Sustainable Private Equity A Growing Market
Defining Sustainable Private Equity
Sustainable private equity (SPE) is a rapidly expanding segment of the private equity market. It focuses on investments in companies that demonstrate strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. This isn’t just about “doing good”; it’s about identifying companies with robust business models that are built on sustainable practices, ultimately leading to better long-term financial returns. SPE firms actively integrate ESG factors into their investment strategy, due diligence, and portfolio company management, going beyond simply checking boxes to actively shaping sustainable business practices within their portfolio.
The Drivers Behind the Growth of Sustainable Private Equity
Several factors are fueling the surge in SPE. Increasingly, institutional investors, such as pension funds and endowments, are incorporating ESG considerations into their investment mandates, demanding more sustainable investment options. Growing awareness of climate change and its economic implications is another key driver. Investors are recognizing that companies with strong ESG profiles are often better positioned to navigate environmental and social risks, leading to enhanced resilience and long-term value creation. Finally, a growing number of consumers are actively choosing to support businesses committed to sustainability, creating a strong market demand for environmentally and socially responsible products and services.
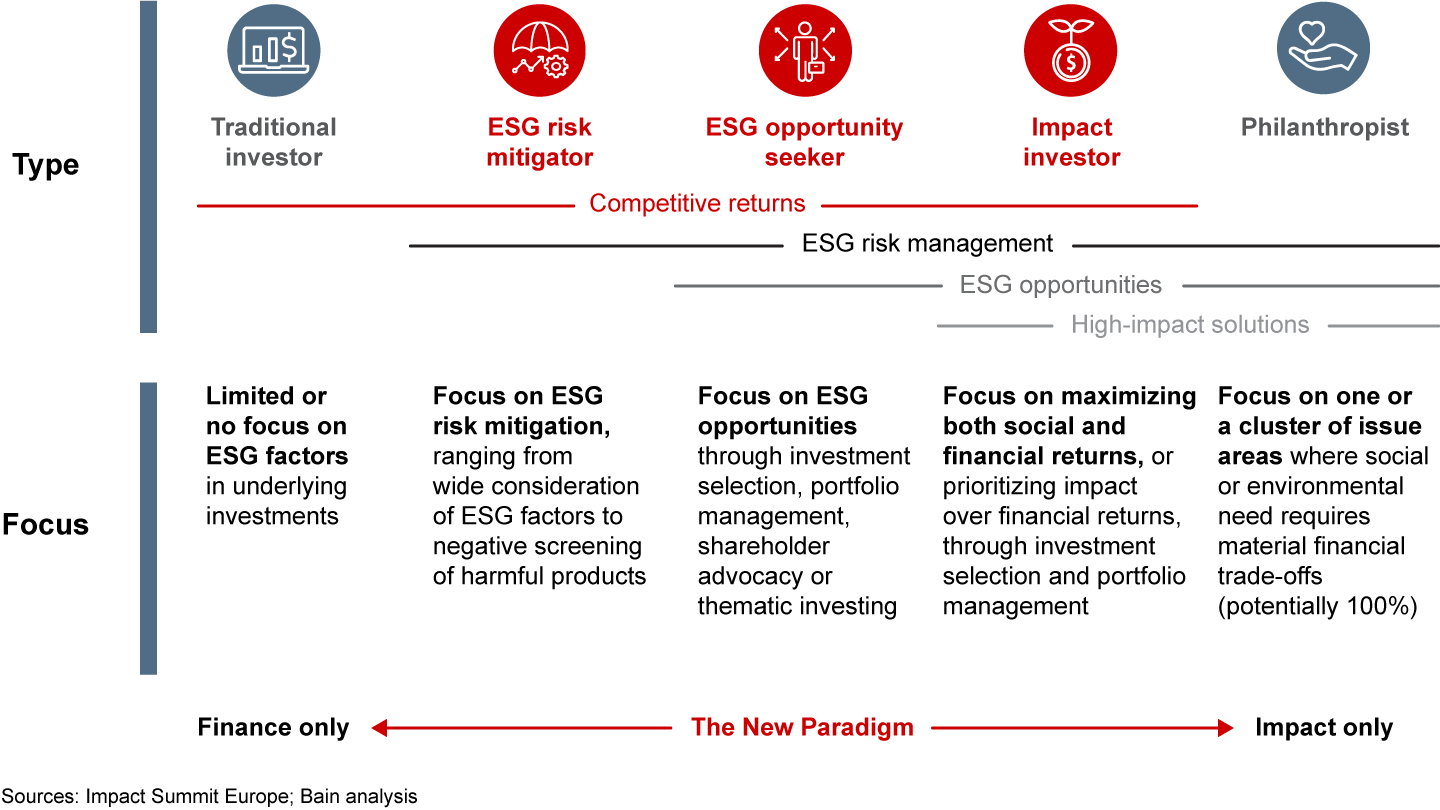
Investment Strategies in Sustainable Private Equity
SPE firms employ diverse strategies, focusing on various sectors and impact areas. Some specialize in clean energy, renewable resources, and green technology, contributing directly to the transition to a low-carbon economy. Others focus on companies improving resource efficiency, reducing waste, or developing sustainable products and services across various industries. Some SPE firms employ a thematic approach, concentrating on specific ESG issues, such as water conservation or circular economy solutions. Others adopt a broader approach, integrating ESG factors across their portfolio companies, regardless of specific sector.
Measuring and Reporting Impact in Sustainable Private Equity
Transparency and accountability are paramount in SPE. To accurately measure and report the impact of their investments, SPE firms utilize various methodologies and frameworks. These include established standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standards, as well as industry-specific metrics. Reporting is increasingly sophisticated, moving beyond simple metrics to incorporate a more holistic view of ESG performance, taking into account both quantitative and qualitative data. This data helps investors understand the positive social and environmental contributions of their investments and enables continuous improvement within portfolio companies.
Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Private Equity
Despite its rapid growth, SPE faces challenges. One key challenge is the standardization of ESG data and metrics. Inconsistencies in reporting can make it difficult to compare investments and assess true impact. Another challenge lies in balancing financial returns with social and environmental impact. Finding companies that meet both financial and sustainability criteria can sometimes be difficult. However, these challenges also present opportunities. The development of robust ESG data and reporting standards is a key area of ongoing innovation. Moreover, the increasing demand for sustainable investments creates a significant opportunity for SPE firms to generate attractive returns while driving positive change.
The Future of Sustainable Private Equity
The future of SPE looks promising. Growing investor demand, coupled with increasing regulatory pressure and consumer awareness, is expected to drive further expansion of this market segment. We can anticipate more innovation in investment strategies, impact measurement, and reporting. Greater collaboration between SPE firms, investors, and policymakers will be essential to overcoming remaining challenges and accelerating the transition to a more sustainable economy. The integration of ESG factors will likely become even more deeply embedded into mainstream investment practices, making SPE not just a niche market, but a significant driver of future economic growth.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Private Equity
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling the growth of SPE. Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly used to screen companies, assess ESG risks, and monitor portfolio company performance. Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, helping SPE firms track and verify the sustainability claims of their portfolio companies. Sophisticated data platforms are also allowing for more granular and impactful reporting on ESG performance, enhancing accountability and improving investment decision-making. Read more about private equity sustainable investing.
Global Energy Policy Shifts: Economic Implications
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy policies, global shifts have profound implications for the world economy. This article explores the economic impacts of changes in energy policies, shedding light on how nations navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the transition to new energy paradigms.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
As the world grapples with environmental concerns, changes in energy policies drive a revolution in renewable energy. Nations investing in and transitioning to cleaner energy sources contribute not only to environmental sustainability but also stimulate economic growth. The renewable energy sector becomes a key player in job creation, innovation, and economic resilience.
Investments in Sustainable Infrastructure:
Changes in energy policies prompt substantial investments in sustainable infrastructure. Governments and businesses allocate resources to build and upgrade energy-efficient systems, creating a foundation for economic activities. These investments not only reduce environmental impact but also contribute to long-term economic sustainability.
Impact on Energy Markets and Prices:
Shifts in energy policies influence energy markets and prices on a global scale. Policies favoring renewable energy sources can impact the cost and availability of energy. As nations transition, fluctuations in energy markets create challenges and opportunities for businesses, shaping economic dynamics.
Technological Advancements and Innovation:
Energy policy changes drive technological advancements and innovation. Policies supporting research and development in clean energy technologies spur economic innovation. Nations at the forefront of these innovations often experience economic benefits, including the growth of new industries and increased global competitiveness.
Supply Chain Resilience and Energy Security:
Diversification of energy sources, a result of policy changes, enhances supply chain resilience and energy security. Nations less dependent on a single energy source are better equipped to withstand external shocks. This resilience contributes to economic stability and continuity in the face of energy-related challenges.
Environmental Externalities and Economic Considerations:
Energy policies often consider environmental externalities, impacting economic decision-making. Nations weighing the economic costs and benefits of energy policies take into account environmental factors, aiming for a balance that promotes economic growth while addressing environmental concerns.
Job Creation and Economic Opportunities:
The transition to new energy policies generates job opportunities and economic growth. The renewable energy sector, in particular, becomes a significant contributor to employment. Policies that facilitate a just transition for workers in traditional energy sectors to cleaner alternatives mitigate economic challenges associated with job displacement.
Global Cooperation in Energy Transition:
The global nature of energy challenges necessitates international cooperation. Changes in energy policies often spark collaborative efforts to address common issues. International partnerships in research, technology transfer, and policy coordination contribute to a more harmonized and economically viable global energy landscape.
Policy Certainty and Investment Attraction:
Policy certainty is crucial for attracting investments in the energy sector. Nations with clear and consistent energy policies create an attractive environment for investments. A stable policy framework encourages businesses to commit to long-term projects, fostering economic growth and sustainability.
For more insights into the world economic impact of changes in energy policies, visit World economic impact of changes in energy policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the world economic impact of changes in energy policies is multi-faceted, influencing various aspects of global economies. From renewable energy revolutions and sustainable infrastructure investments to the reshaping of energy markets and supply chain resilience, the economic implications underscore the interconnected relationship between energy policies and global economic well-being. As nations navigate the path toward cleaner and more sustainable energy, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, businesses, and citizens are paramount for ensuring a resilient and prosperous global economic future.


