Economic Shifts: Global Impact of Labor Market Changes

Navigating the Economic Landscape: International Labor Market Changes
In an era characterized by globalization and rapid technological advancements, international labor markets are experiencing profound shifts. These changes hold far-reaching economic implications, influencing industries, employment dynamics, and the overall structure of economies around the world.
Globalization’s Impact on Workforce Dynamics
Globalization has been a driving force behind international labor market changes. Companies now have the ability to tap into a global talent pool, transcending geographical boundaries. While this fosters diversity and brings specialized skills to different industries, it also introduces complexities in managing cross-cultural teams and navigating regulatory variations across countries.
Technological Advancements Reshaping Job Requirements
The relentless march of technology is reshaping the skills demanded in the international labor market. Automation, artificial intelligence, and digitalization are transforming industries and rendering certain job roles obsolete. This shift necessitates upskilling and adaptability in the workforce to meet the evolving demands of a technologically-driven global economy.
Changing Nature of Employment Contracts
Traditional employment models are giving way to more flexible arrangements. The rise of remote work, freelancing, and gig economy platforms is altering the traditional employer-employee relationship. While providing workers with greater flexibility, these changes also pose challenges related to job security, benefits, and workers’ rights, requiring policymakers to adapt regulations accordingly.
Impact on Income Inequality
International labor market changes contribute to the ongoing discourse on income inequality. Disparities in wages and opportunities both within and between countries are becoming more pronounced. The globalization of labor markets can lead to wage competition, where workers in some regions face pressure due to lower wage standards in others, exacerbating income inequality on a global scale.
Global Workforce Mobility and Talent Migration
The ease of international travel and communication has facilitated greater workforce mobility. Skilled professionals may choose to migrate for better opportunities, creating a brain drain in some regions while contributing to the growth of others. Managing the implications of talent migration requires a delicate balance to ensure fair and equitable development across the globe.
Policy Responses to Labor Market Changes
Governments and international bodies are responding to the economic implications of international labor market changes with policy initiatives. From retraining programs to address skill gaps to crafting regulations that protect workers in non-traditional employment arrangements, policymakers play a crucial role in shaping a labor market that is both dynamic and fair.
Evolving Business Strategies in a Global Context
Businesses are adapting their strategies to thrive in the evolving international labor market. Embracing diversity, investing in employee development, and leveraging technology for remote collaboration are becoming integral components of successful business models. Companies that proactively address these changes are better positioned to attract and retain top talent.
The Intersection of Labor Changes and Economic Growth
The relationship between labor market changes and economic growth is intricate. While a skilled and adaptable workforce can drive innovation and productivity, challenges such as income inequality and job insecurity can hamper economic progress. Striking a balance that fosters inclusive growth is essential for sustainable economic development.
The Future Landscape: Adapting to a New Normal
As we navigate the economic implications of international labor market changes, one thing is certain – adaptation is key. Governments, businesses, and individuals must embrace a mindset of continuous learning and flexibility. Proactive measures, including investments in education and workforce development, are essential for mitigating challenges and harnessing the opportunities presented by a dynamically evolving global labor market.
Explore deeper insights into the Economic Implications of International Labor Market Changes to stay informed about the evolving dynamics of the global workforce.
Economic Impact of Global Environmental Changes
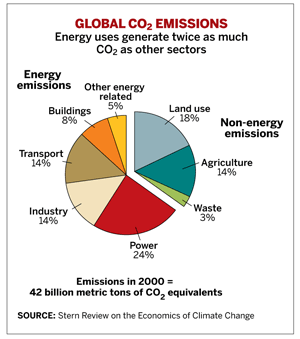
Navigating Global Challenges: Economic Consequences of Environmental Changes
In an era marked by environmental shifts, the global economy finds itself at the intersection of ecological transformations and economic consequences. This article delves into the profound impact that global environmental changes exert on economies worldwide, exploring the multifaceted challenges and opportunities that arise in this complex interplay.
Climate Change and Economic Disruptions
Climate change stands as a primary driver of environmental changes, leading to a cascade of economic disruptions. Extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to agriculture challenge the foundations of economic stability. Nations face the economic consequences of damaged infrastructure, increased disaster response costs, and the need for adaptation strategies to safeguard industries.
Resource Scarcity and Economic Resilience
As environmental changes unfold, resource scarcity becomes a pressing concern with far-reaching economic consequences. Depletion of natural resources, particularly water and arable land, poses challenges to industries dependent on these resources. Economic resilience hinges on strategies that address resource scarcity through sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and innovative solutions.
Biodiversity Loss: Impacts on Industries
The loss of biodiversity, a consequence of environmental changes, has profound implications for various industries. Sectors relying on diverse ecosystems, such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism, face economic challenges. Biodiversity loss disrupts supply chains, affects agricultural productivity, and hampers industries that rely on diverse ecosystems for raw materials and inspiration.
Healthcare Costs in the Face of Environmental Health Risks
Environmental changes contribute to health risks that extend to economic consequences. Increased prevalence of diseases linked to environmental factors, such as air pollution and water contamination, leads to escalated healthcare costs. Nations grapple with the economic burden of treating environmentally induced health conditions, affecting both public health systems and individual economic well-being.
Economic Opportunities in Renewable Energy Transition
Amid challenges, global environmental changes also present economic opportunities, particularly in the transition to renewable energy. Nations investing in renewable energy sources not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also stimulate economic growth. The renewable energy sector creates jobs, fosters innovation, and positions countries at the forefront of the global clean energy market.
Changing Consumer Behavior and Market Dynamics
Environmental awareness influences consumer behavior, ushering in changes in market dynamics. Consumers increasingly favor eco-friendly products and sustainable practices, prompting businesses to adapt. Economic consequences include shifts in demand, opportunities for green businesses, and the need for industries to align with environmentally conscious consumer preferences.
Regulatory Responses: Balancing Environmental Protection and Economic Interests
Governments worldwide grapple with the challenge of crafting regulatory responses that balance environmental protection with economic interests. Stricter environmental regulations can lead to increased compliance costs for industries, impacting their economic viability. Achieving a delicate balance requires innovative policies that foster sustainable practices without stifling economic growth.
Global Trade and Environmental Considerations
Environmental changes influence global trade dynamics. Nations are incorporating environmental considerations into trade agreements, recognizing the interconnectedness of trade and the environment. Economic consequences include the potential for trade disruptions due to environmental regulations, but also opportunities for countries that prioritize sustainable and responsible trade practices.
Economic Adaptation and Innovation
In response to global environmental changes, economic adaptation and innovation become imperatives. Industries must innovate to develop eco-friendly technologies, sustainable practices, and resilience strategies. Economic consequences are shaped by the adaptability of businesses and nations to environmental challenges, influencing their competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Collaborative International Efforts for Sustainability
Addressing the economic consequences of global environmental changes requires collaborative international efforts. Nations come together to formulate agreements, share technologies, and pool resources for sustainable development. Economic benefits arise from cooperative initiatives that address environmental challenges collectively, fostering global economic stability and resilience.
Towards a Sustainable Economic Future
In conclusion, the economic consequences of global environmental changes are intricate and multifaceted. While challenges abound, opportunities for sustainable economic development and innovation emerge. Navigating this intersection requires a concerted effort from governments, industries, and individuals to forge a path towards a more resilient, sustainable, and economically viable future.
Explore more about the Global Economic Consequences of Environmental Changes and the dynamic interplay between environmental shifts and economic landscapes.
Global Economic Resilience: Navigating Labor Law Changes

Introduction:
In an ever-evolving global landscape, changes in labor laws wield a profound influence on economic dynamics. This article explores how nations navigate and exhibit resilience in the face of such changes, highlighting the critical role of adaptability and policy response in sustaining global economic well-being.
Labor Market Dynamics and Adaptation:
Changes in labor laws trigger a ripple effect in labor markets worldwide. The adaptability of nations to these changes determines the resilience of their economies. Governments and businesses must navigate shifts in employment regulations to foster a workforce environment conducive to both worker rights and economic productivity.
Impact on Business Operations:
Labor law changes often impact business operations, influencing everything from hiring practices to workplace conditions. Understanding and responding effectively to these changes are essential for businesses aiming to maintain operational efficiency, human resource management, and overall economic viability.
Worker Protections and Economic Balance:
Labor laws are designed to protect workers’ rights, but finding the right balance is crucial. Excessive regulations can pose challenges for businesses, potentially affecting economic competitiveness. Striking a balance that ensures worker protections without stifling economic growth is a delicate task for policymakers.
Labor Mobility and Global Talent Pool:
Changes in labor laws influence labor mobility and the global talent pool. Nations that can adapt their regulations to attract and retain skilled workers bolster their economic resilience. A flexible approach to labor laws enhances a country’s ability to harness international talent, contributing to economic innovation and competitiveness.
Economic Equality and Social Impact:
Labor law changes play a pivotal role in shaping economic equality within societies. Progressive labor regulations can contribute to reduced income inequality and improved social conditions. Addressing social impact alongside economic considerations is essential for fostering long-term stability.
Legal Compliance Challenges for Businesses:
Businesses often face challenges in adapting to new labor laws. Ensuring legal compliance while maintaining operational efficiency is a delicate balancing act. Investments in HR systems, legal consultations, and employee training become critical components of navigating these changes without adversely affecting economic performance.
Strategies for Economic Resilience:
Nations that prioritize economic resilience in the face of labor law changes often implement strategic measures. This may include proactively updating labor regulations, fostering dialogue between stakeholders, and creating frameworks that encourage a harmonious relationship between labor rights and economic growth.
Global Economic Cooperation:
In an interconnected world, global economic cooperation is paramount. Nations must collaborate to share insights, best practices, and strategies for navigating changes in labor laws. Multilateral efforts can contribute to a more harmonized global economic landscape that prioritizes both worker protections and economic sustainability.
Investments in Education and Skill Development:
As labor laws evolve, so too do the skills required in the workforce. Nations that invest in education and skill development programs enhance their economic resilience. A well-trained and adaptable workforce can more effectively navigate changes in labor laws, contributing to sustained economic growth.
For more insights into global economic resilience in the face of changes in labor laws, visit Global economic resilience in the face of changes in labor laws.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the global economic resilience exhibited in response to changes in labor laws is a testament to the adaptability of nations and businesses. Navigating these changes requires a delicate balance between protecting worker rights and fostering an environment conducive to economic growth. As the world continues to grapple with evolving labor landscapes, the pursuit of strategies that prioritize both economic well-being and labor protections becomes increasingly vital for sustained global prosperity.
Cross-Border Investments: Strategies for Global Growth
Cross-Border Investments: Strategies for Global Growth
The landscape of investment opportunities has expanded beyond domestic markets, with cross-border investments gaining prominence. This article explores the strategies for global growth through cross-border investments and the factors influencing this dynamic approach.
Understanding Cross-Border Investments
Cross-border investments involve allocating capital across different countries, either through direct investments, portfolio investments, or strategic partnerships. This approach allows investors and businesses to diversify their portfolios, access new markets, and capitalize on growth opportunities beyond their home country.
Diversification Benefits and Risk Management
One of the primary motivations for cross-border investments is portfolio diversification. By spreading investments across various geographic regions, industries, and asset classes, investors can reduce risks associated with regional economic downturns or market-specific challenges. Diversification is a key strategy for managing risk and enhancing overall portfolio resilience.
Market Research and Due Diligence
Successful cross-border investments hinge on thorough market research and due diligence. Understanding the regulatory environment, cultural nuances, and economic conditions of the target country is essential. Conducting comprehensive due diligence helps identify potential challenges and opportunities, enabling informed decision-making.
Navigating Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
Each country has its unique regulatory and legal frameworks governing foreign investments. Navigating these structures requires careful consideration of local laws, tax regulations, and compliance requirements. Engaging legal experts and advisors familiar with the target jurisdiction is crucial to ensure adherence to all relevant regulations.
Cultural Sensitivity and Local Partnerships
Cultural sensitivity is paramount in cross-border investments. Building relationships with local partners and understanding cultural nuances contribute to successful business operations in foreign markets. Establishing partnerships with local entities can provide valuable insights, access to networks, and enhance the overall effectiveness of cross-border ventures.
Currency Risks and Hedging Strategies
Currency fluctuations pose a significant risk in cross-border investments. Changes in exchange rates can impact investment returns and financial performance. Implementing effective hedging strategies, such as currency futures or options, helps mitigate these risks and provides a level of certainty in the face of volatile currency markets.
Adapting to Economic and Political Conditions
Economic and political conditions in foreign markets can be dynamic. Adapting to changes in government policies, economic shifts, and geopolitical events is crucial for long-term success. Continuous monitoring of the economic and political landscape helps investors make proactive adjustments to their strategies.
Technology and Global Connectivity
Advancements in technology have facilitated global connectivity, making cross-border investments more accessible. Digital platforms, communication tools, and data analytics enable investors to gather real-time information, conduct virtual meetings, and monitor investments across borders. Leveraging technology enhances the efficiency and speed of cross-border investment processes.
Sector-Specific Opportunities
Different sectors present varying opportunities for cross-border investments. Technology, renewable energy, healthcare, and e-commerce are among the sectors experiencing global growth trends. Identifying sector-specific opportunities aligns investment strategies with broader market dynamics and potential for higher returns.
Long-Term Perspective and Patience
Cross-border investments often require a long-term perspective. Economic cycles, regulatory changes, and market developments may take time to unfold. Patience is a virtue in navigating the complexities of global investments, allowing investors to ride out short-term fluctuations and capitalize on the long-term growth potential.
Conclusion: Navigating the Global Investment Landscape
In conclusion, cross-border investments open doors to a vast and diverse global investment landscape. By embracing strategies such as diversification, thorough research, and cultural understanding, investors and businesses can position themselves for global growth. For those interested in delving deeper into cross-border investments, visit Cross-border investments.
As the world becomes more interconnected, cross-border investments represent a pathway to resilience, innovation, and sustainable growth. Strategic considerations, adaptability, and a commitment to understanding the nuances of each market are key elements in successfully navigating the global investment terrain.
