damage.
Monetary Policy Responses: Navigating Economic Uncertainties
Central banks play a pivotal role in the global economic response to public health challenges. Monetary policy responses involve interest rate adjustments, liquidity injections, and unconventional measures to ensure financial stability. The goal is to ease financial conditions, provide support to credit markets, and bolster confidence in the face of economic uncertainties triggered by health crises.
Adapting Business Models: Innovation Amidst Disruptions
Businesses face the imperative of adapting their models to thrive amidst disruptions. From embracing digital transformations to reevaluating supply chains, companies navigate a new landscape shaped by public health challenges. Innovative solutions, such as remote work arrangements and e-commerce strategies, become integral to sustaining operations and ensuring resilience in the face of uncertainties.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics: A Balancing Act
Public health crises expose vulnerabilities in global supply chains, necessitating a reassessment of dynamics. While there is a trend towards regionalization to mitigate risks, maintaining a delicate balance between efficiency and resilience becomes paramount. Governments and businesses collaborate to enhance supply chain robustness without compromising the benefits of globalization.
Economic Diplomacy in Crisis Management
International cooperation and economic diplomacy assume heightened significance in crisis management. Nations collaborate to share resources, information, and expertise. Economic diplomacy plays a role in trade negotiations, investment collaborations, and collective efforts to stabilize global markets. The shared goal is to foster a coordinated response that transcends borders and addresses the collective challenges posed by public health crises.
Healthcare Investment and Research Collaboration
Public health challenges underscore the importance of healthcare investments and global research collaboration. Governments and private entities direct resources towards strengthening healthcare infrastructure, vaccine development, and pandemic preparedness. The collaboration between the public and private sectors becomes a linchpin in advancing medical solutions and enhancing global health resilience.
Digital Health Innovations: Transforming Healthcare Systems
The intersection of technology and healthcare gains prominence in the global response to public health challenges. Digital health innovations, including telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and data analytics, contribute to more effective healthcare delivery. Governments and businesses invest in these technological advancements to improve healthcare accessibility and responsiveness during crises.
Social Safety Nets and Inclusive Policies
Building resilient societies requires a focus on social safety nets and inclusive policies. Governments design programs to support vulnerable populations, ensure access to healthcare, and address socioeconomic disparities exacerbated by public health challenges. Inclusive policies become a cornerstone for fostering societal resilience and mitigating the long-term economic impact on marginalized communities.
Towards a Resilient Future: Lessons Learned
As the global economic response to public health challenges unfolds, lessons learned become guideposts for a more resilient future. The importance of preparedness, collaboration, and innovation is evident. Governments, businesses, and communities recognize the need for adaptable strategies that can navigate the complexities of interconnected health and economic landscapes.
Explore more about the Global Economic Response to Public Health Challenges and the strategies shaping resilience amidst unprecedented crises.