Global Immigration Regulation Changes: Economic Impacts

Introduction:
The global economic landscape is intricately tied to immigration regulations, and shifts in these policies have profound impacts on economies worldwide. This article delves into the economic effects of changes in immigration regulations, exploring the multifaceted consequences for labor markets, innovation, and overall economic dynamics.
Labor Market Dynamics and Workforce Composition:
Changes in immigration regulations directly influence labor market dynamics. Policies that restrict or facilitate the entry of foreign workers shape the composition of the workforce. Restrictions may lead to labor shortages in certain industries, impacting productivity, while open policies can contribute to a diverse and skilled workforce, positively influencing economic growth.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
Immigration often brings diverse talents and ideas, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship. Policies that encourage the entry of skilled immigrants contribute to a vibrant startup culture and technological advancements. Conversely, stringent regulations may hinder the flow of innovative minds, potentially limiting a nation’s competitiveness in the global innovation landscape.
Economic Growth and Contribution to GDP:
The economic contributions of immigrants play a significant role in a nation’s GDP. Policies that attract skilled immigrants contribute to economic growth by bolstering productivity and consumer spending. Conversely, restrictive policies may lead to talent drain and reduced contributions to the economy, affecting long-term economic prospects.
Entrepreneurial Ecosystem and Startups:
Immigrant entrepreneurs often play a crucial role in fostering a dynamic startup ecosystem. Policies that support immigrant entrepreneurs contribute to job creation and economic vitality. Restrictive immigration policies may impede the growth of startups, limiting innovation and hindering the potential for economic expansion in emerging industries.
Skill Gaps and Economic Competitiveness:
Immigration regulations play a role in addressing skill gaps within a country. Policies that facilitate the entry of skilled workers help bridge skill shortages, enhancing a nation’s economic competitiveness. Conversely, restrictive policies may exacerbate skill gaps, potentially hindering industries that rely on specialized expertise.
Consumer Markets and Demographic Trends:
The influx of immigrants often contributes to the expansion of consumer markets. Policies that attract immigrants lead to demographic diversification, influencing consumer trends and market demands. Restrictive policies may limit demographic diversity, impacting consumer markets and overall economic vibrancy.
Social Services and Public Finances:
Changes in immigration regulations influence the utilization of social services and public finances. Policies that balance immigration with social service accessibility contribute to a sustainable economic model. However, an influx of immigrants without proper policy frameworks may strain public services, affecting government budgets and potentially leading to economic challenges.
Global Talent Competition and Economic Collaboration:
In a globalized world, nations compete for top talent. Policies that attract skilled professionals foster international collaboration and contribute to a nation’s economic standing. Conversely, restrictive immigration policies may result in a brain drain and limit opportunities for economic collaboration on a global scale.
Economic Resilience in Times of Change:
The adaptability of immigration policies is crucial for economic resilience, especially in times of change. Policies that respond to economic needs and global trends contribute to a nation’s ability to navigate uncertainties. Flexibility in immigration regulations ensures that a country can address labor market demands and maintain economic stability.
For more insights into the global economic effects of changes in immigration regulations, visit Global economic effects of changes in immigration regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic effects of changes in immigration regulations are far-reaching, influencing labor markets, innovation, and overall economic growth. Striking a balance between attracting skilled talent and addressing domestic concerns requires nuanced policy approaches. As nations navigate these changes, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, businesses, and the global community are essential to ensuring that immigration regulations contribute positively to economic development and resilience.
Technological Leap: Global Economic Impact of Advancements

Technological Leap: Unraveling the Global Economic Impact of Advancements
The world is in the midst of a technological revolution that transcends borders, reshaping industries, economies, and the very fabric of our daily lives. This article delves into the profound economic impact of technological advancements worldwide, exploring the transformative effects and the strategies needed to navigate this dynamic landscape.
Catalyst for Economic Growth: The Power of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements serve as a powerful catalyst for economic growth on a global scale. Innovations in areas such as artificial intelligence, automation, and the Internet of Things (IoT) propel industries forward, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and creating new avenues for economic expansion. Nations that actively embrace and invest in these advancements position themselves at the forefront of global economic progress.
Job Transformation and Creation: Navigating the Workforce Landscape
The integration of technology into various sectors brings about a transformation in the workforce landscape. While certain traditional jobs may undergo automation, technological advancements simultaneously create new roles and opportunities. The global economy must navigate this transition by fostering skill development, promoting adaptability, and ensuring inclusivity to harness the full potential of a technologically driven job market.
Global Connectivity: Breaking Geographical Barriers
One of the hallmarks of technological advancements is the breaking down of geographical barriers. The world is more connected than ever before, enabling seamless communication, collaboration, and trade across borders. This interconnectedness fosters a global economy where businesses can operate on an international scale, expanding market reach and driving economic collaboration.
E-Commerce Revolution: Transforming Consumer Behavior
Technological advancements have ushered in an e-commerce revolution, fundamentally altering consumer behavior. Online platforms have become global marketplaces, providing businesses with unprecedented access to a diverse consumer base. This shift necessitates a recalibration of traditional business models, emphasizing digital presence, personalized experiences, and efficient supply chain management to thrive in the evolving economic landscape.
Data as a Strategic Asset: Driving Informed Decision-Making
In the era of technological advancements, data emerges as a strategic asset. The ability to collect, analyze, and derive insights from vast amounts of data empowers businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions. Harnessing the potential of data-driven strategies is crucial for optimizing operations, identifying market trends, and ensuring a competitive edge in the global economic arena.
Challenges of Technological Disruption: Navigating Disparities
While technological advancements offer immense opportunities, they also present challenges, particularly in terms of economic disparities. Disruptions caused by automation may lead to job displacement, creating a need for comprehensive strategies to address retraining, reskilling, and ensuring the equitable distribution of benefits. Navigating these disparities is essential for fostering inclusive economic growth.
Sustainable Technology: Balancing Progress with Environmental Responsibility
As the world becomes increasingly reliant on technology, there is a growing imperative to ensure sustainability. Technological advancements should align with environmental responsibility, focusing on innovations that contribute to a sustainable future. Balancing progress with ecological considerations is not only an ethical necessity but also a key aspect of ensuring the long-term economic health of the planet.
Investment in Research and Development: Fostering Innovation
To fully realize the economic impact of technological advancements, nations and businesses must prioritize investment in research and development (R&D). Fostering a culture of innovation, supporting emerging technologies, and collaborating on groundbreaking projects are essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the global economy. R&D investment acts as a driving force for sustained economic growth.
Government Policies for Technological Adoption: A Strategic Approach
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping the economic impact of technological advancements. Strategic policies that encourage innovation, protect intellectual property, and foster a conducive environment for technology adoption are crucial. By creating regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with ethical considerations, governments contribute to a thriving economic ecosystem.
Navigating the Future: Strategies for Global Economic Harmony
In conclusion, the economic impact of technological advancements worldwide is undeniable. To navigate this dynamic landscape successfully, a comprehensive approach is required. This includes embracing innovation, investing in human capital, addressing societal disparities, and ensuring that technological progress aligns with sustainable and ethical considerations. By adopting strategic and inclusive strategies, nations can harness the full potential of technological advancements for global economic harmony.
To explore more about the Economic impact of technological advancements worldwide, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Global Economic Impact: Changes in Tax Policies
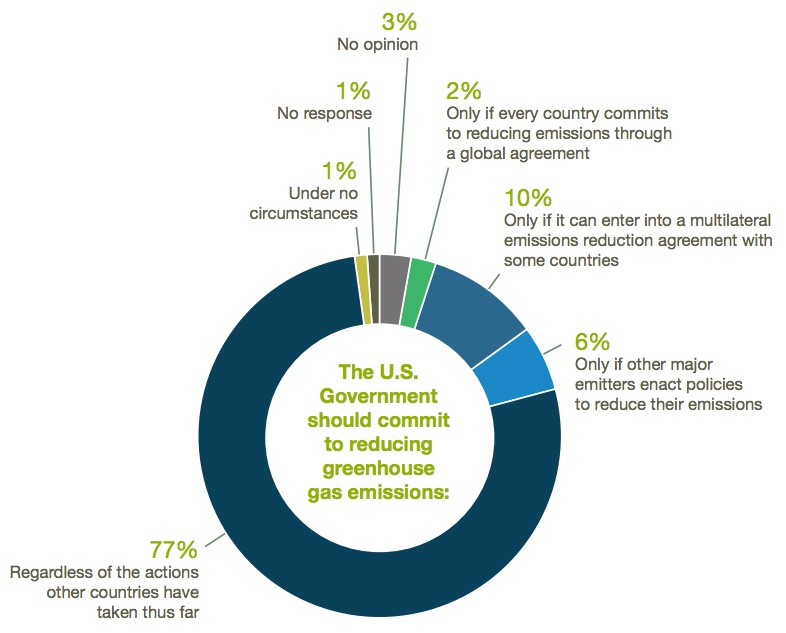
Navigating Fiscal Frontiers: Unraveling the Global Economic Impact of Changes in Tax Policies
In the intricate dance of global economics, changes in tax policies wield significant influence. This article delves into the multifaceted effects that alterations in tax regulations can have on the global economic landscape.
The Dynamics of Revenue Collection and Government Spending
Changes in tax policies play a pivotal role in shaping how governments collect revenue and allocate funds. Shifts in tax rates, structures, and incentives impact the overall revenue available to governments, subsequently influencing public spending on infrastructure, social programs, and other critical initiatives. The delicate balance between taxation and expenditure sets the tone for a nation’s economic trajectory.
Investor Sentiment and Business Landscape
The business community closely monitors changes in tax policies, as these adjustments can significantly impact investor sentiment and the overall business landscape. Alterations in corporate tax rates or regulations may influence investment decisions, capital flows, and the profitability of enterprises. Understanding these dynamics becomes crucial for businesses navigating the ever-evolving global market.
Income Distribution and Social Equity
Tax policies serve as a tool for shaping income distribution and addressing issues of social equity. Progressive or regressive tax structures directly impact the disposable income of individuals and households. Changes in these policies can contribute to either widening or narrowing the wealth gap within a society, influencing social dynamics and public perception of economic fairness.
International Competitiveness and Trade Relations
Nations often adjust tax policies to enhance international competitiveness and foster favorable trade relations. A reduction in corporate tax rates, for example, may attract foreign investment and stimulate economic growth. However, these strategies can also spark competition among nations, creating a dynamic interplay of tax policies as countries vie for a favorable position in the global economic arena.
Impact on Consumer Behavior and Spending Patterns
Changes in tax policies resonate with consumers, influencing their behavior and spending patterns. Adjustments in sales taxes, value-added taxes, or other consumption-related levies directly impact the cost of goods and services. Consumers respond by adjusting their spending habits, affecting industries and sectors differently and contributing to the broader economic landscape.
Innovation and Research & Development Initiatives
Tax incentives can act as catalysts for innovation and research & development (R&D) initiatives. Governments may use tax policies to encourage businesses to invest in technology, innovation, and sustainable practices. Changes in these incentives can shape the direction of corporate strategies, influencing the pace of technological advancements and fostering economic growth through innovation.
Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth
The allure of favorable tax environments often attracts foreign direct investment (FDI), contributing to economic growth. Changes in tax policies can impact the attractiveness of a country as an investment destination. Understanding the correlation between tax regulations and FDI is essential for policymakers seeking to bolster their nation’s economic development.
Challenges and Unintended Consequences
While changes in tax policies aim to achieve specific economic goals, they can also pose challenges and lead to unintended consequences. Sudden adjustments may disrupt established business models, create uncertainties, and result in unanticipated outcomes. Policymakers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against these challenges to formulate effective and sustainable tax strategies.
Global Cooperation and Tax Harmonization
In an interconnected world, achieving global economic stability often requires cooperation and coordination on tax matters. The pursuit of tax harmonization aims to reduce tax evasion, foster fair competition, and create a level playing field for businesses. Global collaboration becomes imperative to address cross-border tax challenges and create a cohesive and equitable international tax framework.
For a more comprehensive understanding of the global economic impact of changes in tax policies, explore this detailed study here. The study offers in-depth analyses of case studies, providing valuable insights into the intricate dynamics of global economies in the wake of evolving tax regulations.
Economic Impacts of Global Political Shifts: Navigating Change

Economic Impacts of Global Political Shifts: Navigating Change
In the dynamic landscape of global affairs, political shifts wield significant influence over economic structures. These changes, whether driven by geopolitical tensions, diplomatic realignments, or policy adjustments, have far-reaching consequences on the world economy. Examining the economic impact of alterations in global political landscapes becomes imperative for understanding the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Economic Interdependence and Global Political Dynamics
The intertwining of economies on a global scale means that alterations in political dynamics can quickly reverberate across borders. Economic interdependence, characterized by intricate trade networks and interconnected financial systems, amplifies the impact of political decisions. A change in diplomatic relations or the imposition of trade restrictions can disrupt established economic patterns, affecting industries and markets worldwide.
Trade Policies and Market Fluctuations
One of the primary channels through which political shifts influence economies is the adjustment of trade policies. Trade agreements, tariffs, and international partnerships play a pivotal role in shaping economic landscapes. A sudden shift in political alliances or the initiation of trade wars can lead to market fluctuations, impacting businesses and investors. Navigating these uncertainties becomes essential for maintaining economic stability.
Investor Confidence and Capital Flows
Global investors closely monitor political developments as they significantly influence market sentiment. Changes in political landscapes can either bolster or erode investor confidence, influencing capital flows. A stable and predictable political environment tends to attract investments, while uncertainty may lead to capital flight. Understanding the nuances of political shifts is crucial for policymakers and business leaders seeking to foster a conducive investment climate.
Regional Economic Blocs and Alliances
Political changes often prompt countries to reassess their participation in regional economic blocs and alliances. The formation or dissolution of such partnerships can reshape trade dynamics and alter economic dependencies. Businesses operating within these regions must adapt to evolving frameworks and regulations, navigating the opportunities and challenges presented by shifting political alliances.
Crisis Management and Economic Resilience
In times of political upheaval, countries and businesses alike must focus on crisis management and economic resilience. Developing strategies to mitigate the impact of sudden political changes becomes crucial. Diversification of trade partners, robust financial planning, and adaptive policy frameworks contribute to building resilience in the face of geopolitical uncertainties.
Technological Advancements and Political Realities
In the contemporary era, technological advancements intersect with political realities, creating a new layer of complexity. The alignment of technological policies with geopolitical objectives shapes economic competitiveness. Countries that strategically leverage technology in alignment with their political goals can gain a competitive edge in the global economic landscape.
Environmental Policies and Sustainable Development
Political shifts also influence the direction of environmental policies, impacting industries with a focus on sustainability. As countries align their political agendas with environmental concerns, businesses must adapt to evolving regulations and consumer preferences. The intersection of politics and sustainability becomes a critical factor in shaping economic activities globally.
Challenges and Opportunities in Emerging Markets
Political changes often create both challenges and opportunities in emerging markets. While uncertainties may pose risks, strategic realignments and policy reforms can open up new avenues for economic growth. Understanding the nuances of political landscapes in emerging markets is essential for businesses seeking to expand their global footprint.
Navigating Change: The Role of Global Economic Recovery Plans
In the wake of political shifts, the implementation of robust global economic recovery plans becomes paramount. Governments and international organizations collaborate to devise strategies that stimulate economic growth, create employment opportunities, and ensure financial stability. These plans serve as a roadmap for navigating the challenges posed by changes in global political landscapes.
To explore further insights into the economic impact of changes in global political landscapes, visit Economic Impact of Changes in Global Political Landscapes.
Navigating Global Economic Downturns: Challenges and Strategies

Navigating Global Economic Downturns: Challenges and Strategies
Global economic downturns are formidable challenges that reverberate across nations, impacting businesses, individuals, and governments alike. In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted impact of these downturns, examining the challenges they pose and unveiling strategies to navigate the turbulent economic landscapes they create.
Understanding the Dynamics of Economic Downturns
Economic downturns are characterized by a contraction in economic activity, often marked by a decline in GDP, rising unemployment, and decreased consumer spending. Understanding the dynamics of these downturns is crucial, as they can be triggered by various factors, including financial crises, geopolitical tensions, or external shocks like pandemics.
To explore the impact of global economic downturns, visit Impact of Global Economic Downturns.
Employment Challenges and Job Insecurity
One of the most immediate and palpable effects of economic downturns is the surge in unemployment rates. Businesses, facing financial constraints, may implement cost-cutting measures, leading to layoffs and hiring freezes. Job insecurity becomes a widespread concern, impacting the livelihoods of individuals and creating challenges for labor markets.
Business Closures and Financial Strain
Economic downturns can trigger a wave of business closures, especially among smaller enterprises with limited financial resilience. The strain on businesses emanates from reduced consumer spending, disrupted supply chains, and financial market uncertainties. This creates a domino effect, contributing to the overall economic contraction.
Financial Market Volatility and Investor Anxiety
Global economic downturns often coincide with heightened volatility in financial markets. Stock market fluctuations, currency devaluations, and fluctuations in commodity prices can induce anxiety among investors. The uncertainty surrounding economic conditions prompts a flight to safety, impacting investment decisions and capital flows.
Consumer Spending Patterns and Economic Slowdown
Consumer confidence takes a hit during economic downturns, leading to altered spending patterns. Individuals may reduce discretionary spending, delay major purchases, and focus on essential goods and services. This shift in consumer behavior contributes to an economic slowdown as demand weakens across various sectors.
Government Responses and Stimulus Measures
Governments play a pivotal role in responding to economic downturns. Fiscal and monetary policies are deployed to stimulate economic activity, mitigate job losses, and stabilize financial markets. Stimulus measures, including tax incentives, infrastructure spending, and interest rate adjustments, aim to rejuvenate economic growth and restore confidence.
Debt Challenges and Financial Stress
Economic downturns often amplify existing debt challenges. Both individuals and businesses may struggle with servicing debts amid reduced incomes and financial uncertainties. This financial stress can lead to a cycle of defaults, impacting the banking sector and exacerbating economic challenges.
International Trade Disruptions and Supply Chain Issues
The interconnected nature of the global economy means that economic downturns can trigger disruptions in international trade. Supply chains face challenges as demand contracts, leading to inventory gluts or shortages. Trade tensions may escalate, impacting diplomatic relations and exacerbating economic difficulties.
Innovation and Adaptation in Business Strategies
Amid challenges, economic downturns can catalyze innovation and adaptation in business strategies. Companies may reevaluate their operations, embrace digital transformation, and explore new markets. Innovations born out of necessity during downturns can contribute to long-term resilience and competitiveness.
Resilience Building for Future Uncertainties
As the global economy grapples with the impact of downturns, there is a growing emphasis on building resilience for future uncertainties. Businesses and individuals alike are recognizing the importance of diversification, risk management, and strategic planning to withstand economic shocks. Governments are investing in social safety nets and infrastructure to enhance overall resilience.
Conclusion: Charting the Path to Recovery
In conclusion, navigating the impact of global economic downturns requires a collective and strategic approach. Understanding the multifaceted challenges, from employment concerns to financial market volatility, is essential. By implementing responsive government policies, fostering innovation, and prioritizing resilience building, nations and businesses can chart a path to recovery and set the stage for sustainable growth in a post-downturn landscape.
International Tech Regulation Shifts: Economic Impacts

Introduction:
The intersection of technology and international regulations is a pivotal factor shaping the global economic landscape. This article explores the profound economic effects of international changes in technology regulations, shedding light on how policies influence innovation, trade, and overall economic dynamics.
Innovation and Technology Development:
Changes in technology regulations at the international level have a direct impact on innovation. Policies that encourage a conducive environment for technological advancements, intellectual property protection, and research and development contribute to economic growth. Conversely, stringent regulations may stifle innovation by creating barriers and compliance challenges for technology companies.
Global Trade and Market Access:
International technology regulations play a crucial role in shaping global trade dynamics. Policies related to market access, trade agreements, and cross-border data flow impact the ability of technology companies to expand globally. Open and collaborative regulatory frameworks facilitate the seamless flow of technology-related goods and services, fostering economic interconnectedness.
Digital Economy and E-commerce:
The digital economy is significantly influenced by changes in technology regulations. Policies governing e-commerce, data privacy, and online transactions shape the landscape for digital businesses. Forward-thinking regulations that provide a balance between consumer protection and business innovation contribute to the growth of the digital economy, positively impacting economic indicators.
Cybersecurity and Resilience:
International technology regulations also address cybersecurity concerns. Policies aimed at enhancing cybersecurity measures and protecting critical infrastructure contribute to economic resilience. The economic consequences of cyber threats can be significant, and robust regulations play a vital role in safeguarding businesses, government institutions, and the overall economy from digital risks.
Cross-Border Collaboration and Research Partnerships:
Collaboration across borders is crucial for technology advancements. Regulations that foster international research partnerships and collaboration contribute to the collective growth of the global technology ecosystem. Policies that facilitate the movement of talent, ideas, and resources across borders enhance the capabilities of the technology sector, positively impacting economic innovation.
Data Governance and Privacy Protection:
As data becomes a cornerstone of the digital era, international regulations governing data governance and privacy protection are paramount. Policies that establish clear guidelines for data handling and protection contribute to user trust and confidence. A robust data governance framework is essential for fostering a secure digital environment, supporting economic activities that rely on data-driven insights.
Competition and Market Dynamics:
Regulations in the technology sector also address issues of competition and market dynamics. Policies that prevent anti-competitive practices, promote fair market competition, and ensure a level playing field contribute to economic efficiency. Striking the right balance between fostering innovation and preventing monopolistic behavior is essential for a healthy and competitive technology market.
Consumer Trust and Regulatory Compliance:
Consumer trust is a key factor in the success of technology products and services. Regulations that prioritize consumer rights, ensure transparency, and enforce regulatory compliance contribute to building and maintaining trust. Consumer confidence in the technology sector is a driving force behind economic adoption and growth.
Job Creation and Workforce Development:
The technology sector is a significant contributor to job creation and workforce development. Regulations that support the growth of technology companies also influence employment opportunities. Policies that encourage skills development, workforce training, and inclusivity in the technology workforce contribute to economic prosperity and societal well-being.
Environmental Sustainability in Technology:
As technology continues to advance, concerns about its environmental impact have come to the forefront. International regulations addressing e-waste management, energy efficiency, and sustainable technology practices contribute to economic sustainability. Policies that promote environmentally responsible technology development align with global efforts for a more sustainable and resilient economy.
For more insights into the economic effects of international changes in technology regulations, visit Economic effects of international changes in technology regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic effects of international changes in technology regulations are far-reaching, influencing innovation, trade, and various facets of the digital economy. Striking a balance between fostering technological advancements and addressing societal concerns is crucial. Collaborative efforts on the international stage are essential to create regulatory frameworks that not only support economic growth but also ensure the responsible and ethical development of technology on a global scale.
Global Economic Ripples: Environmental Policy Changes Impact

Introduction:
In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, changes in global environmental policies have far-reaching consequences on economies worldwide. This article delves into the intricate relationship between shifts in environmental policies and their profound impact on the global economy, highlighting the interconnectedness of environmental sustainability and economic prosperity.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
One of the primary drivers of economic change stemming from environmental policies is the push towards renewable energy. Shifts towards cleaner, sustainable energy sources not only transform the energy sector but also stimulate economic growth by fostering innovation, creating new industries, and generating employment opportunities.
Investments in Green Technologies:
Changes in environmental policies often translate into increased investments in green technologies. Governments and businesses alike allocate resources to research and develop sustainable solutions. This influx of capital into green innovation contributes not only to environmental preservation but also to economic dynamism and competitiveness on a global scale.
Market Shifts and Economic Opportunities:
Environmental policies drive market shifts, influencing consumer preferences and business strategies. As sustainability becomes a key consideration, businesses adapting to environmentally conscious practices find new economic opportunities. Conversely, companies that fail to align with green initiatives may face economic challenges in an evolving market.
Climate Resilience and Risk Mitigation:
Adapting to climate change and mitigating environmental risks are economic imperatives. Nations and businesses that incorporate climate resilience into their strategies are better equipped to navigate challenges posed by extreme weather events and other environmental factors. This resilience fosters economic stability and continuity.
Carbon Pricing and Market Incentives:
Environmental policies often include mechanisms such as carbon pricing, providing market incentives for businesses to reduce their carbon footprint. This not only promotes environmental responsibility but also encourages businesses to adopt sustainable practices, fostering economic growth while mitigating environmental impact.
Supply Chain Sustainability:
Changes in environmental policies influence supply chain dynamics, with a growing emphasis on sustainability. Companies are compelled to assess and minimize the environmental impact of their supply chains. This shift towards sustainability not only aligns with environmental goals but also enhances corporate reputations and resilience in the global market.
Job Creation in the Green Sector:
The transition to a more sustainable economy leads to job creation in the green sector. From renewable energy projects to environmental consulting, a wide array of employment opportunities emerges. This not only addresses unemployment concerns but also contributes to a skilled workforce focused on sustainable practices.
Green Finance and Sustainable Investments:
Environmental policies drive the growth of green finance and sustainable investments. Investors increasingly consider environmental factors in their decision-making processes. The integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment strategies reflects a broader shift towards responsible and sustainable economic practices.
International Collaboration for Environmental Goals:
Environmental challenges transcend borders, necessitating international collaboration. Changes in environmental policies often spark joint efforts to address global issues such as climate change. Collaborative initiatives not only contribute to environmental preservation but also strengthen diplomatic and economic ties between nations.
Linking Economic Impact and Environmental Policies:
Understanding the profound economic impact of changes in environmental policies is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike. Striking a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability is a global imperative. The choices made today will shape the future of our economies, emphasizing the need for a harmonious relationship between environmental policies and worldwide economic well-being.
For more insights into the worldwide economic impact of changes in environmental policies, visit Worldwide economic impact of changes in environmental policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the worldwide economic impact of changes in environmental policies is evident across various facets of the global economy. From renewable energy revolutions to sustainable investments and market shifts, the interplay between environmental responsibility and economic prosperity is undeniable. As nations strive for a more sustainable future, the economic implications of environmental policies underscore the need for collective action and conscientious decision-making on a global scale.
Global Economic Resilience: Navigating Labor Law Changes

Introduction:
In an ever-evolving global landscape, changes in labor laws wield a profound influence on economic dynamics. This article explores how nations navigate and exhibit resilience in the face of such changes, highlighting the critical role of adaptability and policy response in sustaining global economic well-being.
Labor Market Dynamics and Adaptation:
Changes in labor laws trigger a ripple effect in labor markets worldwide. The adaptability of nations to these changes determines the resilience of their economies. Governments and businesses must navigate shifts in employment regulations to foster a workforce environment conducive to both worker rights and economic productivity.
Impact on Business Operations:
Labor law changes often impact business operations, influencing everything from hiring practices to workplace conditions. Understanding and responding effectively to these changes are essential for businesses aiming to maintain operational efficiency, human resource management, and overall economic viability.
Worker Protections and Economic Balance:
Labor laws are designed to protect workers’ rights, but finding the right balance is crucial. Excessive regulations can pose challenges for businesses, potentially affecting economic competitiveness. Striking a balance that ensures worker protections without stifling economic growth is a delicate task for policymakers.
Labor Mobility and Global Talent Pool:
Changes in labor laws influence labor mobility and the global talent pool. Nations that can adapt their regulations to attract and retain skilled workers bolster their economic resilience. A flexible approach to labor laws enhances a country’s ability to harness international talent, contributing to economic innovation and competitiveness.
Economic Equality and Social Impact:
Labor law changes play a pivotal role in shaping economic equality within societies. Progressive labor regulations can contribute to reduced income inequality and improved social conditions. Addressing social impact alongside economic considerations is essential for fostering long-term stability.
Legal Compliance Challenges for Businesses:
Businesses often face challenges in adapting to new labor laws. Ensuring legal compliance while maintaining operational efficiency is a delicate balancing act. Investments in HR systems, legal consultations, and employee training become critical components of navigating these changes without adversely affecting economic performance.
Strategies for Economic Resilience:
Nations that prioritize economic resilience in the face of labor law changes often implement strategic measures. This may include proactively updating labor regulations, fostering dialogue between stakeholders, and creating frameworks that encourage a harmonious relationship between labor rights and economic growth.
Global Economic Cooperation:
In an interconnected world, global economic cooperation is paramount. Nations must collaborate to share insights, best practices, and strategies for navigating changes in labor laws. Multilateral efforts can contribute to a more harmonized global economic landscape that prioritizes both worker protections and economic sustainability.
Investments in Education and Skill Development:
As labor laws evolve, so too do the skills required in the workforce. Nations that invest in education and skill development programs enhance their economic resilience. A well-trained and adaptable workforce can more effectively navigate changes in labor laws, contributing to sustained economic growth.
For more insights into global economic resilience in the face of changes in labor laws, visit Global economic resilience in the face of changes in labor laws.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the global economic resilience exhibited in response to changes in labor laws is a testament to the adaptability of nations and businesses. Navigating these changes requires a delicate balance between protecting worker rights and fostering an environment conducive to economic growth. As the world continues to grapple with evolving labor landscapes, the pursuit of strategies that prioritize both economic well-being and labor protections becomes increasingly vital for sustained global prosperity.
Global Housing Policy Shifts: Economic Ramifications

Introduction:
The global landscape of housing policies is undergoing transformative changes, with profound implications for the world economy. This article explores the economic ramifications of shifts in housing policies, delving into how these changes impact nations, businesses, and individuals.
Housing Market Dynamics:
Changes in housing policies reverberate through the housing market, influencing supply, demand, and pricing dynamics. Policies that encourage affordable housing can stimulate economic activities by making homeownership more accessible. Conversely, shifts that limit housing options may pose challenges for both the real estate industry and aspiring homeowners, affecting economic aspects of housing transactions.
Investments and Economic Growth:
Housing policies play a crucial role in shaping investment patterns and overall economic growth. Policies that incentivize real estate investments can contribute to economic expansion by driving construction activities, creating jobs, and fostering a vibrant housing market. However, policies that create uncertainty or impose restrictions may dampen investor confidence, potentially impacting economic growth.
Social and Economic Equity:
Housing policies are instrumental in addressing social and economic equity. Policies that promote fair housing practices and provide affordable housing options contribute to a more equitable society. Ensuring access to housing for diverse socioeconomic groups is not only a social imperative but also a factor influencing economic stability and inclusivity.
Mortgage Markets and Financial Stability:
The health of mortgage markets is closely tied to housing policies. Changes in policies related to lending practices and mortgage regulations influence financial stability. Policies that strike a balance between facilitating homeownership and preventing excessive risk-taking contribute to a robust and stable financial system, fostering economic resilience.
Urban Development and Infrastructure:
Housing policies intersect with urban development and infrastructure planning. Policies that prioritize sustainable and well-planned urban growth can enhance economic development by creating efficient living spaces, reducing commuting times, and improving overall infrastructure. Smart housing policies align with broader urban development goals, contributing to economic efficiency and quality of life.
Housing Affordability and Consumer Spending:
Affordable housing is linked to consumer spending patterns. Policies that address housing affordability positively impact disposable income, allowing individuals to allocate resources to other areas of the economy. On the contrary, housing policies that lead to inflated prices may constrain consumer spending, affecting the overall economic landscape.
Rental Market Dynamics and Flexibility:
Policies governing the rental market also play a role in economic outcomes. Rental policies that strike a balance between tenant protections and landlord incentives contribute to a stable rental market. A well-regulated rental sector provides housing flexibility, which is essential for a dynamic and adaptable workforce, ultimately influencing economic productivity.
Government Expenditure and Social Programs:
Changes in housing policies influence government expenditure, particularly in social programs related to housing. Policies that prioritize social housing programs may lead to increased public spending. Balancing these expenditures with broader economic considerations is essential to ensure the effectiveness of social programs while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
International Real Estate Investments:
Global economic implications extend to international real estate investments. Changes in housing policies in one country can influence the decisions of international investors. Policies that create a favorable environment for real estate investments may attract foreign capital, contributing to economic growth and cross-border economic interactions.
For more insights into the global economic implications of changes in housing policies, visit Global economic implications of changes in housing policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the global economic implications of changes in housing policies are multifaceted, influencing various facets of economies worldwide. Striking a balance between promoting housing affordability, encouraging investment, and ensuring social equity is crucial for fostering resilient and inclusive economic growth. As nations navigate these policy shifts, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities become essential in shaping a housing landscape that supports both economic prosperity and societal well-being.
World Energy Regulation Shifts: Economic Transformations

Introduction:
The world is undergoing transformative changes in energy regulations, and these shifts have far-reaching economic implications. This article explores the profound impact of changes in energy regulations on the global economy, examining how policies shape energy markets, influence investments, and contribute to broader economic trends.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
One of the primary drivers of changes in energy regulations is the global shift towards renewable energy sources. Policies promoting the use of clean and sustainable energy, such as solar and wind power, contribute to the growth of the renewable energy sector. This revolution not only addresses environmental concerns but also stimulates economic activity by creating jobs and fostering innovation in the renewable energy industry.
Investments in Clean Technologies:
Changes in energy regulations often lead to increased investments in clean technologies. Governments worldwide are incentivizing businesses to adopt energy-efficient practices and invest in green technologies. This trend not only aligns with environmental goals but also stimulates economic growth by driving innovation and creating new markets for clean and sustainable technologies.
Energy Independence and Security:
Strategic changes in energy regulations are aimed at achieving energy independence and security. Policies that diversify energy sources, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and enhance energy efficiency contribute to a more secure and resilient energy infrastructure. This, in turn, has positive economic implications by reducing vulnerabilities to energy supply disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Job Creation in the Energy Sector:
The transition to cleaner energy sources creates job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. Policies supporting the growth of clean energy industries lead to job creation in areas such as solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and green construction. The economic impact extends beyond energy production, positively influencing employment rates and local economies.
Impact on Traditional Energy Industries:
While there is a push towards cleaner energy, changes in regulations also impact traditional energy industries. Policies aimed at reducing reliance on fossil fuels may pose challenges for industries like coal and oil. Governments must navigate a delicate balance between promoting clean energy and managing the economic transition for regions heavily dependent on traditional energy sources.
Smart Grids and Technological Innovation:
Advancements in energy regulations often involve the integration of smart grids and innovative technologies. Policies supporting the development of smart grids enhance energy efficiency, enable better management of energy resources, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. These technological innovations contribute to economic efficiency and the modernization of energy infrastructure.
Global Cooperation in Energy Transition:
Energy regulations are increasingly becoming a focal point of global cooperation. International agreements and collaborations aim to address climate change by transitioning to sustainable energy systems. This cooperation not only has environmental benefits but also fosters economic collaboration between nations, creating opportunities for joint investments and technology exchange.
Consumer Empowerment and Energy Choices:
Changes in energy regulations empower consumers to make sustainable energy choices. Policies that promote consumer access to clean energy options, such as rooftop solar panels or community-based renewable projects, contribute to a decentralized energy landscape. This empowerment enhances economic resilience and supports the growth of local and community-driven energy initiatives.
Economic Challenges and Transition Costs:
While the shift towards cleaner energy is promising, there are economic challenges associated with the transition. Changes in energy regulations may entail upfront costs for businesses and industries adapting to new standards. Governments must carefully manage these challenges to ensure a smooth and economically viable transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Innovation Hubs and Economic Hubs:
Cities and regions that embrace changes in energy regulations become innovation hubs and economic centers. Policies that encourage the development of clean energy technologies attract businesses, research institutions, and skilled professionals. These hubs drive economic growth, creating a ripple effect that extends beyond the energy sector to various industries and services.
For more insights into the world economic impact of changes in energy regulations, visit World economic impact of changes in energy regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, changes in energy regulations are reshaping the global economic landscape. The transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources presents significant opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation. As nations navigate this energy transition, it is crucial to implement policies that balance environmental stewardship with economic considerations, fostering a resilient and prosperous global economy.
