Banking Without the Bank How Embedded Finance Works
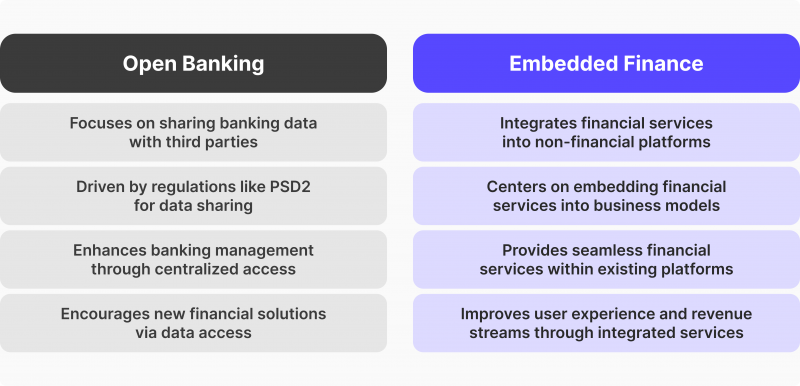
What is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance is the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial products and platforms. Think about it like this: instead of going to a bank for a loan, you apply for it directly through the platform where you’re already buying a product or service. This could be anything from a retailer’s website offering financing for a purchase, to a ride-sharing app providing insurance options to its drivers. The key is that the financial service is integrated directly into the customer’s journey, making it convenient and readily available.
How Embedded Finance Differs from Traditional Banking
Traditional banking involves separate interactions with financial institutions. You go to the bank for a loan, a credit card, or an investment account. Embedded finance eliminates this friction. It leverages existing user relationships and data from platforms already engaging with customers, streamlining access to financial products. This often results in a faster and more personalized experience, tailoring offerings to the customer’s specific needs within the context of their current activity.
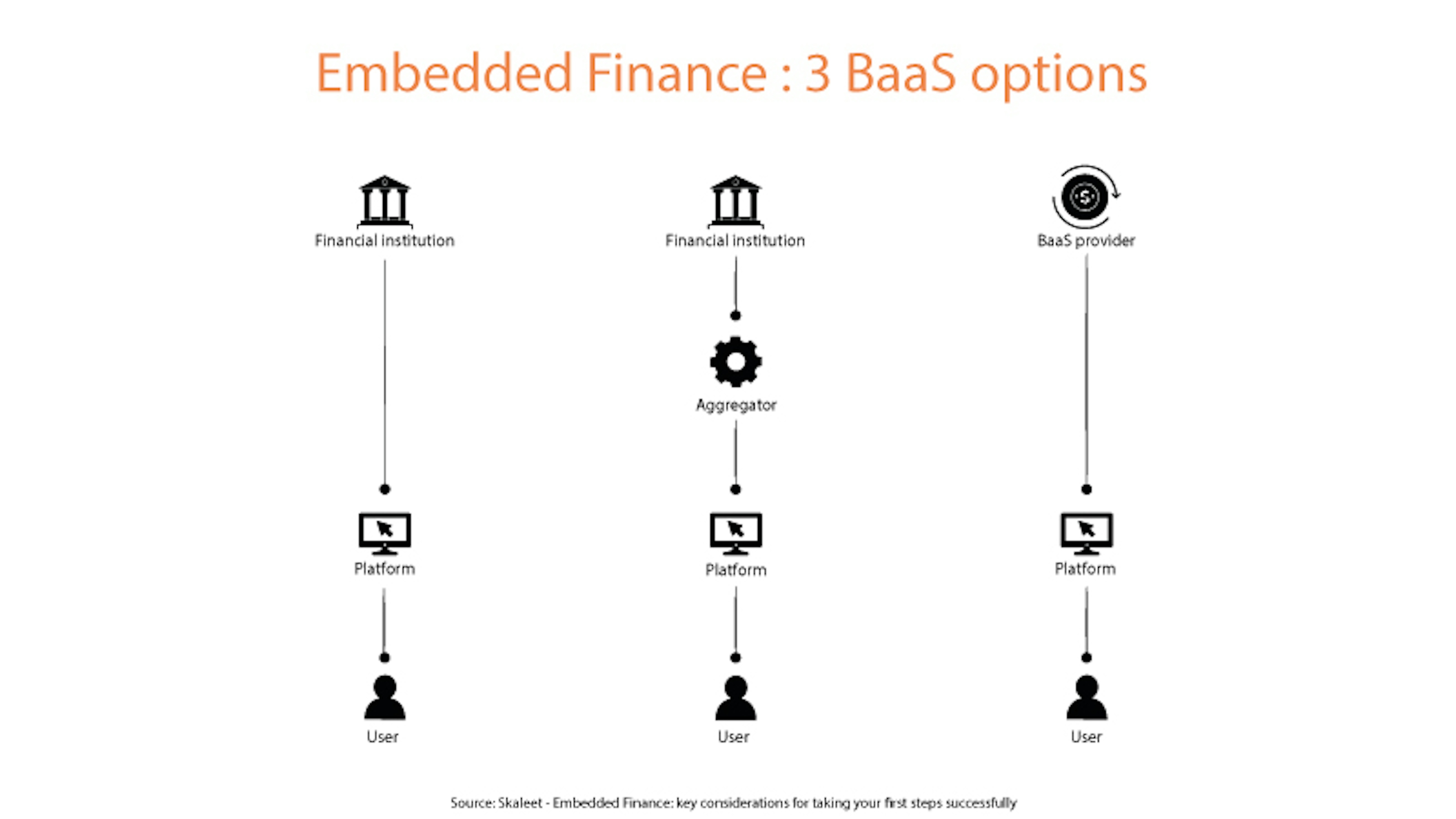
The Key Players in Embedded Finance
Several key players drive this shift in the financial landscape. First, there are the **technology providers** that build the infrastructure to embed these financial services. These are often fintech companies specializing in APIs and payment gateways. Then there are the **financial institutions** (banks, credit unions, insurers) that provide the actual financial products. Finally, we have the **platforms** that integrate these services into their offerings, ranging from e-commerce sites to SaaS providers. The collaboration between these players is crucial for the success of embedded finance.
Benefits for Businesses Integrating Embedded Finance
For businesses, integrating embedded finance unlocks numerous benefits. It increases customer lifetime value by offering additional services that increase engagement and retention. It opens up new revenue streams through commissions or fees generated from the financial services offered. Furthermore, it improves the customer experience by providing a streamlined and convenient way to access financial products at the point of need. This improved experience can foster brand loyalty and enhance the overall customer relationship.
Benefits for Consumers Using Embedded Finance
Consumers benefit from increased convenience and a more personalized experience. They can access financial services at the precise moment they need them, without the hassle of navigating separate applications or visiting a physical branch. This ease of access can lead to better financial decision-making, as consumers can seamlessly manage their finances within the context of their everyday activities. Moreover, tailored financial offerings can cater to specific needs, making financial products more relevant and accessible.
Examples of Embedded Finance in Action
Numerous real-world examples showcase the versatility of embedded finance. A furniture retailer might offer financing options directly at checkout, allowing customers to spread the cost of a purchase. A travel booking platform could provide travel insurance as part of the booking process. A software-as-a-service (SaaS) company might allow users to pay for their subscription with a buy-now-pay-later option. These examples highlight how diverse businesses are leveraging embedded finance to enhance their offerings and improve customer experience.
The Future of Embedded Finance
Embedded finance is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing customer expectations. We can expect to see even more sophisticated integrations, personalized offerings, and a wider range of financial products seamlessly embedded into various platforms. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, embedded finance is poised to become a significant driver of innovation within the financial sector and beyond, fundamentally changing how we access and utilize financial services.
What is Embedded Finance & How Does it Work?
What Exactly is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance is the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial platforms and applications. Instead of users needing to navigate to a separate bank or financial institution’s website or app, they can access financial products and services directly within the platforms they already use regularly. Think of it like this: you’re using your favorite shopping app, and suddenly you have the option to pay with a buy-now-pay-later service, or take out a loan to finance your purchase, all without leaving the app. That’s embedded finance in action.
Examples of Embedded Finance in Action
The applications of embedded finance are incredibly diverse and expanding rapidly. Consider a ride-sharing app offering users instant insurance for each ride, a travel booking site allowing customers to secure travel insurance or finance their trip, or a social media platform enabling peer-to-peer payments. These are all practical examples of how companies are leveraging embedded finance to enhance user experience and expand revenue streams. Even software-as-a-service (SaaS) businesses are getting in on the action, offering integrated invoice financing or payment solutions for their clients directly within their platform.

How Embedded Finance Works: The Technical Side
Behind the scenes, embedded finance relies on a complex network of partnerships and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). The non-financial platform partners with financial service providers (like banks, lenders, and insurers) to offer their services. APIs act as the bridges, connecting the platform’s user interface with the financial institution’s backend systems. This allows for secure and efficient data transfer, enabling users to seamlessly complete financial transactions without ever leaving the main application. Robust security protocols and regulatory compliance are absolutely crucial to ensure the safety and privacy of user data.
Benefits for Businesses Implementing Embedded Finance
For businesses, embedded finance offers a multitude of advantages. Primarily, it enhances customer loyalty by providing a more convenient and personalized user experience. It can also significantly boost revenue through increased sales and added fees from financial products. By offering relevant financial services, businesses can better meet customer needs and increase customer lifetime value. Furthermore, it can lead to the development of new revenue streams and open up opportunities for strategic partnerships with financial institutions.
Benefits for Consumers Using Embedded Finance Services
Consumers benefit greatly from the ease and convenience embedded finance offers. The process is streamlined, making financial transactions quicker and simpler. Users can access needed financial products at the precise moment they need them – no more navigating to separate websites or apps to complete transactions. This integrated approach removes friction and enhances the overall user experience, potentially offering more competitive pricing or tailored financial products based on individual needs and context.
The Role of APIs and Partnerships in Embedded Finance
APIs are the lifeblood of embedded finance, facilitating the communication between the platform and the financial service provider. These APIs allow for secure and efficient transfer of data, including user information, transaction details, and risk assessment factors. Strong partnerships between the technology platform and financial institutions are critical to ensuring compliance with regulations, maintaining data security, and providing a seamless customer experience. Selecting the right partners is essential to success, as they bring the financial expertise and regulatory know-how.
Security and Regulatory Considerations in Embedded Finance
Given the sensitive nature of financial data, security and regulatory compliance are paramount. Robust security measures, including encryption and multi-factor authentication, must be in place to protect user data from unauthorized access. Furthermore, businesses must comply with relevant regulations, such as data privacy laws (like GDPR or CCPA) and financial regulations specific to the offered products. Meeting these stringent requirements is critical to maintaining trust and avoiding legal repercussions.
The Future of Embedded Finance
The future of embedded finance is bright, with ongoing innovations and expansion into new areas. We can expect to see further integration into everyday applications, with even more diverse financial products becoming readily available. The potential to personalize financial services based on individual user behavior and needs is enormous. Expect more sophisticated risk assessment techniques, AI-driven solutions, and a continued focus on improving security and regulatory compliance to fuel the growth of embedded finance across industries. Read also about what is embedded finance.