Sustainable Private Equity A Growing Market
Defining Sustainable Private Equity
Sustainable private equity (SPE) is a rapidly expanding segment of the private equity market. It focuses on investments in companies that demonstrate strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. This isn’t just about “doing good”; it’s about identifying companies with robust business models that are built on sustainable practices, ultimately leading to better long-term financial returns. SPE firms actively integrate ESG factors into their investment strategy, due diligence, and portfolio company management, going beyond simply checking boxes to actively shaping sustainable business practices within their portfolio.
The Drivers Behind the Growth of Sustainable Private Equity
Several factors are fueling the surge in SPE. Increasingly, institutional investors, such as pension funds and endowments, are incorporating ESG considerations into their investment mandates, demanding more sustainable investment options. Growing awareness of climate change and its economic implications is another key driver. Investors are recognizing that companies with strong ESG profiles are often better positioned to navigate environmental and social risks, leading to enhanced resilience and long-term value creation. Finally, a growing number of consumers are actively choosing to support businesses committed to sustainability, creating a strong market demand for environmentally and socially responsible products and services.
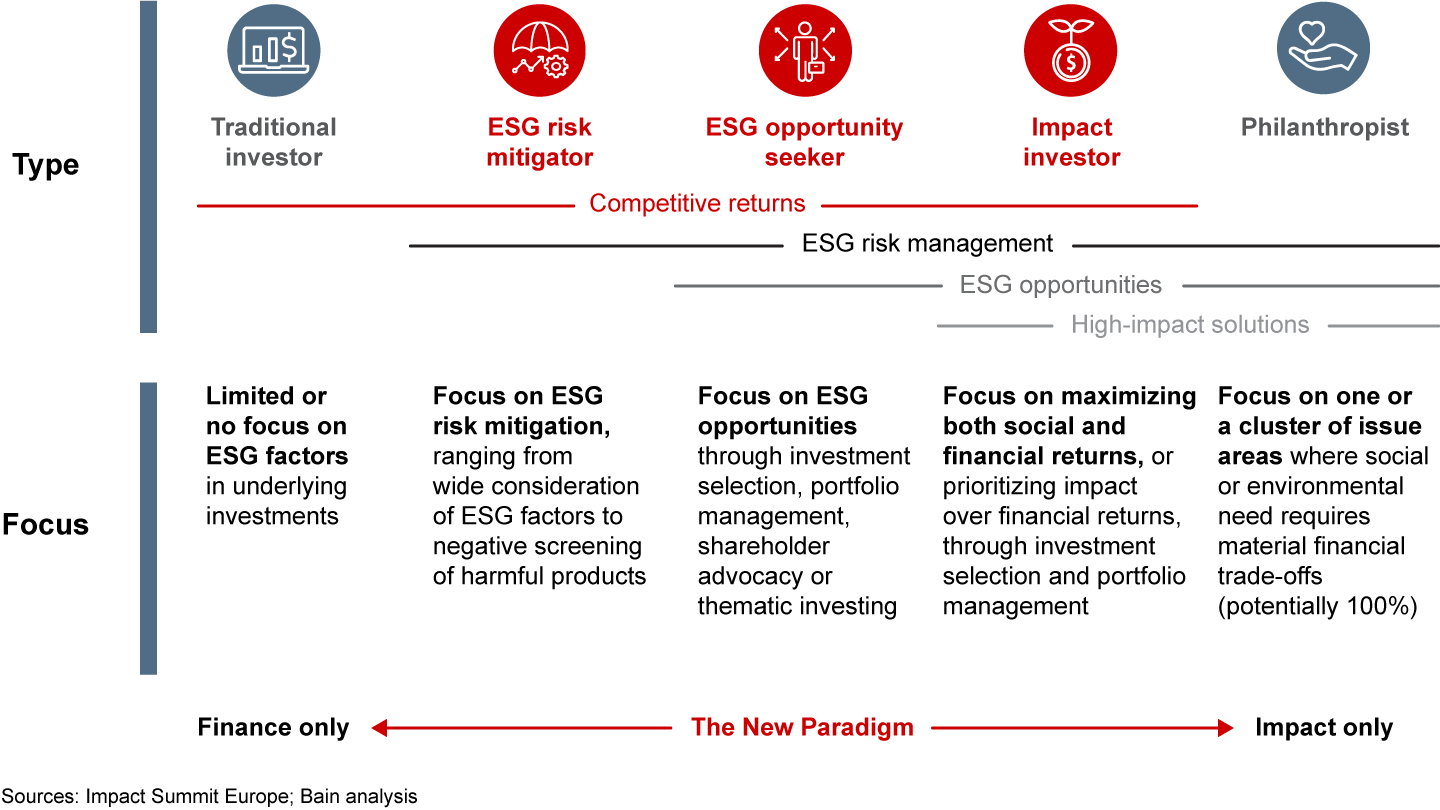
Investment Strategies in Sustainable Private Equity
SPE firms employ diverse strategies, focusing on various sectors and impact areas. Some specialize in clean energy, renewable resources, and green technology, contributing directly to the transition to a low-carbon economy. Others focus on companies improving resource efficiency, reducing waste, or developing sustainable products and services across various industries. Some SPE firms employ a thematic approach, concentrating on specific ESG issues, such as water conservation or circular economy solutions. Others adopt a broader approach, integrating ESG factors across their portfolio companies, regardless of specific sector.
Measuring and Reporting Impact in Sustainable Private Equity
Transparency and accountability are paramount in SPE. To accurately measure and report the impact of their investments, SPE firms utilize various methodologies and frameworks. These include established standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standards, as well as industry-specific metrics. Reporting is increasingly sophisticated, moving beyond simple metrics to incorporate a more holistic view of ESG performance, taking into account both quantitative and qualitative data. This data helps investors understand the positive social and environmental contributions of their investments and enables continuous improvement within portfolio companies.
Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Private Equity
Despite its rapid growth, SPE faces challenges. One key challenge is the standardization of ESG data and metrics. Inconsistencies in reporting can make it difficult to compare investments and assess true impact. Another challenge lies in balancing financial returns with social and environmental impact. Finding companies that meet both financial and sustainability criteria can sometimes be difficult. However, these challenges also present opportunities. The development of robust ESG data and reporting standards is a key area of ongoing innovation. Moreover, the increasing demand for sustainable investments creates a significant opportunity for SPE firms to generate attractive returns while driving positive change.
The Future of Sustainable Private Equity
The future of SPE looks promising. Growing investor demand, coupled with increasing regulatory pressure and consumer awareness, is expected to drive further expansion of this market segment. We can anticipate more innovation in investment strategies, impact measurement, and reporting. Greater collaboration between SPE firms, investors, and policymakers will be essential to overcoming remaining challenges and accelerating the transition to a more sustainable economy. The integration of ESG factors will likely become even more deeply embedded into mainstream investment practices, making SPE not just a niche market, but a significant driver of future economic growth.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Private Equity
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling the growth of SPE. Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly used to screen companies, assess ESG risks, and monitor portfolio company performance. Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, helping SPE firms track and verify the sustainability claims of their portfolio companies. Sophisticated data platforms are also allowing for more granular and impactful reporting on ESG performance, enhancing accountability and improving investment decision-making. Read more about private equity sustainable investing.
Sustainable Investing Making Money, Saving the Planet
What is Sustainable Investing?
Sustainable investing, also known as responsible investing or ESG (environmental, social, and governance) investing, is an investment approach that considers environmental, social, and governance factors alongside financial returns. It’s about aligning your investments with your values, seeking out companies that are not only profitable but also contribute positively to society and the environment. This isn’t just about avoiding “bad” companies; it’s actively seeking out “good” ones that are making a difference.
The Financial Case for Sustainable Investing
Contrary to some misconceptions, sustainable investing isn’t about sacrificing returns for social good. In fact, a growing body of research suggests that incorporating ESG factors can actually improve investment performance. Companies with strong ESG profiles often demonstrate better risk management, more efficient operations, and a stronger long-term outlook, leading to more stable and potentially higher returns. This is because they’re better equipped to adapt to changing regulations, consumer preferences, and environmental challenges.

Environmental Considerations: Protecting Our Planet
A significant aspect of sustainable investing is focusing on companies that are actively working to mitigate their environmental impact. This could include companies investing in renewable energy, reducing their carbon footprint, promoting sustainable agriculture, or developing innovative green technologies. By investing in these companies, you’re not only supporting their efforts but also potentially benefiting from the growth of the burgeoning green economy.
Social Responsibility: Building a Better Society
The “social” aspect of ESG considers how companies treat their employees, customers, and the wider community. This includes factors such as fair labor practices, diversity and inclusion, data privacy, and community engagement. Companies committed to social responsibility tend to have stronger employee morale, better customer loyalty, and a more positive public image – all of which contribute to long-term financial stability.
Governance Matters: Transparency and Accountability
Good governance is essential for any successful business, and it’s a crucial element of sustainable investing. This encompasses factors like board diversity, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and anti-corruption measures. Companies with strong governance structures are generally more transparent, accountable, and less likely to engage in unethical or illegal activities, reducing investment risk.
How to Get Started with Sustainable Investing
There are several ways to incorporate sustainable investing into your portfolio. You can choose from a range of sustainable investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and separately managed accounts. You can also screen individual stocks based on ESG criteria, though this requires more research and understanding. Many brokerage platforms now provide ESG ratings and screening tools to simplify the process.
Different Approaches to Sustainable Investing
The field of sustainable investing encompasses a variety of approaches, from negative screening (excluding companies involved in controversial activities like fossil fuels or weapons manufacturing) to positive screening (actively selecting companies with strong ESG profiles) to impact investing (investing in companies specifically designed to create positive social or environmental impact). The best approach depends on your personal values and investment goals.
The Growing Trend and Future of Sustainable Investing
Sustainable investing is no longer a niche strategy; it’s rapidly gaining mainstream acceptance. Growing awareness of climate change, social inequalities, and corporate responsibility is driving increased demand for sustainable investment products. As more investors incorporate ESG factors into their decision-making, the influence of sustainable investing on corporate behavior and the global economy will only continue to grow, creating a more sustainable and equitable future.
Beyond Financial Returns: The Impact of Sustainable Investing
While financial returns are an important consideration, sustainable investing offers something more. It’s about aligning your investments with your values and contributing to a better world. By choosing to invest sustainably, you’re not only potentially increasing your returns, but you’re also making a tangible impact on the environment and society, leaving a positive legacy for future generations. Read also about sustainable investing strategies.
Navigating Global Financial Markets: Trends and Strategies

Navigating Global Financial Markets: Trends and Strategies
Understanding and navigating global financial markets is essential for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike. In this exploration, we delve into the current trends shaping these markets and strategies to navigate their complexities.
The Ever-Changing Landscape of Global Financial Markets
Global financial markets are dynamic and subject to constant change. Factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and technological advancements contribute to the fluidity of these markets. Staying informed about the evolving landscape is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Key Players and Market Dynamics
Global financial markets are comprised of various key players, including institutional investors, retail traders, and central banks. Understanding the roles and interactions of these entities is essential for grasping market dynamics. Market forces such as supply and demand, liquidity, and investor sentiment significantly impact the trajectory of financial markets.
Technological Innovations Shaping Finance
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in shaping global financial markets. The rise of fintech, blockchain, and artificial intelligence has transformed the way financial transactions are conducted. Embracing these innovations is vital for staying competitive and navigating the increasingly digitized financial landscape.
The Impact of Global Economic Trends
Economic trends at the global level have a direct influence on financial markets. Factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and trade balances shape investor confidence and market sentiment. Analyzing these trends provides insights into potential investment opportunities and risks.
Geopolitical Events and Market Volatility
Geopolitical events have a profound impact on global financial markets. Political instability, trade tensions, and international conflicts can lead to increased market volatility. Investors must factor in geopolitical considerations when developing strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Diversification and Risk Management
Diversification is a fundamental strategy for navigating global financial markets. Spreading investments across different asset classes, regions, and industries helps mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations. Additionally, effective risk management strategies, including setting stop-losses and staying informed about market indicators, are essential for preserving capital.
Market Trends and Emerging Opportunities
Identifying and capitalizing on market trends is crucial for success in global financial markets. Whether it’s the rise of renewable energy investments, the growth of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, or emerging opportunities in developing markets, staying attuned to trends allows investors to position themselves strategically.
The Role of Central Banks in Monetary Policies
Central banks play a significant role in shaping global financial markets through monetary policies. Interest rate decisions, quantitative easing, and other policy measures influence borrowing costs, currency values, and market liquidity. Understanding the stance of central banks is key for predicting market movements.
Digital Transformation in Financial Services
The financial services industry is undergoing a digital transformation. Online trading platforms, robo-advisors, and digital banking have become integral parts of the financial landscape. Embracing these digital tools enhances accessibility and efficiency for investors navigating global financial markets.
Sustainable Investing and Socially Responsible Finance
Sustainable investing, including ESG considerations, is gaining prominence in global financial markets. Investors are increasingly factoring in environmental, social, and governance criteria when making investment decisions. This shift towards socially responsible finance reflects a growing awareness of the impact of investments on broader societal and environmental issues.
In conclusion, navigating global financial markets requires a multifaceted approach. By staying informed about market dynamics, embracing technological innovations, and implementing effective strategies such as diversification and risk management, investors can navigate the complexities of the financial world. For deeper insights into global financial markets, visit Global financial markets.


