Navigating Global Economic Stability
Understanding the Pillars of Global Economic Stability
In the ever-changing landscape of the global economy, achieving and maintaining stability is a paramount goal for nations and international organizations. Let’s delve into the key components that contribute to global economic stability and explore the challenges and strategies involved.
Macroeconomic Policies and Their Impact
Central to maintaining stability on a global scale are the macroeconomic policies implemented by individual countries. Fiscal policies, monetary policies, and exchange rate management play crucial roles in influencing economic activity. Coordinated efforts among nations to align these policies can contribute significantly to overall stability.
Trade Relationships and Interdependence
The interconnectedness of economies through international trade is a double-edged sword. While it fosters economic growth, it also exposes nations to external shocks. Ensuring fair trade practices, resolving disputes, and promoting a rules-based international trading system are essential for creating a foundation of stability in the global economy.
Financial System Resilience
A stable global economy relies heavily on the resilience of financial systems worldwide. Strengthening regulatory frameworks, ensuring transparency, and addressing vulnerabilities in financial institutions are key factors. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of financial policies contribute to the prevention of systemic risks that could jeopardize global economic stability.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements introduces both opportunities and challenges to global economic stability. Innovation can drive economic growth, but the uneven adoption of technology can create disparities. Striking a balance that fosters innovation while addressing potential disruptions is crucial for sustaining stability across diverse economies.
Sustainable Development Goals as a Foundation
A commitment to sustainable development is fundamental to achieving global economic stability. Countries must align their economic strategies with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Addressing issues such as poverty, inequality, and environmental sustainability creates a solid foundation for a stable and inclusive global economy.
Geopolitical Dynamics and Their Impact
Geopolitical tensions can have profound effects on global economic stability. Trade wars, political conflicts, and regional disputes can disrupt economic activities and hinder international cooperation. Diplomatic efforts and dialogue become essential in mitigating these challenges and fostering an environment conducive to stability.
Climate Change and Economic Resilience
The increasing threat of climate change poses significant risks to global economic stability. Extreme weather events, resource scarcity, and the transition to a low-carbon economy are challenges that nations must collectively address. Sustainable practices and international cooperation are crucial for building resilience against the economic impact of climate change.
Social Inclusion and Economic Stability
A stable global economy must prioritize social inclusion. Addressing issues of inequality, promoting access to education and healthcare, and fostering inclusive economic policies contribute to social stability. In turn, social stability creates an environment conducive to sustained economic growth on a global scale.
International Cooperation in Times of Crisis
The true test of global economic stability often comes during times of crisis. The ability of nations to collaborate, share resources, and implement coordinated responses is crucial. Institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank play pivotal roles in facilitating international cooperation during challenging economic times.
Building a Resilient Future
In conclusion, achieving and maintaining global economic stability requires a multifaceted approach. From sound macroeconomic policies and resilient financial systems to addressing social issues and navigating geopolitical challenges, the path to stability is complex. However, through international cooperation, innovation, and a commitment to sustainable development, nations can build a more resilient and stable global economy.
To explore more about Global economic stability, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Global Economic Rebound: Trends and Projections

Global Economic Rebound: Trends and Projections
The world is witnessing a concerted effort towards global economic recovery, spurred by collaborative measures and resilience in the face of unprecedented challenges. This article explores the trends and projections shaping the current landscape and the path forward.
Post-Pandemic Economic Landscape
The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the global economic landscape. Nations are grappling with the dual challenge of addressing public health concerns and kickstarting economic recovery. Government interventions, fiscal stimulus packages, and vaccination campaigns are pivotal in shaping the post-pandemic era.
Vaccine Rollouts and Economic Optimism
The successful deployment of vaccines globally has been a game-changer in instilling confidence and optimism. As vaccination rates increase, countries are experiencing a gradual return to normalcy. This positive momentum is essential for rebuilding consumer confidence, reviving industries, and fostering economic growth.
Supply Chain Challenges and Resilience
The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to disruptions across industries. Efforts are underway to enhance supply chain resilience through diversification, technological integration, and strategic planning. Adapting to a more resilient supply chain model is crucial for mitigating future challenges.
Digital Transformation Acceleration
The pandemic accelerated digital transformation across sectors. Businesses that embraced technology found innovative solutions and adapted swiftly to changing circumstances. The continuation of this digital shift is expected to drive efficiency, enhance competitiveness, and contribute to economic growth in the recovery phase.
Shifts in Consumer Behavior and Spending Patterns
Consumer behavior underwent significant shifts during the pandemic, with increased reliance on e-commerce, remote services, and digital entertainment. Understanding these evolving preferences is essential for businesses realigning their strategies to meet changing demands and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Green Recovery and Sustainable Practices
The global economic recovery is witnessing a growing emphasis on sustainability. Many nations are incorporating green initiatives and sustainable practices into their recovery plans. Investments in renewable energy, eco-friendly technologies, and environmentally conscious policies are integral components of the green recovery movement.
Government Stimulus Packages and Fiscal Policies
Governments worldwide have implemented substantial stimulus packages to boost economic recovery. These measures include financial aid to individuals and businesses, infrastructure investments, and tax incentives. The effectiveness of these policies in stimulating economic activity and job creation is a key factor in the recovery trajectory.
Challenges in Emerging Markets and Global Cooperation
While developed economies are making strides in recovery, emerging markets face unique challenges. Disparities in vaccine access, debt burdens, and external shocks pose obstacles to their economic resurgence. Global cooperation in addressing these challenges is crucial for achieving a balanced and inclusive global recovery.
Geopolitical Factors and Trade Dynamics
Geopolitical tensions and trade relations play a significant role in shaping the global economic recovery. Navigating diplomatic challenges, resolving trade disputes, and fostering international collaboration are essential for creating a conducive environment for sustained economic growth.
Future Outlook: Adapting to a New Normal
As the world progresses on the path of global economic recovery, the outlook involves adapting to a new normal. Hybrid work models, resilient supply chains, and sustainable practices are likely to persist. Innovations arising from adversity, coupled with lessons learned during the crisis, will contribute to shaping a more adaptive and robust global economy.
In conclusion, the global economic rebound is a multifaceted journey marked by resilience, adaptation, and collaboration. For those interested in a deeper exploration of global economic recovery, visit Global economic recovery. Navigating through evolving trends and projections requires vigilance, flexibility, and a collective commitment to building a more resilient and sustainable economic future.
Global Economic Risk Landscape: Assessing Challenges Ahead

Navigating Uncertainties: Global Economic Risk Assessment
In the complex tapestry of the global economy, assessing risks is a crucial endeavor. This article delves into the realm of global economic risk assessment, exploring the myriad challenges that shape the risk landscape, strategies for mitigation, and the imperative for businesses and policymakers to navigate uncertainties with resilience.
Understanding the Risk Landscape
The global economic risk assessment begins with a comprehensive understanding of the risk landscape. Geopolitical tensions, economic imbalances, natural disasters, and public health crises are among the myriad factors that contribute to the intricate web of risks. Examining these elements provides a foundation for proactive risk management strategies.
Geopolitical Dynamics: Unraveling Global Relations
Geopolitical tensions and power dynamics among nations have a significant impact on the global economic risk assessment. Trade disputes, sanctions, and diplomatic strains can disrupt international commerce and financial markets. Understanding these geopolitical nuances is essential for businesses with a global footprint, allowing for informed decision-making in an ever-shifting geopolitical landscape.
To delve deeper into the complexities of global economic risk assessment, visit Global Economic Risk Assessment.
Economic Vulnerabilities: Addressing Systemic Weaknesses
Systemic weaknesses within economic structures contribute to vulnerabilities that amplify risks. Overreliance on specific industries, high levels of debt, and inadequate regulatory frameworks can expose economies to severe shocks. Global economic risk assessment involves identifying these vulnerabilities and implementing measures to enhance economic resilience and stability.
Market Volatility: Navigating Fluctuations
Market volatility is an inherent aspect of the global economic risk landscape. Fluctuations in stock prices, currency values, and commodity markets can impact businesses and investors. Mitigating the impact of market volatility involves robust risk management strategies, diversification of investments, and staying attuned to market dynamics.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Lessons from Recent Challenges
The upheavals in global supply chains, heightened by events like the COVID-19 pandemic, underscore the importance of supply chain risk assessment. Businesses are reevaluating their supply chain strategies to enhance resilience, diversify suppliers, and leverage technology for better visibility. A thorough global economic risk assessment incorporates lessons from recent disruptions.
Climate Change: A Growing Concern
The impact of climate change is an increasingly significant factor in global economic risk assessment. Extreme weather events, regulatory changes, and the transition to a low-carbon economy pose risks to industries across sectors. Businesses are adapting by incorporating climate risk into their strategies, fostering sustainability, and aligning with global efforts to address environmental challenges.
Technological Risks: The Double-Edged Sword
While technological advancements drive innovation, they also introduce new risks. Cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and the rapid pace of technological change can pose challenges for businesses and governments alike. Global economic risk assessment involves understanding and mitigating these technological risks, ensuring the responsible and secure adoption of new technologies.
Health Crises: Preparedness and Response
The recent experience with the COVID-19 pandemic has emphasized the critical importance of health risk assessment. Preparedness, rapid response mechanisms, and international cooperation are integral components of mitigating health-related economic risks. Businesses and governments are reevaluating their contingency plans to enhance resilience in the face of potential future health crises.
Policy and Regulatory Risks: Navigating Uncertain Terrain
Changes in government policies and regulatory landscapes can introduce uncertainties for businesses operating globally. Global economic risk assessment involves monitoring political developments, trade policies, and regulatory changes that could impact industries. Agility and adaptability are key for businesses to navigate the dynamic regulatory environment.
Collaborative Risk Mitigation: A Shared Responsibility
Mitigating global economic risks is a shared responsibility that involves collaboration among governments, businesses, and international organizations. Multilateral efforts to address systemic risks, enhance crisis response mechanisms, and foster global cooperation are essential for building a resilient global economic system.
Conclusion: Building Resilience in a Dynamic World
In conclusion, the intricacies of the global economic risk assessment underscore the need for proactive and adaptive strategies. Businesses and governments must navigate the dynamic risk landscape with resilience, leveraging insights from risk assessments to inform decision-making. By addressing vulnerabilities, embracing innovation, and fostering international collaboration, we can collectively build a more resilient global economy.
Unveiling Global Energy Market Trends
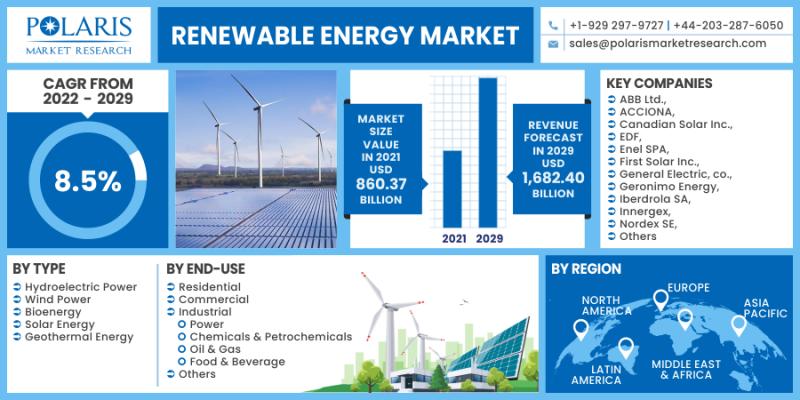
Exploring the Dynamics of Global Energy Market Trends
The global energy landscape is undergoing rapid transformations, shaped by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and geopolitical shifts. In this article, we will delve into the current trends influencing the global energy market and the implications for the future.
Rise of Renewable Energy Sources
One of the most notable trends in the global energy market is the increasing prominence of renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power are witnessing substantial growth as nations strive to reduce carbon emissions and transition to sustainable energy alternatives. This shift is not only driven by environmental considerations but also by the declining costs and increased efficiency of renewable technologies.
Technological Innovations Driving Efficiency
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in shaping the energy landscape. Innovations in energy storage, smart grids, and digital technologies are enhancing the efficiency and reliability of energy systems. These innovations not only optimize energy production and distribution but also contribute to the integration of renewable energy sources into the mainstream energy grid.
Decentralization and Distributed Energy Systems
The traditional centralized model of energy generation and distribution is undergoing a transformation towards decentralization. Distributed energy systems, including microgrids and localized renewable energy installations, are gaining popularity. This trend not only enhances energy resilience but also empowers communities to have greater control over their energy sources and consumption.
Transition to Electric Vehicles
The global shift towards sustainable transportation is a key factor influencing energy market trends. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is driving up the demand for electricity while challenging traditional oil-dependent transportation systems. This trend is reshaping energy consumption patterns, necessitating investments in EV infrastructure and charging technologies.
Natural Gas as a Transition Fuel
While renewable energy is on the rise, natural gas continues to play a significant role as a transition fuel. Its lower carbon emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels make it a more environmentally friendly option. The global energy market is witnessing increased exploration and utilization of natural gas reserves, particularly as a complement to intermittent renewable sources.
Energy Market Trends and Geopolitical Considerations
Geopolitical factors continue to shape global energy markets. Shifts in political alliances, trade dynamics, and regional tensions impact energy supply chains and pricing. Nations are strategically positioning themselves to secure energy resources, leading to fluctuations in the global energy market and influencing long-term energy security considerations.
Investments in Energy Storage Solutions
As the share of intermittent renewable energy sources grows, investments in energy storage solutions become crucial. Battery technologies, pumped storage, and other innovative storage methods are gaining attention to address the challenge of storing excess energy for use during periods of low renewable generation. These investments are essential for maintaining a stable and reliable energy supply.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Initiatives
Amid concerns about resource depletion and environmental impact, energy efficiency and conservation initiatives are gaining prominence. Governments, businesses, and individuals are increasingly focused on optimizing energy use to reduce waste and lower carbon footprints. This trend is influencing consumer behavior, regulatory frameworks, and corporate sustainability practices.
Emergence of Energy Market Digitalization
The digital transformation wave is reaching the energy sector, bringing forth the emergence of energy market digitalization. Smart grids, IoT (Internet of Things) applications, and data analytics are enhancing grid management, predictive maintenance, and overall operational efficiency. This digitalization trend is creating more adaptive and resilient energy systems.
Global Collaboration for Sustainable Energy
Addressing the challenges of climate change and ensuring a sustainable energy future requires global collaboration. International partnerships, agreements, and initiatives are fostering the exchange of expertise, technology, and resources to accelerate the transition to clean and sustainable energy. This collaborative approach is essential for overcoming shared challenges and achieving global energy security.
In conclusion, the global energy market is in a state of flux, driven by a complex interplay of technological, environmental, and geopolitical factors. Embracing renewable energy, investing in innovative technologies, and fostering international cooperation are key strategies for navigating the evolving energy landscape. To explore more about Global energy market trends, visit tankionlineaz.com.
