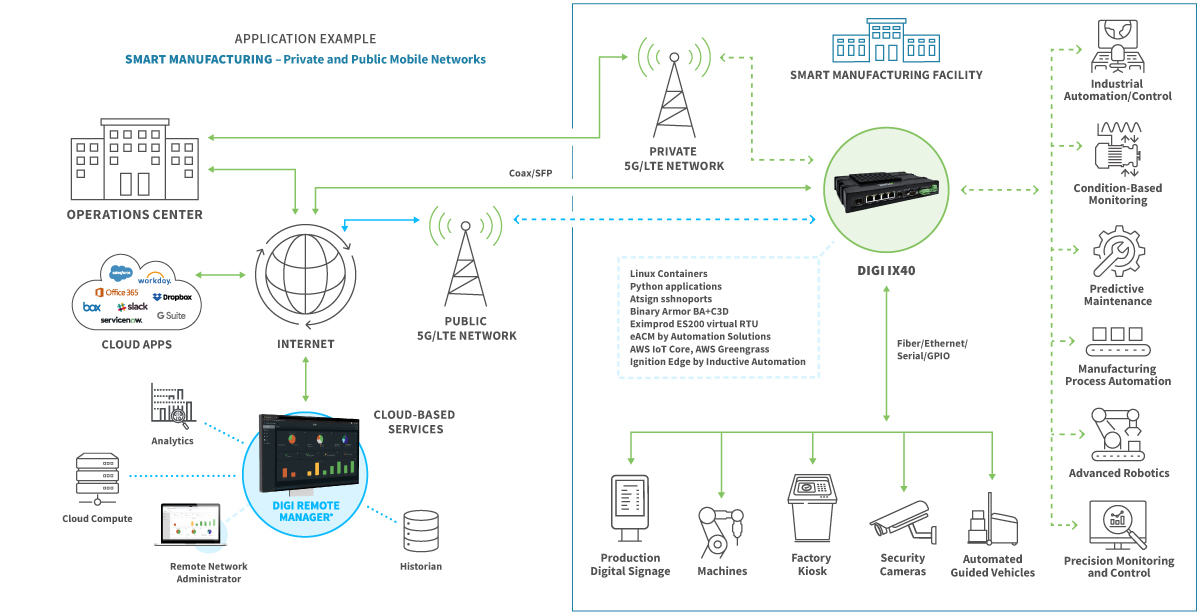
Economic Impacts of Global Political Shifts: Navigating Change

Economic Impacts of Global Political Shifts: Navigating Change
In the dynamic landscape of global affairs, political shifts wield significant influence over economic structures. These changes, whether driven by geopolitical tensions, diplomatic realignments, or policy adjustments, have far-reaching consequences on the world economy. Examining the economic impact of alterations in global political landscapes becomes imperative for understanding the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Economic Interdependence and Global Political Dynamics
The intertwining of economies on a global scale means that alterations in political dynamics can quickly reverberate across borders. Economic interdependence, characterized by intricate trade networks and interconnected financial systems, amplifies the impact of political decisions. A change in diplomatic relations or the imposition of trade restrictions can disrupt established economic patterns, affecting industries and markets worldwide.
Trade Policies and Market Fluctuations
One of the primary channels through which political shifts influence economies is the adjustment of trade policies. Trade agreements, tariffs, and international partnerships play a pivotal role in shaping economic landscapes. A sudden shift in political alliances or the initiation of trade wars can lead to market fluctuations, impacting businesses and investors. Navigating these uncertainties becomes essential for maintaining economic stability.
Investor Confidence and Capital Flows
Global investors closely monitor political developments as they significantly influence market sentiment. Changes in political landscapes can either bolster or erode investor confidence, influencing capital flows. A stable and predictable political environment tends to attract investments, while uncertainty may lead to capital flight. Understanding the nuances of political shifts is crucial for policymakers and business leaders seeking to foster a conducive investment climate.
Regional Economic Blocs and Alliances
Political changes often prompt countries to reassess their participation in regional economic blocs and alliances. The formation or dissolution of such partnerships can reshape trade dynamics and alter economic dependencies. Businesses operating within these regions must adapt to evolving frameworks and regulations, navigating the opportunities and challenges presented by shifting political alliances.
Crisis Management and Economic Resilience
In times of political upheaval, countries and businesses alike must focus on crisis management and economic resilience. Developing strategies to mitigate the impact of sudden political changes becomes crucial. Diversification of trade partners, robust financial planning, and adaptive policy frameworks contribute to building resilience in the face of geopolitical uncertainties.
Technological Advancements and Political Realities
In the contemporary era, technological advancements intersect with political realities, creating a new layer of complexity. The alignment of technological policies with geopolitical objectives shapes economic competitiveness. Countries that strategically leverage technology in alignment with their political goals can gain a competitive edge in the global economic landscape.
Environmental Policies and Sustainable Development
Political shifts also influence the direction of environmental policies, impacting industries with a focus on sustainability. As countries align their political agendas with environmental concerns, businesses must adapt to evolving regulations and consumer preferences. The intersection of politics and sustainability becomes a critical factor in shaping economic activities globally.
Challenges and Opportunities in Emerging Markets
Political changes often create both challenges and opportunities in emerging markets. While uncertainties may pose risks, strategic realignments and policy reforms can open up new avenues for economic growth. Understanding the nuances of political landscapes in emerging markets is essential for businesses seeking to expand their global footprint.
Navigating Change: The Role of Global Economic Recovery Plans
In the wake of political shifts, the implementation of robust global economic recovery plans becomes paramount. Governments and international organizations collaborate to devise strategies that stimulate economic growth, create employment opportunities, and ensure financial stability. These plans serve as a roadmap for navigating the challenges posed by changes in global political landscapes.
To explore further insights into the economic impact of changes in global political landscapes, visit Economic Impact of Changes in Global Political Landscapes.
Crafting SEO-Friendly URL Structures for Optimal Visibility

Unlocking Visibility: Crafting SEO-Friendly URL Structures
In the intricate realm of SEO, the structure of your URLs plays a pivotal role in determining your website’s visibility. Crafting SEO-friendly URL structures is not just about aesthetics; it significantly impacts your search engine rankings and user experience. Let’s delve into the key principles and strategies for optimizing your URLs.
The Importance of SEO-Friendly URLs
SEO-friendly URLs contribute to the overall success of your website by providing both search engines and users with clear, relevant information about the page’s content. A well-structured URL can enhance click-through rates, improve user experience, and positively influence your search rankings.
Keep it Simple and Descriptive
One fundamental principle in creating SEO-friendly URLs is simplicity. A clean and straightforward URL is not only easier for users to remember but also for search engines to understand. Include relevant keywords in your URL that accurately reflect the content of the page. Avoid unnecessary characters or parameters that can make the URL complex and confusing.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words
When creating URLs, opt for hyphens to separate words instead of underscores or spaces. Search engines interpret hyphens as space, contributing to better readability and comprehension. For example, use “seo-friendly-urls” instead of “seo_friendly_urls” for improved search engine understanding.
Avoid Dynamic Parameters When Possible
Dynamic parameters in URLs, often seen as strings of numbers and symbols, can be challenging for search engines to crawl and index effectively. Whenever possible, aim for static and descriptive URLs. This not only aids search engines but also enhances the overall user experience by providing clear and predictable URLs.
Include Target Keywords Strategically
Strategically include your target keywords in the URL. This reinforces the relevance of your content to both users and search engines. However, it’s crucial to strike a balance – don’t overstuff your URL with keywords, as this can appear spammy and negatively impact your rankings.
Create a Logical Hierarchy
Structure your URLs in a logical hierarchy that mirrors the organization of your website. This helps users and search engines navigate your site more efficiently. For instance, use a format like “example.com/category/subcategory/page” to indicate the hierarchical relationship between different sections of your website.
Utilize Canonical URLs for Duplicate Content
In cases where you have identical or similar content accessible through multiple URLs, implement canonicalization. Canonical URLs help search engines understand the preferred version of a page, consolidating the ranking signals and avoiding issues related to duplicate content. This is particularly crucial for large websites with diverse content.
Optimize for Readability and User Experience
Consider the human element in URL creation. A user-friendly URL is one that is easily readable and understandable. A clear and concise URL enhances user trust and encourages click-through. When users can quickly comprehend the content from the URL itself, it contributes to a positive overall browsing experience.
Regularly Audit and Update URLs
As your website evolves, conduct regular audits of your URLs. Remove or update outdated URLs, ensuring that they accurately represent the current structure and content of your site. This practice aids search engines in maintaining an accurate index of your website.
Exploring Tankionlineaz.com for Additional Insights
For a comprehensive guide on crafting SEO-friendly URL structures, visit tankionlineaz.com. This valuable resource offers additional insights and actionable tips to elevate your website’s performance in the competitive world of search engine optimization.
In conclusion, the significance of SEO-friendly URL structures cannot be overstated. By implementing these strategies, you not only enhance your website’s visibility in search results but also contribute to an improved user experience, ultimately fostering the success of your online presence.
Maximizing SEO for Bing and Other Search Engines: Effective Strategies

Maximizing SEO for Bing and Other Search Engines: Effective Strategies
In today’s digital landscape, a comprehensive SEO strategy is crucial for online success. While Google dominates the search engine market, it’s essential not to overlook other players like Bing. Let’s delve into effective strategies to enhance your website’s visibility across search engines.
Understanding Bing’s Algorithm
Bing, although similar to Google, has its unique algorithm. To optimize for Bing, it’s vital to understand its preferences. Unlike Google, Bing places more emphasis on social media signals and values exact match keywords. Tailor your content accordingly, ensuring it aligns with Bing’s algorithmic nuances.
Quality Content is Key
Regardless of the search engine, content remains king. Create high-quality, relevant content that addresses users’ needs. Bing, like Google, rewards informative and engaging content. Ensure your articles are well-researched, offer value, and are free from grammatical errors.
Optimizing Meta Tags
Meta tags play a crucial role in search engine optimization. Craft compelling meta titles and descriptions with relevant keywords. Bing relies heavily on these tags, so make them concise, compelling, and reflective of your content. This optimization helps improve click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs).
Mobile-Friendly Design
Bing, like Google, prioritizes mobile-friendly websites. Ensure your site is responsive and provides an optimal user experience across various devices. A mobile-friendly design not only improves your search engine rankings but also enhances the overall usability of your website.
Backlink Diversity
Diversify your backlink profile to appeal to Bing’s algorithm. While Google values high-authority links, Bing places importance on the diversity of sources. Seek quality backlinks from various domains, including social media platforms, to establish credibility in the eyes of Bing’s algorithm.
Local SEO Optimization
Bing has a particular focus on local search. If your business caters to local audiences, optimize for local SEO. Claim your Bing Places for Business listing, ensure accurate business information, and encourage customer reviews. This can significantly boost your visibility in Bing’s local search results.
Social Media Integration
As mentioned earlier, Bing values social media signals. Integrate social media into your SEO strategy by sharing content on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. Encourage social sharing and engagement, as these signals can positively impact your rankings on Bing.
The Importance of Image Optimization
Bing places importance on image optimization. Use descriptive filenames and alt tags for your images, providing context to search engines. This not only enhances your SEO but also improves the accessibility of your content.
Regular Content Updates
Keep your content fresh and regularly updated. Bing rewards websites that consistently provide up-to-date information. Regularly publish new content, refresh existing articles, and ensure that your website reflects the latest trends in your industry.
Incorporating SEO for Bing and Other Search Engines
To maximize your SEO efforts, it’s crucial to cater to multiple search engines. Consider incorporating specific strategies for Bing, such as optimizing for exact match keywords and leveraging social media signals.
For a comprehensive guide on SEO for Bing and other search engines, visit tankionlineaz.com. This valuable resource offers in-depth insights and actionable tips to elevate your website’s performance across various search engines.
In conclusion, a well-rounded SEO strategy that considers the unique preferences of different search engines is key to achieving optimal online visibility. By understanding and implementing these strategies, you can position your website for success in the dynamic world of search engine optimization.
Navigating World Economic Disparities
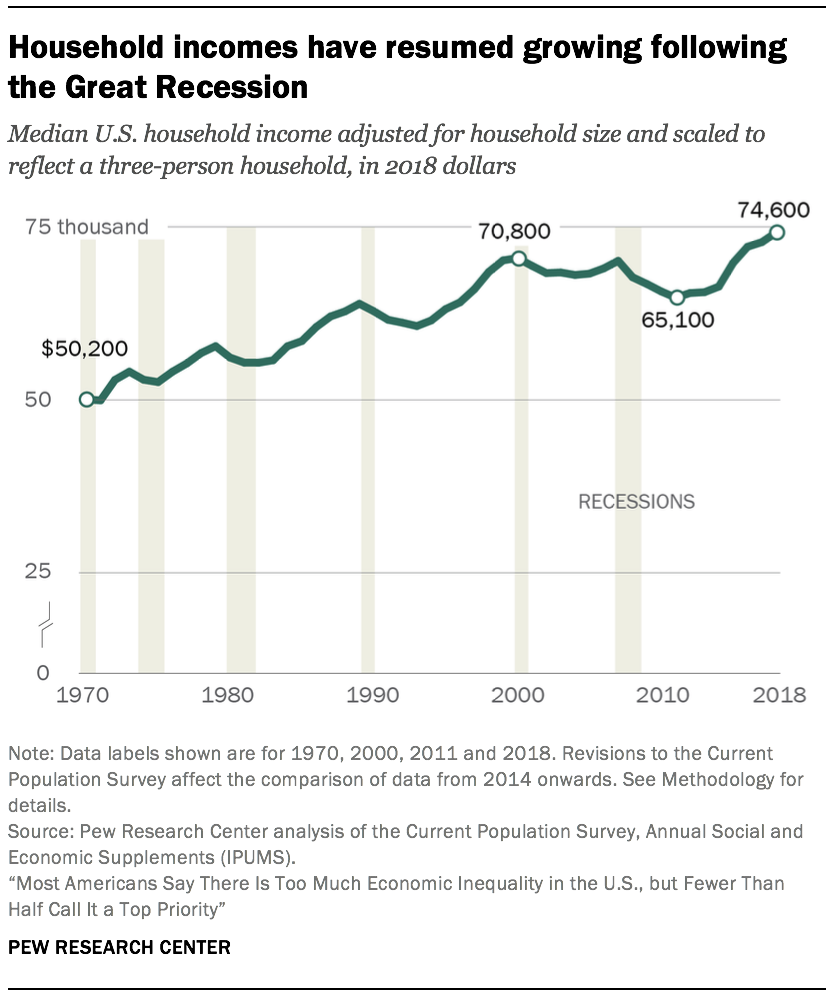
Understanding the Nuances of Global Economic Inequality
Economic disparities across the world have long been a topic of concern, with vast differences in wealth and development among nations. Examining the intricate factors contributing to these imbalances allows us to comprehend the complexities of global economic inequality.
Historical Roots and Modern Realities
The roots of world economic disparities can be traced back to historical events such as colonialism and unequal trade relationships. In the modern era, these disparities persist and are exacerbated by various factors, including geopolitical power dynamics, resource distribution, and systemic inequalities.
Global Trade and Wealth Accumulation
One major contributor to economic disparities is the uneven distribution of benefits from global trade. While some countries thrive on exports and economic integration, others face challenges in accessing international markets. The link between global trade policies and the widening wealth gap is a critical aspect that demands attention.
Technology Divide and Innovation Gaps
Advancements in technology play a significant role in shaping economic landscapes. However, the unequal adoption and access to technology contribute to a widening gap between technologically advanced nations and those struggling to keep pace. Addressing this “technology divide” is pivotal for fostering inclusive global economic growth.
Educational Disparities and Economic Mobility
Education serves as a cornerstone for economic development, but disparities in educational opportunities create barriers to upward mobility. Nations with robust educational systems tend to experience higher levels of economic prosperity. Bridging the educational gap is essential for fostering a more equitable distribution of wealth on a global scale.
Financial Inclusion and Access to Capital
Access to financial resources is a key determinant of economic success. Disparities in financial inclusion and access to capital contribute to a cycle of poverty in many regions. Efforts to enhance financial literacy and create avenues for inclusive financial systems are critical steps toward addressing economic disparities.
Environmental Challenges and Economic Impact
Environmental issues pose a dual challenge, affecting both developed and developing nations. However, the economic impact of environmental challenges often disproportionately burdens less developed countries. Sustainable development initiatives that address environmental concerns while promoting economic growth can contribute to narrowing global economic gaps.
Government Policies and Inequality Mitigation
Effective governance and policy implementation play a crucial role in mitigating economic disparities. Countries with well-designed social policies, progressive taxation systems, and inclusive economic strategies tend to experience more balanced wealth distribution. Analyzing successful policy models becomes imperative for nations striving to address economic inequalities.
International Cooperation for Sustainable Development
In an interconnected world, addressing economic disparities requires a collaborative approach. International organizations, partnerships, and agreements become instrumental in fostering cooperation among nations. By working together to implement sustainable development goals, countries can make strides toward a more equitable global economic landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While economic disparities pose significant challenges, they also present opportunities for positive change. Innovative solutions, inclusive policies, and a collective commitment to addressing the root causes can pave the way for a more balanced and sustainable global economy.
In the pursuit of understanding and addressing world economic disparities, it is essential to recognize the multifaceted nature of the issue. By fostering global awareness, encouraging inclusive policies, and promoting international cooperation, we can strive towards a world where economic opportunities are more evenly distributed.
To explore more about World economic disparities, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Navigating Global Economic Downturns: Challenges and Strategies

Navigating Global Economic Downturns: Challenges and Strategies
Global economic downturns are formidable challenges that reverberate across nations, impacting businesses, individuals, and governments alike. In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted impact of these downturns, examining the challenges they pose and unveiling strategies to navigate the turbulent economic landscapes they create.
Understanding the Dynamics of Economic Downturns
Economic downturns are characterized by a contraction in economic activity, often marked by a decline in GDP, rising unemployment, and decreased consumer spending. Understanding the dynamics of these downturns is crucial, as they can be triggered by various factors, including financial crises, geopolitical tensions, or external shocks like pandemics.
To explore the impact of global economic downturns, visit Impact of Global Economic Downturns.
Employment Challenges and Job Insecurity
One of the most immediate and palpable effects of economic downturns is the surge in unemployment rates. Businesses, facing financial constraints, may implement cost-cutting measures, leading to layoffs and hiring freezes. Job insecurity becomes a widespread concern, impacting the livelihoods of individuals and creating challenges for labor markets.
Business Closures and Financial Strain
Economic downturns can trigger a wave of business closures, especially among smaller enterprises with limited financial resilience. The strain on businesses emanates from reduced consumer spending, disrupted supply chains, and financial market uncertainties. This creates a domino effect, contributing to the overall economic contraction.
Financial Market Volatility and Investor Anxiety
Global economic downturns often coincide with heightened volatility in financial markets. Stock market fluctuations, currency devaluations, and fluctuations in commodity prices can induce anxiety among investors. The uncertainty surrounding economic conditions prompts a flight to safety, impacting investment decisions and capital flows.
Consumer Spending Patterns and Economic Slowdown
Consumer confidence takes a hit during economic downturns, leading to altered spending patterns. Individuals may reduce discretionary spending, delay major purchases, and focus on essential goods and services. This shift in consumer behavior contributes to an economic slowdown as demand weakens across various sectors.
Government Responses and Stimulus Measures
Governments play a pivotal role in responding to economic downturns. Fiscal and monetary policies are deployed to stimulate economic activity, mitigate job losses, and stabilize financial markets. Stimulus measures, including tax incentives, infrastructure spending, and interest rate adjustments, aim to rejuvenate economic growth and restore confidence.
Debt Challenges and Financial Stress
Economic downturns often amplify existing debt challenges. Both individuals and businesses may struggle with servicing debts amid reduced incomes and financial uncertainties. This financial stress can lead to a cycle of defaults, impacting the banking sector and exacerbating economic challenges.
International Trade Disruptions and Supply Chain Issues
The interconnected nature of the global economy means that economic downturns can trigger disruptions in international trade. Supply chains face challenges as demand contracts, leading to inventory gluts or shortages. Trade tensions may escalate, impacting diplomatic relations and exacerbating economic difficulties.
Innovation and Adaptation in Business Strategies
Amid challenges, economic downturns can catalyze innovation and adaptation in business strategies. Companies may reevaluate their operations, embrace digital transformation, and explore new markets. Innovations born out of necessity during downturns can contribute to long-term resilience and competitiveness.
Resilience Building for Future Uncertainties
As the global economy grapples with the impact of downturns, there is a growing emphasis on building resilience for future uncertainties. Businesses and individuals alike are recognizing the importance of diversification, risk management, and strategic planning to withstand economic shocks. Governments are investing in social safety nets and infrastructure to enhance overall resilience.
Conclusion: Charting the Path to Recovery
In conclusion, navigating the impact of global economic downturns requires a collective and strategic approach. Understanding the multifaceted challenges, from employment concerns to financial market volatility, is essential. By implementing responsive government policies, fostering innovation, and prioritizing resilience building, nations and businesses can chart a path to recovery and set the stage for sustainable growth in a post-downturn landscape.
Navigating Google’s Algorithm Changes: A Guide for Success

Decoding the Impact of Google Algorithm Updates
Google’s algorithm updates are pivotal events that can significantly influence the digital landscape, affecting websites’ rankings and visibility. Navigating these changes requires a strategic approach and a keen understanding of how they shape the online environment.
The Dynamic Nature of Google’s Algorithms
Google continually refines its algorithms to enhance user experience and provide more accurate search results. These updates can range from minor tweaks to major overhauls, and staying abreast of these changes is crucial for anyone invested in maintaining a robust online presence.
Adaptability: The Key to Success
With each algorithm update, website owners and digital marketers face the challenge of adapting their strategies to meet the new criteria set by Google. Flexibility and a willingness to adjust tactics are essential components of a successful online presence in the face of ever-evolving algorithms.
User-Centric Approach: Core of Algorithmic Changes
Many updates aim to prioritize user experience, rewarding websites that offer valuable content, easy navigation, and fast loading times. By focusing on creating a positive experience for users, website owners align their strategies with Google’s algorithmic goals.
Content Quality Reigns Supreme
Algorithm updates often place increased emphasis on content quality. Websites providing informative, well-researched, and engaging content are more likely to benefit from algorithmic changes. Quality content not only attracts users but also helps establish authority in the eyes of search engines.
Technical Optimization: A Continuous Requirement
Ensuring your website meets technical optimization standards is an ongoing necessity. Regular audits for factors such as mobile-friendliness, site speed, and structured data ensure compliance with Google’s preferences and enhance your site’s performance in search results.
Link Building Strategies in the New Landscape
Algorithm updates also impact the significance of backlinks. While quality links remain crucial, the focus has shifted towards natural, authoritative link-building strategies. Building relationships and creating shareable content are integral components of successful link-building post-update.
Local SEO and Algorithmic Enhancements
Local businesses are particularly affected by algorithm updates that refine local search results. Ensuring your business information is accurate and optimized for local searches becomes even more critical in the wake of such updates.
Staying Informed: The Role of Industry Insights
To navigate Google’s algorithm updates successfully, staying informed about industry insights is imperative. Platforms like Tankionlineaz.com provide advanced insights and the latest trends, offering a valuable resource for understanding and adapting to algorithmic changes.
The Continuous Journey of Adaptation
Adapting to Google’s algorithm updates is not a one-time task but a continuous journey. Regularly monitor your website’s performance using tools like Google Analytics and Search Console. Analyze the impact of algorithmic changes on your site’s visibility and adjust your strategy accordingly.
In conclusion, mastering the impact of Google algorithm updates is about understanding the dynamic nature of these changes and adopting an adaptive, user-centric, and quality-focused approach. By staying informed, embracing flexibility, and leveraging valuable resources like Tankionlineaz.com, you position yourself for sustained success in the ever-changing realm of online visibility.
Talent Triumph: SEO Strategies for HR & Recruitment Success
Introduction:
In the dynamic realm of human resources and recruitment, online visibility is paramount. This article navigates through the landscape of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategies uniquely tailored for HR and recruitment websites. Uncover insights that can elevate your platform’s reach, attract top talent, and redefine success in the competitive hiring landscape.
Understanding the Recruitment Landscape:
Before diving into SEO tactics, it’s essential to comprehend the competitive nature of the HR and recruitment industry. As platforms connecting employers with potential candidates, standing out is crucial. Tailoring SEO strategies to the specific needs of this dynamic sector is essential for HR and recruitment websites aiming to be leaders in the hiring game.
Keyword Research for Talent Attraction:
At the heart of successful SEO lies comprehensive keyword research. Identify terms and phrases relevant to the HR and recruitment landscape, job roles, and industries your platform serves. Craft content that aligns with the language used by job seekers and employers seeking talent online.
Optimizing Content for Candidate Engagement:
Content on HR and recruitment websites is not just about job listings; it’s a tool for engaging candidates. Craft compelling job descriptions, company profiles, and industry insights. Optimize this content with relevant keywords, creating an immersive experience that resonates with job seekers and employers looking for the perfect match.
Structuring Your Website for User-Friendly Hiring:
A well-structured website is critical for user experience and SEO. Categorize job listings logically, use clear navigation, and employ descriptive headings. Ensure that the structure of your website aligns with the efficiency and professionalism expected in the HR and recruitment industry, providing visitors with an intuitive and streamlined hiring experience.
Leveraging Social Media for Industry Connection:
Social media platforms are powerful tools for HR and recruitment websites to showcase job opportunities, company culture, and industry expertise. Share job highlights, career advice, and engaging content on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook. Engaging with your audience through these channels not only builds brand awareness but also contributes to increased visibility and community engagement.
Building Backlinks for Recruitment Authority:
Quality backlinks from reputable sources play a crucial role in SEO success. Collaborate with industry influencers, participate in recruitment events, and engage in cross-promotional activities. These backlinks enhance your website’s authority within the HR and recruitment sector, positively impacting search engine rankings and positioning your platform as a trusted leader.
Mobile Optimization for On-the-Go Job Seekers:
In a world where job searches happen on the go, ensure your website is optimized for mobile devices. Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites, making this optimization crucial for favorable search rankings and accessibility to job seekers looking for opportunities while on the move.
Monitoring Performance with Analytics:
Regularly monitoring your website’s performance using analytics tools is vital. Track metrics such as website traffic, user engagement, and application rates. Analyzing this data provides insights into the effectiveness of your SEO efforts, allowing you to refine your strategy based on user behavior and the evolving needs of the HR and recruitment community.
Encouraging Job Seeker and Employer Interaction:
Foster a sense of community on your website by encouraging interaction. Create comment sections, forums, and events that invite job seekers and employers to share their experiences and insights. User interaction not only strengthens the sense of community but also signals positive indicators to search engines about the vibrancy of your HR and recruitment platform.
SEO for HR and Recruitment Websites: Redefining Hiring Success:
For a comprehensive understanding of SEO strategies tailored for HR and recruitment websites, visit SEO for HR and recruitment websites. Implementing these techniques will not only elevate your website’s visibility but also position it as a go-to destination for top talent and employers seeking the perfect match.
Conclusion:
In the competitive landscape of HR and recruitment, mastering SEO is a strategic imperative. By understanding the recruitment landscape, optimizing content, and leveraging social media and backlinks, HR and recruitment websites can redefine success in the hiring game, connecting top talent with the opportunities that match their skills and aspirations.
Decoding LSI: Enhancing SEO with Latent Semantic Indexing
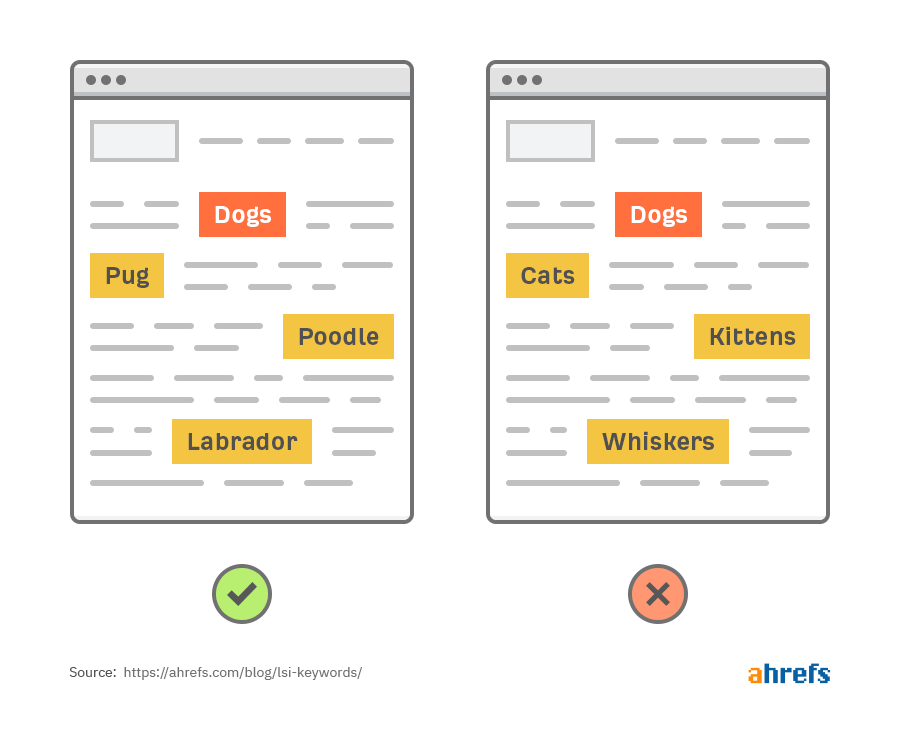
Unlocking SEO Potential: Decoding Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)
In the ever-evolving landscape of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), understanding advanced concepts like Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) can be a game-changer. LSI is not just a buzzword; it’s a powerful tool that can significantly impact your website’s visibility in search results.
Understanding the Essence of LSI in SEO
Latent Semantic Indexing is a sophisticated algorithm used by search engines to understand the context of words in a given piece of content. Unlike traditional keyword matching, LSI considers the relationship between words, enabling search engines to comprehend the meaning behind the text more effectively.
Beyond Keywords: Embracing Semantic Relationships
Traditionally, SEO heavily relied on exact keyword matching. However, as search engines become more sophisticated, LSI allows for a more nuanced approach. It explores the semantic relationships between words, recognizing that different phrases can convey similar meanings. This shift from strict keywords to semantic understanding is pivotal in modern SEO.
Enhancing Content Relevance with LSI Keywords
One of the significant advantages of LSI is its ability to enhance content relevance. By incorporating LSI keywords naturally within your content, you signal to search engines that your page is comprehensive and contextually rich. This not only improves your chances of ranking for specific queries but also contributes to a more satisfying user experience.
Optimizing On-Page Content Using LSI Keywords
Incorporating LSI keywords into your on-page content is a strategic move. These keywords should seamlessly blend into your text, providing additional context without appearing forced. As search engines analyze your content, the presence of LSI keywords helps reinforce the overall theme and relevance of your page.
LSI in Action: Semantic Clusters and Topic Modeling
LSI facilitates the creation of semantic clusters within your content. This involves grouping together words and phrases that share similar meanings. Search engines use these semantic clusters to understand the overarching topics covered on your page, contributing to more accurate indexing and improved search rankings.
Content Diversification for LSI Integration
To leverage LSI effectively, diversify your content. Create comprehensive articles that cover various aspects of a topic, naturally incorporating different but contextually relevant terms. This diversity caters to a broader range of search queries and aligns with the semantic understanding that LSI brings to the table.
Avoiding Keyword Stuffing: A Balanced Approach
While LSI encourages the use of diverse and contextually relevant terms, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced approach. Avoid keyword stuffing, as this can lead to a negative impact on your SEO. Focus on providing value to your audience by creating high-quality, informative content that naturally integrates LSI keywords.
LSI and User Experience: A Symbiotic Relationship
The implementation of LSI isn’t solely about appeasing search engines; it also enhances the user experience. By creating content that reflects a deep understanding of the topic, you engage users more effectively. This engagement, coupled with improved search rankings, creates a symbiotic relationship between LSI and positive user experiences.
Strategizing Your SEO Approach with LSI
As you delve into the intricacies of SEO, integrating LSI into your strategy can yield substantial benefits. Understand the semantic relationships within your niche, identify relevant LSI keywords, and create content that reflects a comprehensive understanding of your industry or subject matter.
Exploring Advanced SEO Techniques on Tankionlineaz.com
For more insights and advanced techniques on incorporating Latent Semantic Indexing into your SEO strategy, visit tankionlineaz.com. This comprehensive resource offers additional strategies and tips to elevate your SEO efforts and maximize the impact of LSI.
In conclusion, Latent Semantic Indexing is a powerful ally in the realm of SEO. By embracing the nuances of semantic relationships, you not only enhance your website’s visibility but also provide a more valuable and contextually rich experience for your audience.
International Tech Regulation Shifts: Economic Impacts

Introduction:
The intersection of technology and international regulations is a pivotal factor shaping the global economic landscape. This article explores the profound economic effects of international changes in technology regulations, shedding light on how policies influence innovation, trade, and overall economic dynamics.
Innovation and Technology Development:
Changes in technology regulations at the international level have a direct impact on innovation. Policies that encourage a conducive environment for technological advancements, intellectual property protection, and research and development contribute to economic growth. Conversely, stringent regulations may stifle innovation by creating barriers and compliance challenges for technology companies.
Global Trade and Market Access:
International technology regulations play a crucial role in shaping global trade dynamics. Policies related to market access, trade agreements, and cross-border data flow impact the ability of technology companies to expand globally. Open and collaborative regulatory frameworks facilitate the seamless flow of technology-related goods and services, fostering economic interconnectedness.
Digital Economy and E-commerce:
The digital economy is significantly influenced by changes in technology regulations. Policies governing e-commerce, data privacy, and online transactions shape the landscape for digital businesses. Forward-thinking regulations that provide a balance between consumer protection and business innovation contribute to the growth of the digital economy, positively impacting economic indicators.
Cybersecurity and Resilience:
International technology regulations also address cybersecurity concerns. Policies aimed at enhancing cybersecurity measures and protecting critical infrastructure contribute to economic resilience. The economic consequences of cyber threats can be significant, and robust regulations play a vital role in safeguarding businesses, government institutions, and the overall economy from digital risks.
Cross-Border Collaboration and Research Partnerships:
Collaboration across borders is crucial for technology advancements. Regulations that foster international research partnerships and collaboration contribute to the collective growth of the global technology ecosystem. Policies that facilitate the movement of talent, ideas, and resources across borders enhance the capabilities of the technology sector, positively impacting economic innovation.
Data Governance and Privacy Protection:
As data becomes a cornerstone of the digital era, international regulations governing data governance and privacy protection are paramount. Policies that establish clear guidelines for data handling and protection contribute to user trust and confidence. A robust data governance framework is essential for fostering a secure digital environment, supporting economic activities that rely on data-driven insights.
Competition and Market Dynamics:
Regulations in the technology sector also address issues of competition and market dynamics. Policies that prevent anti-competitive practices, promote fair market competition, and ensure a level playing field contribute to economic efficiency. Striking the right balance between fostering innovation and preventing monopolistic behavior is essential for a healthy and competitive technology market.
Consumer Trust and Regulatory Compliance:
Consumer trust is a key factor in the success of technology products and services. Regulations that prioritize consumer rights, ensure transparency, and enforce regulatory compliance contribute to building and maintaining trust. Consumer confidence in the technology sector is a driving force behind economic adoption and growth.
Job Creation and Workforce Development:
The technology sector is a significant contributor to job creation and workforce development. Regulations that support the growth of technology companies also influence employment opportunities. Policies that encourage skills development, workforce training, and inclusivity in the technology workforce contribute to economic prosperity and societal well-being.
Environmental Sustainability in Technology:
As technology continues to advance, concerns about its environmental impact have come to the forefront. International regulations addressing e-waste management, energy efficiency, and sustainable technology practices contribute to economic sustainability. Policies that promote environmentally responsible technology development align with global efforts for a more sustainable and resilient economy.
For more insights into the economic effects of international changes in technology regulations, visit Economic effects of international changes in technology regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic effects of international changes in technology regulations are far-reaching, influencing innovation, trade, and various facets of the digital economy. Striking a balance between fostering technological advancements and addressing societal concerns is crucial. Collaborative efforts on the international stage are essential to create regulatory frameworks that not only support economic growth but also ensure the responsible and ethical development of technology on a global scale.
Global Economic Outlook: Trends and Projections

Global Economic Outlook: Trends and Projections
Understanding the current global economic landscape and anticipating future trends is essential for informed decision-making. In this exploration, we delve into the factors shaping the global economic outlook, offering insights into trends and projections.
Current State of the Global Economy
The global economic outlook is influenced by various factors, including GDP growth, employment rates, and trade dynamics. As of the latest data, the world is experiencing a recovery from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Governments and central banks have implemented measures to stimulate economic growth, and businesses are adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
GDP Growth and Economic Resilience
GDP growth remains a key indicator of economic health. While some regions are showing robust recovery, others face challenges. Factors such as vaccination rates, fiscal policies, and global supply chain disruptions contribute to variations in economic resilience. Projections indicate a gradual return to pre-pandemic growth levels, with emerging economies playing a significant role.
Employment Trends and Labor Market Dynamics
Examining employment trends provides insights into the labor market’s resilience and adaptability. Despite recovery, disparities exist, with certain sectors facing persistent challenges. Remote work and technological advancements are shaping the future of work, impacting job types and required skill sets. Global collaboration on workforce development is crucial for addressing these shifts.
Trade Dynamics in a Post-Pandemic World
Global trade dynamics are evolving as nations recover from the pandemic. Supply chain disruptions and changes in consumer behavior have prompted a reevaluation of trade strategies. The global economic outlook anticipates a recalibration of trade relationships, with an emphasis on resilience, sustainability, and adaptability to future disruptions.
Inflation and Central Bank Policies
Inflation trends and central bank policies are central to the global economic outlook. While some regions grapple with rising inflation, others maintain accommodative monetary policies. Central banks are carefully balancing the need for economic stimulus with the risk of overheating. Coordinated efforts are essential to manage inflationary pressures effectively.
Technology and Digital Transformation
The acceleration of digital transformation is a significant driver of the global economic outlook. Technology adoption has become synonymous with resilience and competitiveness. Nations and businesses embracing digital innovation are better positioned to navigate uncertainties and capitalize on emerging opportunities, contributing to sustained economic growth.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Considerations
The global economic outlook incorporates a growing emphasis on ESG considerations. Sustainable practices, social responsibility, and governance principles are integral to long-term economic resilience. Businesses and investors integrating ESG criteria into decision-making contribute to a more sustainable and inclusive global economy.
Challenges and Opportunities on the Horizon
While the global economic outlook is optimistic, challenges persist. Geopolitical tensions, cybersecurity threats, and the uneven distribution of vaccines pose risks to global recovery. However, these challenges also underscore the need for international collaboration, innovation, and adaptive strategies to build a more robust and equitable economic future.
Investment Strategies in a Changing Landscape
In a dynamic economic landscape, strategic investment is paramount. Investors are evaluating opportunities across sectors, with a focus on industries driving digital innovation, sustainable practices, and resilience. Diversification and risk management are key considerations for navigating uncertainties and optimizing investment portfolios.
Shaping a Sustainable and Inclusive Future
The global economic outlook is not just a projection of numbers; it’s a narrative of resilience, adaptation, and collective efforts to shape a sustainable and inclusive future. As the world moves forward, international cooperation, innovative solutions, and a commitment to shared prosperity will play pivotal roles in determining the trajectory of the global economy.
In conclusion, the global economic outlook is a tapestry woven with diverse factors and influenced by a myriad of forces. For those interested in exploring this complex landscape further, visit Global economic outlook. By staying informed and adaptable, stakeholders can actively contribute to and thrive in the evolving global economic landscape.