Support for Small Businesses Global Market Growth Rise
Small businesses are the lifeblood of economies worldwide, acting as engines of innovation, job creation, and community development. Their success directly translates to broader economic prosperity, especially when they can tap into the vast potential of the global market. However, expanding internationally presents unique challenges, requiring access to resources, expertise, and a supportive ecosystem. This article explores the critical role of support for small businesses in facilitating global market growth, examining the various forms this support takes and its impact on entrepreneurial ventures.
Key Takeaways:
- Support for small businesses is crucial for driving global market growth and creating economic opportunities.
- Access to funding, mentorship programs, and specialized resources are vital for SMBs expanding internationally.
- Government initiatives and private sector collaborations play a key role in providing effective support for small businesses.
- Strategic partnerships and leveraging digital technologies can significantly enhance a small business’s ability to compete globally.
Understanding the Importance of Support for Small Businesses
Small businesses often face hurdles that larger corporations don’t. These include limited access to capital, lack of specialized knowledge in international trade, and difficulty navigating complex regulatory environments in foreign markets. Support for small businesses bridges these gaps by providing the necessary tools and guidance to compete effectively. This support can come in many forms, including:
- Financial Assistance: Grants, loans, and venture capital specifically targeted at helping small businesses expand internationally.
- Mentorship Programs: Connecting experienced business leaders with entrepreneurs to provide guidance on market entry strategies, cultural nuances, and operational best practices.
- Educational Resources: Workshops, seminars, and online courses that equip small business owners with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in the global market.
- Networking Opportunities: Platforms for connecting with potential partners, distributors, and customers in international markets.
- Government Initiatives: Export promotion programs, trade missions, and access to market research data provided by government agencies.
These forms of support for small businesses, when effectively implemented, create a level playing field, empowering them to seize opportunities and contribute to global economic growth.
Financial Support for Small Businesses in Global Markets
One of the biggest barriers to global expansion for small businesses is often a lack of funding. Securing financing for international ventures can be particularly challenging, as traditional lenders may be hesitant to provide capital for unproven markets or unfamiliar business models. Therefore, targeted financial support for small businesses becomes essential.
Several avenues exist to provide this crucial financial assistance:
- Government Grants and Loans: Many governments offer grants and low-interest loans specifically designed to help small businesses expand their export activities. These programs often require a detailed business plan and a clear strategy for entering the target market. We can see examples of this in the US with the Small Business Administration (SBA) offering various export loan programs.
- Venture Capital and Angel Investors: Investors with a focus on international growth opportunities can provide significant capital infusions in exchange for equity. This type of funding is particularly attractive for small businesses with innovative products or services that have high growth potential.
- Trade Finance: Trade finance solutions, such as export credit insurance and factoring, can help small businesses manage the risks associated with international trade and improve their cash flow.
- Microfinance Institutions: In developing countries, microfinance institutions can provide small loans to entrepreneurs who lack access to traditional banking services, enabling them to start or expand their businesses and participate in global supply chains.
Access to adequate financial support for small businesses allows entrepreneurs to invest in essential resources, such as market research, product development, and international marketing campaigns, increasing their chances of success in the global arena.
Non-Financial Support for Small Businesses for International Growth
While financial assistance is crucial, non-financial support for small businesses is equally important. This encompasses a range of services and resources that help entrepreneurs build the skills, knowledge, and networks needed to thrive in the global market.
Some key forms of non-financial support include:
- Mentorship Programs: Pairing experienced business leaders with small business owners can provide invaluable guidance on navigating the complexities of international trade, understanding cultural differences, and building relationships with foreign partners. These programs offer personalized advice and support tailored to the specific needs of the business.
- Business Incubators and Accelerators: These programs provide a supportive environment for startups and small businesses, offering access to office space, shared resources, and mentorship from experienced entrepreneurs. Many incubators and accelerators have a specific focus on international expansion, helping businesses prepare for the challenges of entering new markets.
- Export Training and Education: Workshops, seminars, and online courses can equip small business owners with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in international trade. Topics covered may include export regulations, customs procedures, international marketing, and cross-cultural communication.
- Market Research and Analysis: Access to reliable market research data is essential for small businesses making informed decisions about which markets to target
Global Economic Shifts: Changes in Transportation Regulations
Revolutionizing Connectivity: Examining Global Economic Effects of Changes in Transportation Regulations
The evolution of transportation regulations is a catalyst for profound changes in the global economic landscape. This article explores the far-reaching effects of adjustments in transportation regulations, dissecting how these shifts influence economies on a worldwide scale.
Efficiency Gains and Supply Chain Dynamics
Changes in transportation regulations often aim to enhance efficiency in the movement of goods and people. Reforms may address aspects such as logistics, shipping, and air travel, optimizing supply chain dynamics. Streamlining transportation processes results in cost savings for businesses, positively impacting their competitiveness and contributing to economic efficiency.
Impact on Trade and Global Commerce
Transportation regulations are intricately linked with international trade. Alterations in these regulations can facilitate or hinder the flow of goods across borders. Efficient transportation systems foster global commerce, enabling businesses to reach broader markets. Conversely, restrictive regulations may impede trade, affecting industries and potentially leading to shifts in economic balances.
Infrastructure Investment and Economic Stimulus
Changes in transportation regulations often coincide with increased infrastructure investment. Governments may implement reforms to encourage private sector participation in transportation projects, stimulating economic activity. Investment in roads, ports, and other transportation infrastructure creates jobs, boosts local industries, and acts as a powerful economic stimulus.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Transport
Modern transportation regulations increasingly prioritize environmental sustainability. Revisions may target fuel efficiency standards, emissions reductions, and the promotion of sustainable transport modes. These changes not only contribute to environmental conservation but also align with the growing global emphasis on sustainable practices, shaping economic activities in harmony with ecological goals.
Technological Integration and Smart Mobility
The intersection of transportation regulations and technology is reshaping mobility. Regulations may encourage the integration of smart technologies, such as autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management systems. These innovations improve transportation efficiency, reduce congestion, and lay the foundation for smart cities, influencing economic activities in urban centers.
Logistics and the E-Commerce Revolution
E-commerce relies heavily on efficient logistics and transportation systems. Changes in regulations impact how goods are transported and delivered, influencing the logistics landscape. Easier access to global markets and faster delivery times can spur the growth of e-commerce, contributing to the expansion of online businesses and shaping the digital economy.
Global Connectivity and Tourism Impact
Transportation regulations play a vital role in shaping global connectivity and tourism. Policies that facilitate easier movement of people between countries contribute to the growth of the tourism industry. Conversely, restrictive regulations may deter international travel. The tourism sector, closely tied to transportation, significantly influences economies worldwide.
Challenges in Regulatory Alignment and Standardization
Harmonizing transportation regulations across borders is a complex challenge. Divergent regulations can create inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs for international transport. Achieving regulatory alignment and standardization becomes essential for smooth cross-border transportation, fostering international trade and economic cooperation.
Job Creation in Transportation Industries
The transportation sector is a significant source of employment globally. Changes in regulations, especially those promoting infrastructure projects and technological advancements, contribute to job creation. Jobs in logistics, shipping, aviation, and related industries play a crucial role in shaping local and national economies.
Resilience and Adaptation in a Changing Landscape
As transportation regulations evolve, businesses and industries must adapt to new realities. Resilience in the face of change becomes a key factor for economic success. Businesses that can navigate and capitalize on the evolving transportation landscape are better positioned to thrive in the global economy.
For an in-depth exploration of the global economic effects of changes in transportation regulations, refer to this comprehensive study here. The study offers detailed analyses of case studies, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of global economies responding to evolving transportation regulations.
Decoding International Trade Statistics: Trends and Insights
Decoding International Trade Statistics: Trends and Insights
International trade statistics are a treasure trove of information, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of global commerce. In this exploration, we unravel the complexities behind these statistics, providing a comprehensive overview of trends and essential insights.
Understanding the Significance of International Trade Statistics
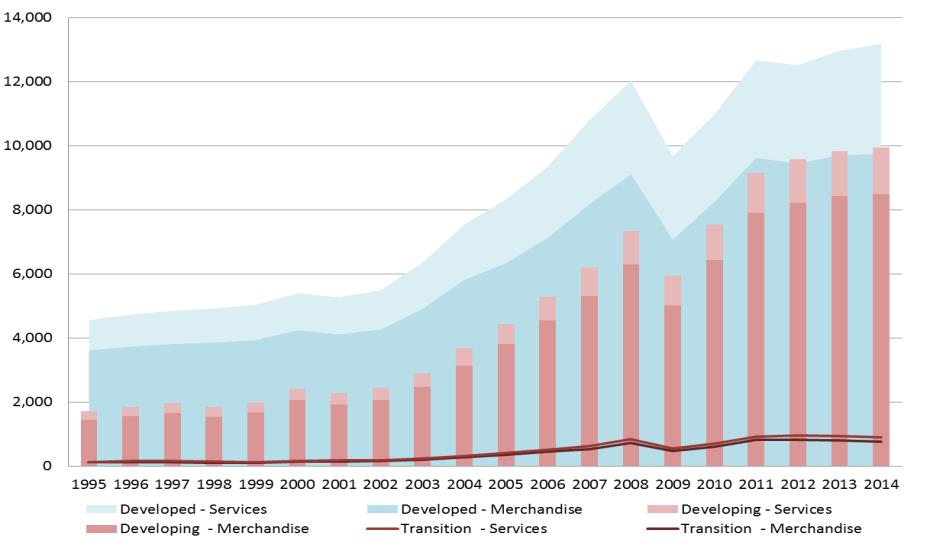
International trade statistics serve as a crucial barometer of the global economy. They encompass data on imports, exports, trade balances, and more. Analyzing these figures offers a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of nations and the economic forces at play.
Key Indicators in International Trade Statistics
Delving into international trade statistics involves examining key indicators. From trade volumes and values to tariff rates and trade balances, these indicators paint a detailed picture of how countries engage in commerce. Understanding these metrics aids in forecasting economic trends and potential shifts in global trade dynamics.
Regional Disparities and Trade Patterns
Analyzing international trade statistics unveils regional disparities and distinctive trade patterns. Certain regions specialize in specific industries or commodities, influencing the global supply chain. Recognizing these patterns is essential for businesses, policymakers, and investors seeking strategic opportunities.
Impact of Trade Agreements on Statistics
International trade statistics are significantly influenced by trade agreements. Agreements such as free trade pacts and economic alliances can spur increased trade volumes between participating nations. Understanding the influence of these agreements is vital for businesses looking to expand their market reach.
Trade Statistics as Economic Indicators
Beyond the realm of commerce, trade statistics are powerful economic indicators. Changes in export or import volumes can signal shifts in a country’s economic health. Governments and financial institutions closely monitor these statistics to make informed decisions and adjust economic policies accordingly.
Challenges in Data Accuracy and Reporting
While international trade statistics offer valuable insights, challenges exist in ensuring data accuracy and consistent reporting. Discrepancies in reporting standards and data collection methods can impact the reliability of these statistics, requiring careful interpretation and consideration.
Technological Advances in Trade Data Analysis
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the analysis of international trade statistics. Big data analytics and machine learning algorithms enable more sophisticated interpretations, uncovering hidden trends and providing a more nuanced understanding of global trade dynamics.
Environmental Considerations in Trade Statistics
In recent years, environmental considerations have become integral to international trade discussions. Analyzing trade statistics reveals the environmental impact of global commerce, prompting discussions on sustainable trade practices and the ecological footprint of different industries.
Trade Statistics and Market Forecasting
Businesses leverage international trade statistics for market forecasting. By analyzing historical trade patterns and anticipating shifts, companies can make informed decisions about market entry, product development, and supply chain management.
The Future of International Trade Statistics
As we navigate a rapidly changing global landscape, the future of international trade statistics holds exciting possibilities. Continued advancements in technology, increased transparency in reporting, and a growing awareness of sustainable practices will shape the evolution of these critical economic metrics.
In conclusion, decoding international trade statistics requires a nuanced understanding of economic trends, regional dynamics, and the broader global context. For an in-depth exploration of these trends and insights, visit International trade statistics. By staying informed, businesses and policymakers can make strategic decisions that contribute to a more resilient and interconnected global economy.
World Economic Governance: Navigating Global Dynamics

Navigating the Global Landscape: World Economic Governance
The intricate dance of global economic dynamics necessitates effective governance to ensure stability and sustainable growth. This article delves into the realm of world economic governance, examining the challenges and complexities it addresses, exploring the institutions and mechanisms in play, and highlighting the imperative for collaborative efforts in steering the course of the global economy.
Challenges in a Globalized World
In an increasingly interconnected world, economic challenges transcend borders. From financial crises to trade disputes and pandemics, the complexities faced by nations require a coordinated response. World economic governance emerges as the linchpin in addressing these challenges, providing a framework for collaboration and collective decision-making on a global scale.
To explore the nuances of world economic governance, visit World Economic Governance.
Institutions Shaping Global Economic Policies
Central to world economic governance are the institutions that shape and implement global economic policies. International organizations like the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and World Trade Organization (WTO) play pivotal roles in coordinating monetary policy, providing development assistance, and facilitating international trade agreements. These institutions serve as forums for dialogue and decision-making among nations.
Policy Coordination for Macroeconomic Stability
Macroeconomic stability is a shared goal, and world economic governance involves policy coordination among nations. This coordination aims to prevent global economic imbalances, currency fluctuations, and trade distortions. Through forums such as the G7 and G20, nations engage in dialogues to align policies, harmonize regulations, and promote stability in the face of economic uncertainties.
Trade Governance and Multilateral Agreements
Trade governance is a critical facet of world economic governance, shaping the rules and norms that govern international trade. Multilateral agreements, such as the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and its successor, the WTO, provide frameworks for negotiations, dispute resolution, and the establishment of a rules-based global trading system. These agreements foster open markets and contribute to global economic integration.
Financial Regulation and Stability
In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, the importance of robust financial regulation became evident. World economic governance addresses the need for coordinated efforts to regulate financial institutions, prevent systemic risks, and enhance the resilience of the global financial system. Bodies like the Financial Stability Board (FSB) work towards developing and implementing international financial regulations.
Addressing Global Inequalities and Sustainable Development
World economic governance extends beyond financial and trade considerations to address global inequalities and promote sustainable development. The United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) serve as a framework for collective action on issues ranging from poverty and inequality to climate change. Governance mechanisms aim to align national policies with these broader global objectives.
Technology Governance in the Digital Age
In the digital age, technology governance has become a crucial dimension of world economic governance. As technological advancements reshape industries and societies, governance mechanisms must adapt to address issues like data privacy, cybersecurity, and the ethical use of emerging technologies. International collaboration on technology governance ensures that standards and norms align with global interests.
Environmental Governance for a Sustainable Future
Environmental sustainability is a pressing global concern, and world economic governance recognizes the need for coordinated efforts to address climate change and environmental degradation. Agreements like the Paris Agreement bring nations together to set emission reduction targets and promote sustainable practices. Environmental governance intertwines with economic policies to build a resilient and sustainable global future.
Emerging Challenges and Adaptive Governance
The landscape of global challenges is ever-evolving, with new complexities emerging over time. World economic governance must be adaptive, anticipating and addressing emerging challenges such as public health crises, geopolitical shifts, and technological disruptions. The ability of governance mechanisms to evolve ensures their relevance in steering the global economy through uncertain terrains.
Collaborative Leadership for Global Prosperity
In conclusion, world economic governance is a complex tapestry of institutions, policies, and collaborative efforts aimed at steering the global economy towards prosperity. As nations grapple with shared challenges, from economic uncertainties to environmental threats, collaborative leadership becomes imperative. By fostering dialogue, aligning policies, and embracing shared responsibilities, world economic governance charts a course for a more stable, inclusive, and sustainable global economy.
Housing Regulation Changes: Global Economic Dynamics

The Dynamics of Housing Regulations: A Global Perspective
In recent years, housing regulations have become a focal point of discussion and debate worldwide. Governments around the globe are continuously reassessing and tweaking policies to address the ever-evolving needs of their citizens. These changes, though often seen at a local level, can have profound implications on a global scale, impacting economies, markets, and the lives of people. In this article, we delve into the global economic implications of changes in housing regulations.
Local Impact on Real Estate Markets
The first and most immediate impact of housing regulation changes is felt at the local level, particularly in real estate markets. Alterations in zoning laws, rent control, or building codes can significantly influence property values, rental prices, and the overall demand for housing. For instance, the relaxation of building restrictions may lead to a surge in construction activity, boosting the local economy, while stringent rent control measures might dampen property investment.
Effects on Employment and Construction Industries
One of the ripple effects of housing regulation changes is the influence on employment, especially in the construction sector. Loosening regulations often results in increased construction projects, creating job opportunities and stimulating economic growth. Conversely, stricter regulations might lead to a slowdown in construction activities, impacting jobs and potentially contributing to economic downturns in regions dependent on the housing industry.
Financial Market Responses
Changes in housing regulations can also trigger responses in financial markets. Real estate investments are significant components of many investment portfolios, and alterations in regulations can affect the value of these investments. Investors closely watch for policy shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly, leading to fluctuations in stock markets and other financial instruments tied to the housing sector.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Advancements in technology and innovative solutions play a crucial role in shaping the impact of housing regulations globally. The rise of proptech, for example, has provided new tools for governments to manage and enforce housing policies more efficiently. Additionally, technology has enabled the growth of alternative housing models, such as co-living and micro-housing, which may present solutions to housing challenges posed by regulatory changes.
Social and Demographic Shifts
Housing regulations are intrinsically tied to societal needs and demographic trends. Changes in regulations often reflect a response to shifting demographics, such as an aging population or an influx of young professionals. These demographic changes can have broader economic implications, influencing workforce dynamics, healthcare demands, and social welfare systems.
Global Economic Interconnectedness
The global economy is an intricate web of interconnected factors, and changes in housing regulations in one country can send ripples across borders. The interconnectedness is particularly evident in the wake of globalization, where economic ties between nations are stronger than ever. A shift in housing policies in a major economic player can affect international trade, capital flows, and investment patterns.
Global Economic Implications of Changes in Housing Regulations
For a more in-depth analysis of the global economic implications of changes in housing regulations, you can explore a comprehensive study here. This study delves into case studies from various countries, examining how their housing policy changes have reverberated through the global economic landscape. Understanding these implications is crucial for policymakers, investors, and individuals navigating the complex world of real estate and housing regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, changes in housing regulations have far-reaching consequences beyond the boundaries of individual nations. From impacting local real estate markets to influencing global economic dynamics, these regulatory shifts are integral components of the intricate tapestry of our interconnected world. As we move forward, it becomes imperative to recognize and understand the implications of these changes to make informed decisions that contribute to sustainable and resilient global economies.


