Navigating World Economic Disparities
Understanding the Nuances of Global Economic Inequality
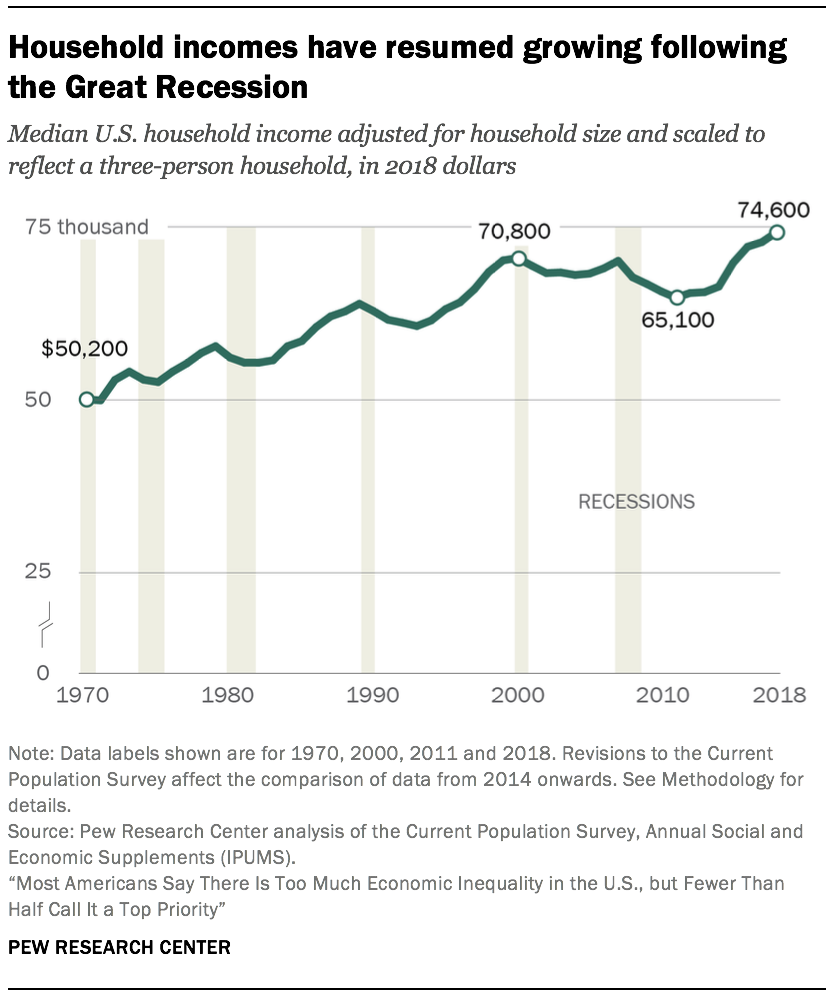
Economic disparities across the world have long been a topic of concern, with vast differences in wealth and development among nations. Examining the intricate factors contributing to these imbalances allows us to comprehend the complexities of global economic inequality.
Historical Roots and Modern Realities
The roots of world economic disparities can be traced back to historical events such as colonialism and unequal trade relationships. In the modern era, these disparities persist and are exacerbated by various factors, including geopolitical power dynamics, resource distribution, and systemic inequalities.
Global Trade and Wealth Accumulation
One major contributor to economic disparities is the uneven distribution of benefits from global trade. While some countries thrive on exports and economic integration, others face challenges in accessing international markets. The link between global trade policies and the widening wealth gap is a critical aspect that demands attention.
Technology Divide and Innovation Gaps
Advancements in technology play a significant role in shaping economic landscapes. However, the unequal adoption and access to technology contribute to a widening gap between technologically advanced nations and those struggling to keep pace. Addressing this “technology divide” is pivotal for fostering inclusive global economic growth.
Educational Disparities and Economic Mobility
Education serves as a cornerstone for economic development, but disparities in educational opportunities create barriers to upward mobility. Nations with robust educational systems tend to experience higher levels of economic prosperity. Bridging the educational gap is essential for fostering a more equitable distribution of wealth on a global scale.
Financial Inclusion and Access to Capital
Access to financial resources is a key determinant of economic success. Disparities in financial inclusion and access to capital contribute to a cycle of poverty in many regions. Efforts to enhance financial literacy and create avenues for inclusive financial systems are critical steps toward addressing economic disparities.
Environmental Challenges and Economic Impact
Environmental issues pose a dual challenge, affecting both developed and developing nations. However, the economic impact of environmental challenges often disproportionately burdens less developed countries. Sustainable development initiatives that address environmental concerns while promoting economic growth can contribute to narrowing global economic gaps.
Government Policies and Inequality Mitigation
Effective governance and policy implementation play a crucial role in mitigating economic disparities. Countries with well-designed social policies, progressive taxation systems, and inclusive economic strategies tend to experience more balanced wealth distribution. Analyzing successful policy models becomes imperative for nations striving to address economic inequalities.
International Cooperation for Sustainable Development
In an interconnected world, addressing economic disparities requires a collaborative approach. International organizations, partnerships, and agreements become instrumental in fostering cooperation among nations. By working together to implement sustainable development goals, countries can make strides toward a more equitable global economic landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While economic disparities pose significant challenges, they also present opportunities for positive change. Innovative solutions, inclusive policies, and a collective commitment to addressing the root causes can pave the way for a more balanced and sustainable global economy.
In the pursuit of understanding and addressing world economic disparities, it is essential to recognize the multifaceted nature of the issue. By fostering global awareness, encouraging inclusive policies, and promoting international cooperation, we can strive towards a world where economic opportunities are more evenly distributed.
To explore more about World economic disparities, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Shaping the Future: Global Economic Governance

Navigating the Landscape of Global Economic Governance
The structure and mechanisms of global economic governance play a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of nations, fostering cooperation, and addressing challenges on a worldwide scale. Delving into the intricacies of this system unveils a complex web of policies, institutions, and collaborations that influence the global economic order.
International Institutions: Pillars of Economic Cooperation
At the heart of global economic governance are international institutions that serve as the pillars of economic cooperation. Entities like the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and World Trade Organization (WTO) play crucial roles in fostering financial stability, facilitating development projects, and regulating international trade. Their policies and decisions have far-reaching implications for the economic well-being of nations.
Global Economic Policies: Coordinating Macro Strategies
Coordinating macroeconomic policies is a key aspect of global economic governance. Nations collaborate to establish frameworks that guide fiscal, monetary, and exchange rate policies. Through dialogue and agreements, they aim to avoid conflicts, balance economic growth, and address issues like inflation, unemployment, and trade imbalances on a global scale.
Trade Agreements and Economic Integration
Trade agreements are instrumental in promoting economic integration among nations. These agreements facilitate the flow of goods and services, reduce trade barriers, and foster a more interconnected global economy. Regional economic blocs, such as the European Union (EU) and ASEAN, exemplify the aspirations of nations to achieve economic integration through shared policies and cooperative governance.
Addressing Global Challenges: Climate Change and Inequality
Global economic governance extends its reach to address pressing challenges beyond traditional economic issues. Climate change and economic inequality have become focal points for international cooperation. Agreements like the Paris Agreement on climate change and initiatives to reduce income inequality underscore the evolving role of global economic governance in tackling multifaceted challenges.
Digital Economy Governance: Navigating the Digital Frontier
As the world becomes increasingly digitized, governance extends to the digital economy. Issues related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and e-commerce require international collaboration. Global economic governance must adapt to regulate and navigate the complexities of the digital frontier, ensuring a balance between innovation, security, and ethical considerations.
Crisis Response and Resilience Building
The global economic governance framework is tested during times of crises. Whether facing financial downturns, pandemics, or geopolitical tensions, coordinated responses become imperative. Institutions like the IMF step in to provide financial assistance, and collaborative efforts aim to build resilience, stabilize economies, and ensure a swift recovery from unforeseen challenges.
Inclusive Governance: Ensuring Representation for All
The question of inclusivity is central to effective global economic governance. Ensuring that the voices of all nations, regardless of size or economic strength, are heard is essential. Reforms in governance structures and decision-making processes strive to create a more inclusive system that reflects the diversity of the global economic landscape.
Challenges and Criticisms: Navigating Complexity
While global economic governance serves a crucial role, it is not without challenges and criticisms. Issues of power imbalances, transparency, and the effectiveness of decision-making processes are subjects of debate. Striking a balance between the interests of developed and developing nations remains an ongoing challenge in the pursuit of fair and equitable global economic governance.
The Future of Global Economic Governance: Adapting to Change
In a rapidly changing world, the future of global economic governance lies in its ability to adapt. Emerging technologies, geopolitical shifts, and evolving global challenges require a nimble and responsive governance structure. Nations must collaborate to reform institutions, update policies, and create a framework that can effectively navigate the uncertainties of the future.
In conclusion, global economic governance is a dynamic and intricate system that influences the economic well-being of nations and shapes the course of international cooperation. As the world continues to evolve, the governance framework must evolve with it, fostering inclusivity, addressing challenges, and guiding nations toward shared prosperity.
To explore more about Global economic governance, visit tankionlineaz.com.
