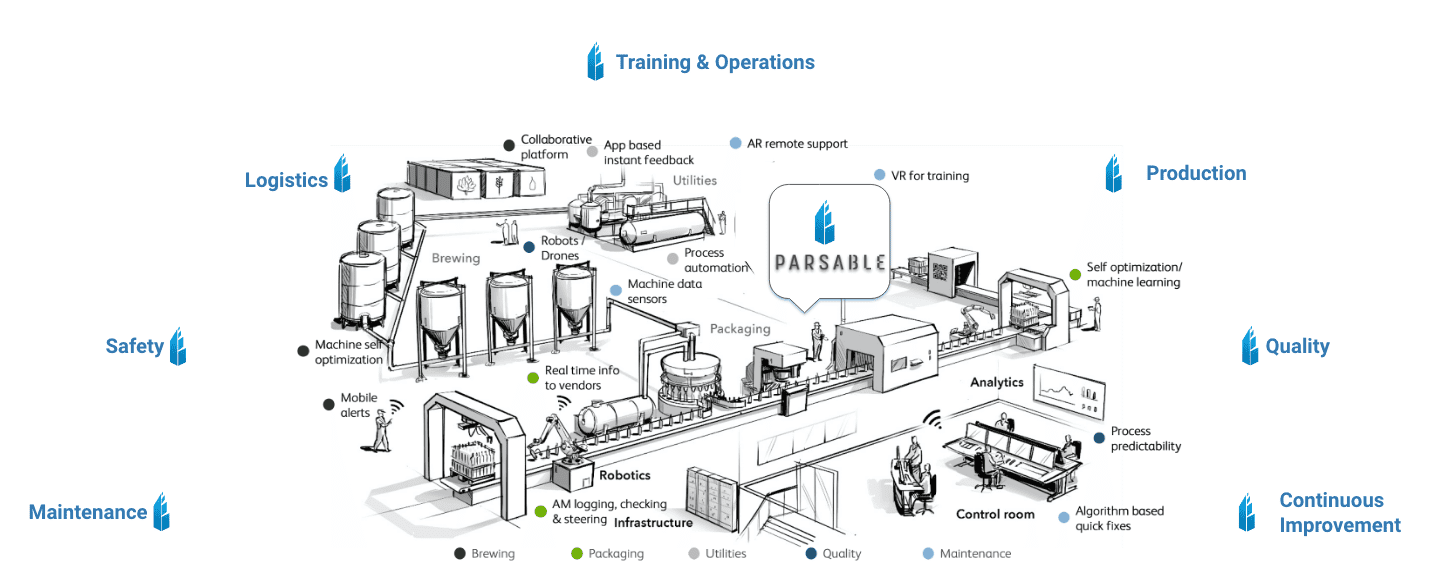
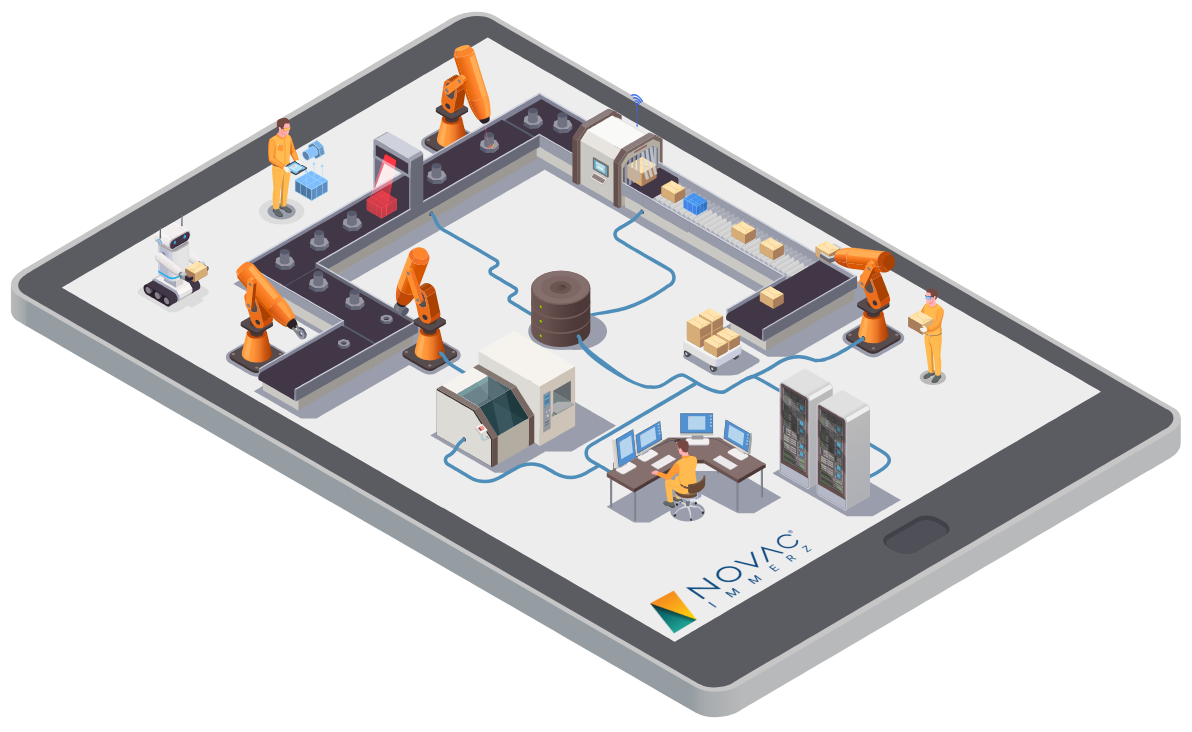
What is a Smart Factory?
A smart factory, also known as an intelligent factory, leverages technology to optimize every aspect of manufacturing. This isn’t just about automating individual processes; it’s about creating a connected ecosystem where machines, software, and people work together seamlessly. Think interconnected sensors, data analytics, AI-powered decision-making, and robotic automation all collaborating to create a highly efficient and responsive production environment. The ultimate goal is to improve productivity, reduce waste, and enhance product quality – all while adapting quickly to changing market demands.
Key Technologies Driving Smart Factories
Several key technologies underpin the smart factory revolution. The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role, connecting machines and devices to collect real-time data. This data is then analyzed using advanced analytics, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, to identify patterns, predict potential problems, and optimize processes. Robotics, particularly collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly important for automating tasks, working alongside human employees. Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure for storing and processing vast amounts of data, while cybersecurity is crucial for protecting the sensitive information flowing through the network.

Benefits of Implementing Smart Factory Technologies
The advantages of transitioning to a smart factory are numerous. Perhaps the most significant is increased productivity. Automation and optimized processes lead to faster production cycles and higher output. Smart factories also excel at reducing waste, identifying inefficiencies, and minimizing downtime. Improved product quality is another key benefit, as data-driven insights enable manufacturers to fine-tune processes and eliminate defects. Furthermore, the enhanced flexibility and adaptability of smart factories allow manufacturers to respond quickly to changing customer demands and market trends. This agility can be a significant competitive advantage.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Factory Solutions
Despite the considerable benefits, implementing smart factory technologies presents significant challenges. The initial investment can be substantial, requiring substantial upfront capital expenditure on new equipment, software, and integration services. Furthermore, integrating disparate systems and legacy technologies can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized expertise. Data security is a paramount concern, as smart factories generate and process vast quantities of sensitive data. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is essential to prevent data breaches and disruptions. Finally, training employees to operate and maintain the new technologies is crucial to ensure a successful transition.
The Human Element in the Smart Factory
Contrary to popular misconceptions, smart factories don’t eliminate the need for human workers. Instead, they transform the nature of work. While automation handles repetitive and dangerous tasks, human employees are increasingly focused on higher-level activities such as problem-solving, innovation, and strategic decision-making. Reskilling and upskilling the workforce is essential to adapt to the changing demands of a smart factory environment. Focusing on collaborative robots allows humans and machines to work together, leveraging the strengths of each. This creates a more engaging and rewarding work environment.
The Future of Smart Factories and its Impact on Manufacturing
The future of smart factories is bright. Ongoing advancements in technology will continue to drive innovation and efficiency. We can expect to see greater integration of artificial intelligence, leading to even more autonomous and adaptable manufacturing processes. The rise of digital twins – virtual representations of physical factories – will further enhance simulation and optimization capabilities. As the technology becomes more accessible and affordable, more manufacturers will adopt smart factory solutions, leading to a more efficient, sustainable, and competitive global manufacturing landscape. This will not only impact manufacturing processes but also the wider economy, creating new job opportunities and driving economic growth.
Sustainability in Smart Factories
Smart factories are not only about efficiency but also sustainability. By optimizing processes and reducing waste, they contribute significantly to environmental responsibility. Data analytics can be used to monitor energy consumption and identify areas for improvement, leading to reduced carbon emissions. The ability to adapt to changing resource availability also contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing model. Integrating renewable energy sources further enhances the environmental credentials of smart factories. The focus on sustainability is increasingly crucial for businesses and consumers alike, making smart factory technology a cornerstone of environmentally conscious manufacturing. Please click here to learn about what smart factories are an example of.