Japan’s April 2025 Interest Rate Decision What it Means
The Context: A Balancing Act for the BOJ
Japan’s economy, in April 2025, will likely be navigating a complex landscape. Global economic uncertainty, potential inflationary pressures, and the ongoing recovery from the pandemic will all be significant factors influencing the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) decision on interest rates. The BOJ will be carefully weighing the need to stimulate growth against the risk of fueling inflation, a delicate balancing act that requires a nuanced understanding of the domestic and international economic climate. The strength of the Yen, export performance, and domestic consumption will all play a key role in shaping the BOJ’s assessment.
Inflationary Pressures and the BOJ’s Target
Inflation will be a paramount concern. While Japan has historically struggled with deflation, the global rise in energy and commodity prices could push inflation above the BOJ’s target of 2%. The BOJ will be analyzing the persistence and breadth of inflation, differentiating between temporary supply-side shocks and more entrenched demand-pull inflation. If inflation proves to be more persistent than anticipated, the pressure to adjust interest rates upwards will mount, even if it risks slowing economic growth.

Global Economic Uncertainty and its Impact
The global economic outlook will heavily influence the BOJ’s decision. A global recession, for example, could significantly impact Japanese exports and dampen domestic demand, potentially necessitating a continuation of low interest rates or even further monetary easing. Conversely, a strong global recovery might embolden the BOJ to normalize its monetary policy more aggressively. Geopolitical factors, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine and its impact on energy prices, will also play a significant role.
Domestic Economic Indicators: A Key Consideration
The BOJ will closely monitor key domestic economic indicators to gauge the health of the Japanese economy. These include GDP growth, employment rates, consumer spending, and business investment. Stronger-than-expected economic performance might lead to a more hawkish stance on interest rates, whereas weaker-than-expected data could necessitate a more accommodative approach. The interplay between these indicators and global economic conditions will be crucial in the decision-making process.
Potential Scenarios and Their Implications
Several scenarios are possible. The BOJ might maintain its current ultra-low interest rate policy if inflation remains subdued and global economic uncertainty persists. Alternatively, a gradual increase in interest rates might be implemented if inflation proves more persistent and the domestic economy shows resilience. A more aggressive rate hike is less likely, given Japan’s history of deflation and the government’s focus on economic growth. Each scenario has distinct implications for various sectors of the economy, including businesses, consumers, and the financial markets.
The Yen and its Influence on the Decision
The value of the Yen is another key factor. A weaker Yen can boost exports but also increases the cost of imported goods, potentially contributing to inflation. The BOJ will need to consider the impact of its interest rate decision on the Yen’s exchange rate. A significant appreciation of the Yen might necessitate maintaining a lower interest rate to support export competitiveness, while a weakening Yen might allow for a more hawkish approach, although the latter carries the risk of imported inflation.
Political Considerations and Public Opinion
While the BOJ strives for independence, political considerations and public opinion cannot be entirely disregarded. The Japanese government’s economic policies and public sentiment towards inflation and economic growth will inevitably influence the BOJ’s approach. A government pushing for rapid economic growth might encourage a more accommodative monetary policy, while concerns about inflation among the public might push the BOJ towards a more cautious approach.
Long-Term Implications and Market Reactions
The April 2025 interest rate decision will have significant long-term implications for the Japanese economy and its financial markets. A shift towards higher interest rates could attract foreign investment and strengthen the Yen, but it also carries risks of slowing economic growth. Conversely, maintaining ultra-low interest rates could support economic growth in the short term but might contribute to asset bubbles and further weaken the Yen. Market reactions will be swift and significant, with potential implications for bond yields, stock prices, and the currency exchange rate. Please click here for information about the Bank of Japan’s interest rate policy in April 2025.
Japan’s Interest Rates 2025 Outlook & Economic Impact
Japan’s Current Monetary Policy Stance
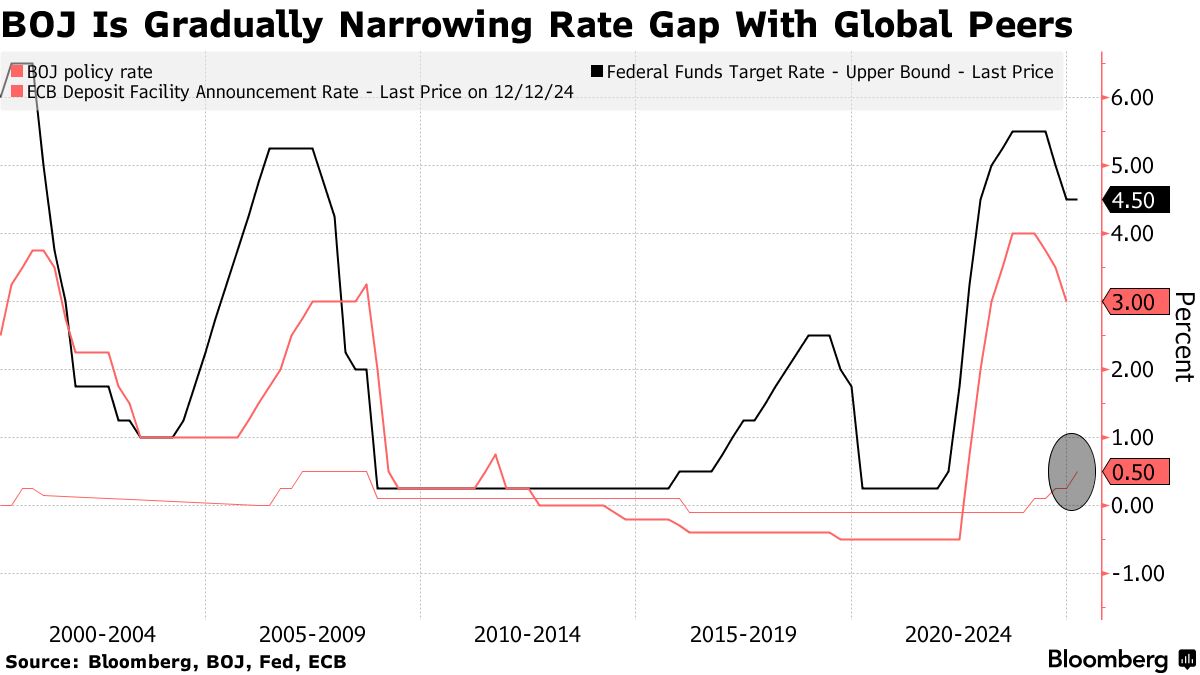
As of late 2023, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) continues to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy, characterized by negative interest rates on some commercial bank reserves and a commitment to yield curve control (YCC). This means the BOJ actively intervenes in the bond market to keep the 10-year government bond yield around zero. This policy, implemented to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation, has been a cornerstone of Japan’s economic strategy for years. However, the effectiveness and long-term sustainability of this approach remain a subject of ongoing debate, both domestically and internationally.
Global Inflationary Pressures and Their Impact on Japan
The global inflationary environment presents a significant challenge to the BOJ’s current policy. While Japan has experienced relatively subdued inflation compared to other developed nations, rising import costs due to global energy prices and supply chain disruptions are putting upward pressure on prices. This inflationary pressure, while currently moderate, could force a recalibration of the BOJ’s approach in the coming years. The balance between supporting economic growth and controlling inflation will be a key consideration for policymakers.
Potential Shifts in BOJ Policy in 2025
Predicting the BOJ’s actions in 2025 is inherently uncertain, but several scenarios are possible. One possibility is a gradual exit from YCC, potentially involving a slow and controlled increase in long-term interest rates. This approach would aim to minimize market disruption while allowing the BOJ to respond to evolving economic conditions. Another scenario might involve a more abrupt shift, driven by unexpectedly high inflation or a significant change in global economic dynamics. A complete abandonment of negative interest rates is also a possibility, though the timing and execution remain highly debated.
The Yen’s Volatility and its Influence on Interest Rates
The value of the Japanese yen plays a crucial role in shaping the BOJ’s policy decisions. A weakening yen can exacerbate inflationary pressures by increasing import costs, making it more difficult for the BOJ to maintain its ultra-loose stance. Conversely, a strengthening yen could provide some breathing room, allowing for a more gradual adjustment of monetary policy. The yen’s volatility will be a key factor influencing the BOJ’s strategy in the lead-up to and throughout 2025.
Economic Growth Projections for Japan in 2025
Japan’s economic growth outlook for 2025 is subject to considerable uncertainty. Factors such as global economic conditions, domestic consumption patterns, and the success of government structural reform initiatives will all play a role. While sustained, albeit moderate, growth is anticipated by many economists, the pace of expansion remains a key unknown. This uncertainty further complicates the BOJ’s task in balancing growth and inflation management.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Businesses and Consumers
Any changes to interest rates in Japan will have significant consequences for businesses and consumers. Higher interest rates could increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially slowing investment and economic growth. Consumers might also face higher mortgage rates and reduced borrowing capacity. Conversely, lower interest rates, while stimulating borrowing and investment, could potentially fuel inflation if not carefully managed. The impact will depend heavily on the magnitude and speed of any interest rate adjustments.
The Role of Government Fiscal Policy
The BOJ’s monetary policy decisions are intertwined with the government’s fiscal policies. Fiscal stimulus measures can support economic growth, potentially reducing the need for aggressive monetary tightening. However, excessive government spending could lead to higher inflation and complicate the BOJ’s efforts to control price increases. The coordination between monetary and fiscal policies will be crucial in navigating the economic challenges of 2025.
Risks and Uncertainties for the Japanese Economy
The outlook for Japan’s economy in 2025 is fraught with uncertainties. Geopolitical risks, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and tensions in the Taiwan Strait, could disrupt global supply chains and trigger further inflationary pressures. Domestic factors such as an aging population and shrinking workforce also present challenges to long-term economic growth. The BOJ will need to carefully consider these risks when formulating its monetary policy strategy.
Potential for Unexpected Events and Their Impact
The economic landscape is inherently unpredictable, and unexpected events could significantly impact Japan’s interest rates and economic performance in 2025. Sudden shifts in global commodity prices, unforeseen geopolitical developments, or unexpected changes in domestic political dynamics could all necessitate rapid adjustments in BOJ policy. The ability of the BOJ to adapt to these unforeseen circumstances will be a critical determinant of Japan’s economic success in the coming years. Learn more about the Bank of Japan’s interest rate policy in 2025 here: [link to tankionlineaz.com]
Fed’s 2025 Rate Hike Impact on Your Wallet
The Looming Shadow of Higher Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) decisions on interest rates significantly impact the everyday lives of Americans. While predicting the future is impossible, we can look at potential scenarios for 2025, considering the Fed’s ongoing battle with inflation and the possibility of further rate hikes. Even small adjustments can ripple through the economy, affecting your savings accounts, loans, and overall financial well-being. The uncertainty itself can cause stress, making financial planning that much harder.
How Higher Rates Affect Your Savings Accounts
If the Fed raises interest rates in 2025, your savings accounts could see a modest boost. Banks typically increase the interest they pay on savings and money market accounts to remain competitive and reflect the higher cost of borrowing. This means your money could earn a bit more, although the increase might not be dramatic enough to offset inflation. The key here is to compare rates offered by different banks and credit unions to maximize your returns. Don’t be afraid to switch institutions if you find a better deal.
The Impact on Credit Card Debt
Higher interest rates usually translate to higher credit card interest rates. If you carry a balance on your credit cards, you’ll be paying more in interest charges. This can significantly impact your monthly budget, leaving less money available for other expenses. The best approach is to aggressively pay down your credit card debt as quickly as possible. Consider strategies like the debt snowball or avalanche methods to tackle high-interest debt efficiently.
Mortgages and Home Equity Loans: A Double-Edged Sword
For those considering buying a home in 2025 or refinancing their existing mortgage, higher interest rates mean higher monthly payments. This makes homeownership less accessible for some, while for others, it potentially reduces the value of their existing property. However, if you already own your home and have a fixed-rate mortgage, your monthly payments won’t change, even if the Fed raises rates. Home equity loans, however, are usually tied to the prevailing interest rates, meaning you’ll likely pay more if the rates increase.
Auto Loans and Other Consumer Loans
Similar to mortgages, borrowing money for a car or other large purchases will become more expensive if the Fed increases rates. Auto loan rates typically track the Fed’s actions, so expect higher monthly payments if you’re planning to purchase a vehicle in 2025. This applies to other consumer loans as well, including personal loans and student loans (although student loan interest rates often have different regulatory mechanisms). Shop around for the best rates and consider pre-approval to secure better terms.
Investing in a Rising Rate Environment
Higher interest rates can impact investment returns. While it’s never wise to panic-sell, understanding how different asset classes react to rising rates is crucial. Bonds, for example, often lose value when interest rates rise. Conversely, some investors might find opportunities in sectors less sensitive to interest rate changes, or even invest in higher-yielding fixed-income securities. It’s always best to consult a qualified financial advisor to craft a strategy tailored to your individual circumstances and risk tolerance.
Budgeting and Financial Planning in Uncertain Times
The best defense against the uncertainties of fluctuating interest rates is a well-crafted budget and a proactive approach to financial planning. Track your income and expenses, identify areas where you can cut back, and build an emergency fund to cushion against unexpected expenses. Regularly review your financial goals and adjust your strategies as needed. Consider consulting a financial advisor to gain personalized insights and build a resilient financial plan that withstands economic fluctuations.
Understanding the Fed’s Actions and Their Ripple Effects
The Fed’s actions aren’t random; they aim to manage inflation and maintain economic stability. Understanding the reasoning behind rate hikes—and the potential consequences—is critical for making informed financial decisions. Following economic news and staying aware of the Fed’s announcements can help you anticipate potential changes and adjust your financial strategies accordingly. Remember that even small rate changes can have significant long-term effects, underlining the importance of careful financial planning. Please click here to learn about US interest rate policy in 2025.
Driving Global Prosperity Through Economic Innovation
Driving Global Prosperity Through Economic Innovation
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and interconnected global economies, the imperative for economic innovation has never been more pronounced. This article explores the pivotal role that global economic innovation plays in fostering prosperity, examining key aspects and highlighting its profound impact on various sectors.
Fostering Collaboration for Sustainable Growth
Global economic innovation necessitates collaboration among nations, businesses, and research institutions. By fostering an environment of open communication and shared knowledge, countries can harness collective intelligence to address complex challenges. Collaborative initiatives enable the pooling of resources and expertise, laying the foundation for sustainable economic growth on a global scale.
Technological Advancements as Catalysts for Change
The relentless march of technology continues to reshape the global economic landscape. Innovations in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and renewable energy have the potential to revolutionize industries, enhance productivity, and create new opportunities. Embracing these advancements allows nations to stay competitive, adapt to changing market dynamics, and build a resilient economic foundation.
Empowering Entrepreneurs and Small Businesses
Global economic innovation goes hand in hand with empowering entrepreneurs and small businesses. Creating an environment that nurtures innovation at the grassroots level is essential for driving economic growth. Accessible funding, supportive policies, and mentorship programs can catalyze the emergence of innovative startups, fostering a diverse and dynamic global economy.
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Impact
As the world grapples with environmental challenges, integrating sustainable practices into economic innovation becomes imperative. Innovations that prioritize environmental sustainability contribute not only to economic growth but also to the long-term well-being of the planet. Striking a balance between economic progress and ecological responsibility is crucial for a harmonious and resilient global economy.
Global Economic Innovation in Action
A prime example of global economic innovation in action is the ongoing collaboration among nations to address pressing issues. Initiatives like the Paris Agreement on climate change demonstrate how countries can come together to find innovative solutions with far-reaching implications. These global agreements underscore the importance of shared responsibility and coordinated efforts to address challenges that transcend borders.
The Role of Education in Shaping the Future
Education plays a pivotal role in driving global economic innovation. Fostering a culture of continuous learning and providing access to quality education equips individuals with the skills needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving economic landscape. Governments and organizations must invest in education to cultivate a workforce capable of driving innovation across diverse sectors.
Global Economic Innovation: A Call to Action
In conclusion, global economic innovation is not a mere buzzword but a call to action for nations, businesses, and individuals alike. Embracing innovation on a global scale requires a commitment to collaboration, sustainable practices, and education. It is a journey that requires collective effort to unlock the full potential of our interconnected world.
To learn more about the exciting developments in global economic innovation, visit Global Economic Innovation.
In the pursuit of a prosperous and sustainable future, embracing economic innovation is not just an option—it is an imperative that will shape the trajectory of our global community.
Competing Globally: Dynamics of Economic Competitiveness

Competing Globally: Unraveling the Dynamics of Economic Competitiveness
In the dynamic landscape of the global economy, the concept of economic competitiveness plays a pivotal role in shaping the success of nations. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of global economic competitiveness, exploring the factors influencing it, strategies for enhancement, and the implications for sustained prosperity.
Understanding Economic Competitiveness: A Holistic View
Economic competitiveness goes beyond simplistic notions of profit margins; it encompasses a nation’s ability to create an environment conducive to productivity, innovation, and sustainable growth. At its core, competitiveness reflects the capacity to produce goods and services efficiently, enabling a nation to thrive in the global marketplace.
Key Determinants: Factors Influencing Global Competitiveness
Numerous factors contribute to a nation’s economic competitiveness. Infrastructure, education, technological readiness, and innovation are vital components. Additionally, factors like political stability, governance efficiency, and macroeconomic policies significantly impact a nation’s ability to attract investment, foster entrepreneurship, and compete effectively on the world stage.
Innovation and Technology: Catalysts for Competitiveness
In the 21st century, innovation and technology stand as linchpins for economic competitiveness. Nations that invest in research and development, foster a culture of innovation, and embrace emerging technologies gain a competitive edge. The ability to adapt and integrate technological advancements is crucial for industries to stay relevant and globally competitive.
Education and Skill Development: Nurturing Human Capital
A highly skilled and educated workforce is a cornerstone of economic competitiveness. Nations that prioritize education and skill development create a talent pool capable of driving innovation, efficiency, and productivity. Continuous learning initiatives and vocational training programs contribute to the adaptability of the workforce in a rapidly changing economic landscape.
Infrastructure and Connectivity: Building a Strong Foundation
Infrastructure development, including transportation, communication, and energy systems, is integral to economic competitiveness. A robust infrastructure enhances connectivity, reduces operational costs, and facilitates the efficient movement of goods and services. Nations with well-developed infrastructure are better positioned to attract investment and foster economic growth.
Global Trade and Market Access: Expanding Opportunities
Participation in global trade and securing market access is paramount for economic competitiveness. Nations that actively engage in international trade agreements, reduce trade barriers, and diversify export markets open avenues for economic expansion. Strategic trade policies contribute to a nation’s resilience and competitiveness in the face of economic uncertainties.
Government Policies: Shaping the Economic Landscape
Government policies play a decisive role in shaping economic competitiveness. Policies that promote business-friendly environments, streamline regulations, and provide incentives for innovation create a fertile ground for economic growth. Political stability and effective governance are fundamental for implementing policies that foster competitiveness.
Sustainability and Inclusivity: Cornerstones of Long-Term Competitiveness
In the pursuit of economic competitiveness, sustainability and inclusivity are non-negotiable principles. Long-term competitiveness requires balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship and addressing societal inequalities. Nations that prioritize sustainability and inclusivity create resilient economies capable of withstanding global challenges.
Challenges and Adaptability: Navigating the Competitive Terrain
The global economic landscape is rife with challenges ranging from geopolitical tensions to health crises. Economic competitiveness demands adaptability. Nations must navigate challenges with resilience, agile policymaking, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Flexibility is key in maintaining competitiveness in the face of unpredictable global events.
Strategies for Enhancement: Sustaining and Scaling Competitiveness
Enhancing economic competitiveness requires a comprehensive approach. Nations must invest in education, innovation, and infrastructure continually. Moreover, fostering a business-friendly environment, promoting sustainable practices, and adapting policies to the evolving global landscape are crucial strategies. Collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors further amplify the impact of these strategies.
Implications for Global Prosperity: A Shared Vision
In conclusion, global economic competitiveness is not a zero-sum game; rather, it is a collective journey towards shared prosperity. Nations that prioritize competitiveness contribute not only to their own economic well-being but also to the global economy. By fostering innovation, nurturing human capital, and embracing sustainability, nations can collectively build a future where economic competitiveness is synonymous with inclusive and sustainable growth.
To explore more about Global economic competitiveness, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment: Building Global Prosperity
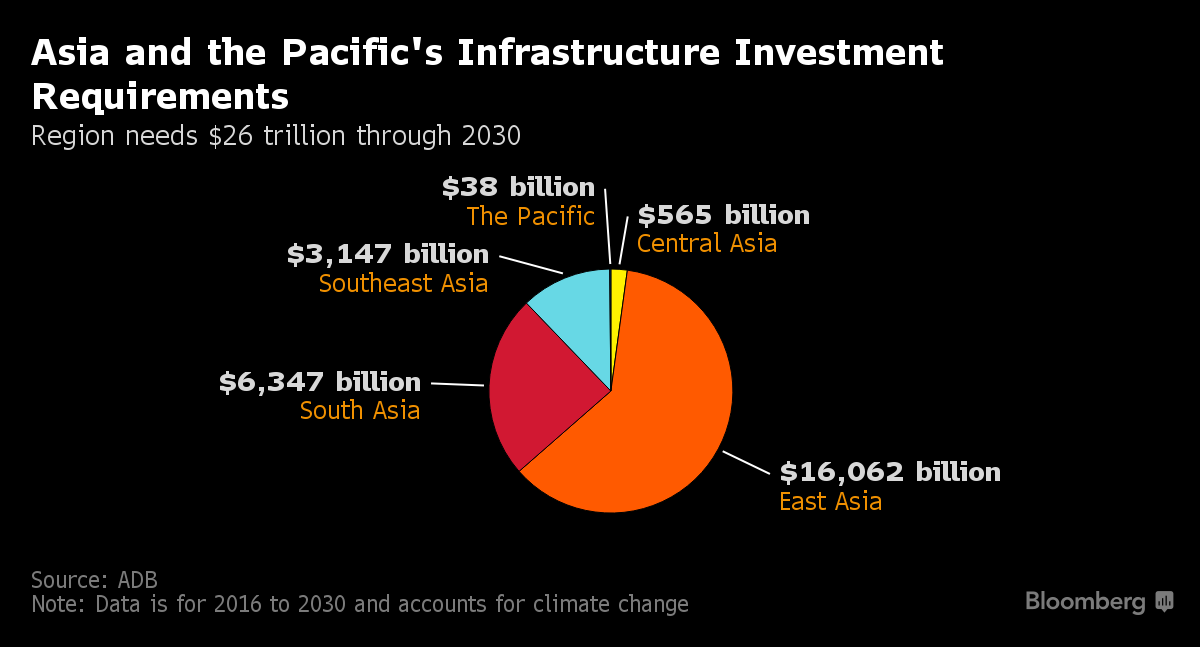
Building Global Prosperity through Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the role of economic infrastructure investment takes center stage. Governments and businesses globally are recognizing the importance of building and maintaining robust infrastructure to foster economic growth and ensure long-term prosperity.
The Foundation of Economic Development
Investment in economic infrastructure forms the bedrock for sustainable development. Roads, bridges, airports, and other essential facilities are critical components that facilitate the movement of goods and people. This physical connectivity is vital for fostering trade, attracting investments, and creating a conducive environment for economic activities to flourish.
Enhancing Connectivity for Trade
One of the primary objectives of worldwide economic infrastructure investment is to enhance connectivity for international trade. Efficient transportation networks and modern logistics systems reduce transit times and costs, making it more attractive for businesses to engage in cross-border trade. This connectivity also opens up new markets and opportunities for global economic integration.
Strategic Importance of Energy Infrastructure
Energy infrastructure plays a strategic role in powering economic activities. Investments in reliable and sustainable energy sources contribute to economic stability and growth. Countries that prioritize diverse and resilient energy infrastructures are better positioned to weather fluctuations in energy markets, ensuring a stable and affordable energy supply for businesses and households.
Digital Infrastructure for the Modern Economy
In the digital age, robust information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure are indispensable for economic competitiveness. High-speed internet, data centers, and advanced communication networks support the growth of digital economies. Nations that invest in cutting-edge digital infrastructure foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of new industries.
Job Creation and Economic Stimulus
Beyond the tangible benefits of improved connectivity and efficiency, worldwide economic infrastructure investment serves as a powerful tool for job creation and economic stimulus. Infrastructure projects, whether they involve construction, maintenance, or upgrades, create employment opportunities, injecting funds directly into local economies. This, in turn, stimulates consumer spending and overall economic activity.
Sustainable Infrastructure for Environmental Resilience
In the era of climate change, there is a growing emphasis on incorporating sustainability into infrastructure projects. Worldwide economic infrastructure investment can align with environmental goals by prioritizing sustainable practices. Green infrastructure, renewable energy projects, and eco-friendly transportation solutions contribute to environmental resilience and long-term economic viability.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Collaborative Approach
Many countries are turning to public-private partnerships (PPPs) to fund and implement large-scale infrastructure projects. This collaborative approach allows governments to leverage private sector expertise and financing, sharing both risks and rewards. PPPs can accelerate the delivery of infrastructure solutions, addressing critical needs more efficiently.
Challenges in Infrastructure Investment
While the benefits of worldwide economic infrastructure investment are evident, challenges persist. Funding constraints, regulatory hurdles, and geopolitical considerations can impede progress. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, transparent governance, and international cooperation to ensure that infrastructure projects meet the needs of diverse communities.
Resilience in the Face of Global Challenges
Investing in resilient infrastructure is essential for mitigating the impact of global challenges, such as pandemics and natural disasters. Resilient infrastructure can withstand shocks and disruptions, enabling communities to recover quickly and continue their economic activities. This resilience is a key component of building a more secure and prosperous future.
Navigating the Future: Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment
As we navigate the complex landscape of a rapidly changing world, worldwide economic infrastructure investment emerges as a critical driver of global prosperity. The interconnectedness of economies demands a concerted effort to build infrastructure that not only meets current needs but also anticipates future challenges. By prioritizing strategic investments and embracing innovative solutions, nations can lay the foundation for sustained economic growth and shared prosperity.
To explore more about the transformative impact of Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment, visit our comprehensive guide.
Global Impact: Immigration Policy Changes and Economic Effects
Introduction:
In an era of interconnected economies, changes in immigration policies resonate far beyond national borders. This article delves into the intricate relationship between shifts in immigration policies and their profound impact on the global economy, exploring the ripple effects that transcend geopolitical boundaries.
Labor Market Dynamics:
One of the primary channels through which changes in immigration policies affect the global economy is the alteration of labor market dynamics. Tightening or loosening immigration regulations directly influences the availability of skilled and unskilled labor, thereby shaping the workforce composition and impacting industries worldwide.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
Immigrants often contribute significantly to innovation and entrepreneurship in their adopted countries. Changes in immigration policies can either foster or hinder this contribution. Access to a diverse pool of talent stimulates creativity and economic growth, making immigration policies a key determinant of a nation’s innovation ecosystem.
Economic Growth and Productivity:
The nexus between immigration policies and economic growth is pronounced. Policies that attract skilled immigrants can enhance a country’s productivity, leading to increased economic output. Conversely, restrictive policies may stifle growth by limiting the influx of talent and hampering the dynamism of the workforce.
Investments and Financial Markets:
Global investments and financial markets are sensitive to changes in immigration policies. Investor confidence is influenced by a nation’s openness to talent and its ability to adapt to demographic shifts. Changes in immigration regulations may impact the perception of a country as an attractive destination for investments, influencing capital flows.
Trade Relations and Global Competitiveness:
The global competitiveness of nations is closely tied to their ability to attract skilled professionals. Changes in immigration policies can impact a country’s standing in the global arena, affecting trade relations and economic alliances. Openness to immigration can enhance a nation’s competitiveness by fostering diverse talent pools.
Demographic Challenges and Social Welfare:
Immigration policies play a crucial role in addressing demographic challenges, such as aging populations and declining birth rates. Countries with progressive immigration policies can mitigate these challenges by replenishing the workforce and contributing to the sustainability of social welfare systems.
Cultural Diversity and Consumer Markets:
The cultural diversity brought about by immigration has profound implications for consumer markets. Changes in immigration policies influence the composition of populations, shaping consumer preferences and behaviors. Businesses that understand and adapt to these changes can gain a competitive edge in diverse global markets.
Education and Research Collaborations:
Immigration policies significantly impact international collaborations in education and research. Academic institutions thrive on diverse perspectives and global talent. Restrictive immigration policies can hinder the exchange of knowledge and expertise, potentially impeding progress in various fields.
Human Capital Mobility and Skill Transfer:
The ability of skilled professionals to move freely across borders is a hallmark of a globalized economy. Changes in immigration policies can either facilitate or impede human capital mobility and skill transfer. Nations that embrace openness in immigration stand to benefit from the exchange of skills and knowledge.
For more insights into the global economic effects of changes in immigration policies, visit Global economic effects of changes in immigration policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the global economic effects of changes in immigration policies are profound and multifaceted. As nations navigate the delicate balance between protecting domestic interests and embracing a globalized world, the implications on labor markets, innovation, economic growth, and international relations underscore the interconnected nature of our modern economies. Understanding and carefully managing the impact of immigration policies is essential for shaping a resilient and adaptive global economic landscape.
Global Immigration Regulation Changes: Economic Impacts

Introduction:
The global economic landscape is intricately tied to immigration regulations, and shifts in these policies have profound impacts on economies worldwide. This article delves into the economic effects of changes in immigration regulations, exploring the multifaceted consequences for labor markets, innovation, and overall economic dynamics.
Labor Market Dynamics and Workforce Composition:
Changes in immigration regulations directly influence labor market dynamics. Policies that restrict or facilitate the entry of foreign workers shape the composition of the workforce. Restrictions may lead to labor shortages in certain industries, impacting productivity, while open policies can contribute to a diverse and skilled workforce, positively influencing economic growth.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
Immigration often brings diverse talents and ideas, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship. Policies that encourage the entry of skilled immigrants contribute to a vibrant startup culture and technological advancements. Conversely, stringent regulations may hinder the flow of innovative minds, potentially limiting a nation’s competitiveness in the global innovation landscape.
Economic Growth and Contribution to GDP:
The economic contributions of immigrants play a significant role in a nation’s GDP. Policies that attract skilled immigrants contribute to economic growth by bolstering productivity and consumer spending. Conversely, restrictive policies may lead to talent drain and reduced contributions to the economy, affecting long-term economic prospects.
Entrepreneurial Ecosystem and Startups:
Immigrant entrepreneurs often play a crucial role in fostering a dynamic startup ecosystem. Policies that support immigrant entrepreneurs contribute to job creation and economic vitality. Restrictive immigration policies may impede the growth of startups, limiting innovation and hindering the potential for economic expansion in emerging industries.
Skill Gaps and Economic Competitiveness:
Immigration regulations play a role in addressing skill gaps within a country. Policies that facilitate the entry of skilled workers help bridge skill shortages, enhancing a nation’s economic competitiveness. Conversely, restrictive policies may exacerbate skill gaps, potentially hindering industries that rely on specialized expertise.
Consumer Markets and Demographic Trends:
The influx of immigrants often contributes to the expansion of consumer markets. Policies that attract immigrants lead to demographic diversification, influencing consumer trends and market demands. Restrictive policies may limit demographic diversity, impacting consumer markets and overall economic vibrancy.
Social Services and Public Finances:
Changes in immigration regulations influence the utilization of social services and public finances. Policies that balance immigration with social service accessibility contribute to a sustainable economic model. However, an influx of immigrants without proper policy frameworks may strain public services, affecting government budgets and potentially leading to economic challenges.
Global Talent Competition and Economic Collaboration:
In a globalized world, nations compete for top talent. Policies that attract skilled professionals foster international collaboration and contribute to a nation’s economic standing. Conversely, restrictive immigration policies may result in a brain drain and limit opportunities for economic collaboration on a global scale.
Economic Resilience in Times of Change:
The adaptability of immigration policies is crucial for economic resilience, especially in times of change. Policies that respond to economic needs and global trends contribute to a nation’s ability to navigate uncertainties. Flexibility in immigration regulations ensures that a country can address labor market demands and maintain economic stability.
For more insights into the global economic effects of changes in immigration regulations, visit Global economic effects of changes in immigration regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic effects of changes in immigration regulations are far-reaching, influencing labor markets, innovation, and overall economic growth. Striking a balance between attracting skilled talent and addressing domestic concerns requires nuanced policy approaches. As nations navigate these changes, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, businesses, and the global community are essential to ensuring that immigration regulations contribute positively to economic development and resilience.
Global Housing Policy Shifts: Economic Ramifications

Introduction:
The global landscape of housing policies is undergoing transformative changes, with profound implications for the world economy. This article explores the economic ramifications of shifts in housing policies, delving into how these changes impact nations, businesses, and individuals.
Housing Market Dynamics:
Changes in housing policies reverberate through the housing market, influencing supply, demand, and pricing dynamics. Policies that encourage affordable housing can stimulate economic activities by making homeownership more accessible. Conversely, shifts that limit housing options may pose challenges for both the real estate industry and aspiring homeowners, affecting economic aspects of housing transactions.
Investments and Economic Growth:
Housing policies play a crucial role in shaping investment patterns and overall economic growth. Policies that incentivize real estate investments can contribute to economic expansion by driving construction activities, creating jobs, and fostering a vibrant housing market. However, policies that create uncertainty or impose restrictions may dampen investor confidence, potentially impacting economic growth.
Social and Economic Equity:
Housing policies are instrumental in addressing social and economic equity. Policies that promote fair housing practices and provide affordable housing options contribute to a more equitable society. Ensuring access to housing for diverse socioeconomic groups is not only a social imperative but also a factor influencing economic stability and inclusivity.
Mortgage Markets and Financial Stability:
The health of mortgage markets is closely tied to housing policies. Changes in policies related to lending practices and mortgage regulations influence financial stability. Policies that strike a balance between facilitating homeownership and preventing excessive risk-taking contribute to a robust and stable financial system, fostering economic resilience.
Urban Development and Infrastructure:
Housing policies intersect with urban development and infrastructure planning. Policies that prioritize sustainable and well-planned urban growth can enhance economic development by creating efficient living spaces, reducing commuting times, and improving overall infrastructure. Smart housing policies align with broader urban development goals, contributing to economic efficiency and quality of life.
Housing Affordability and Consumer Spending:
Affordable housing is linked to consumer spending patterns. Policies that address housing affordability positively impact disposable income, allowing individuals to allocate resources to other areas of the economy. On the contrary, housing policies that lead to inflated prices may constrain consumer spending, affecting the overall economic landscape.
Rental Market Dynamics and Flexibility:
Policies governing the rental market also play a role in economic outcomes. Rental policies that strike a balance between tenant protections and landlord incentives contribute to a stable rental market. A well-regulated rental sector provides housing flexibility, which is essential for a dynamic and adaptable workforce, ultimately influencing economic productivity.
Government Expenditure and Social Programs:
Changes in housing policies influence government expenditure, particularly in social programs related to housing. Policies that prioritize social housing programs may lead to increased public spending. Balancing these expenditures with broader economic considerations is essential to ensure the effectiveness of social programs while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
International Real Estate Investments:
Global economic implications extend to international real estate investments. Changes in housing policies in one country can influence the decisions of international investors. Policies that create a favorable environment for real estate investments may attract foreign capital, contributing to economic growth and cross-border economic interactions.
For more insights into the global economic implications of changes in housing policies, visit Global economic implications of changes in housing policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the global economic implications of changes in housing policies are multifaceted, influencing various facets of economies worldwide. Striking a balance between promoting housing affordability, encouraging investment, and ensuring social equity is crucial for fostering resilient and inclusive economic growth. As nations navigate these policy shifts, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities become essential in shaping a housing landscape that supports both economic prosperity and societal well-being.
World Economic Impact: Changes in Education Regulations

Charting the Course: Navigating World Economic Consequences of Changes in Education Regulations
The global landscape is continuously shaped by the policies that govern education. This article delves into the economic ramifications of changes in education regulations worldwide, exploring the intricate connections between educational reforms and economic outcomes.
Education as an Economic Engine
Education is often considered a cornerstone for economic development. Changes in education regulations can have a profound impact on the skills and knowledge of the workforce, influencing productivity, innovation, and overall economic competitiveness. As nations evolve their education policies, they set the stage for economic consequences that resonate across industries.
Workforce Dynamics and Employability
Changes in education regulations directly influence the dynamics of the workforce. Reforms may focus on aligning education with the needs of industries, introducing new skills training programs, or emphasizing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education. These changes contribute to a more skilled and adaptable workforce, positively impacting employability and addressing the demands of a rapidly evolving job market.
Investments in Human Capital and Economic Growth
Education regulations are a key driver in shaping a nation’s human capital. Investments in education, whether through increased funding, innovative programs, or curriculum enhancements, contribute to the growth of human capital. A well-educated populace fosters economic growth by fueling innovation, entrepreneurship, and the overall productivity of the workforce.
Global Competitiveness and Innovation
In a interconnected world, nations vie for global competitiveness, and education plays a pivotal role in this race. Changes in education regulations can impact a country’s standing in the global economic arena. Emphasis on research, innovation, and the development of critical skills enhances a nation’s competitiveness, attracting investments and fostering economic success on the international stage.
Challenges in Access and Inequality
While education reforms aim to drive economic progress, challenges in access and inequality must be addressed. Changes in regulations may inadvertently widen the gap between privileged and underprivileged populations, impacting access to quality education. Bridging this divide is essential to ensure that economic benefits are distributed equitably across society.
Entrepreneurship and Economic Resilience
Education regulations that foster entrepreneurship contribute to economic resilience. An entrepreneurial mindset cultivated through education can lead to the creation of innovative startups and small businesses. These ventures, in turn, become engines of economic growth, creating jobs and contributing to the diversification and stability of the economy.
Technological Integration and Industry Alignment
The rapid pace of technological advancement requires education systems to adapt and integrate technology into curricula. Changes in education regulations may emphasize the importance of digital literacy, coding skills, and technology-driven learning approaches. Aligning education with industry needs ensures that the workforce remains relevant and capable in an increasingly technology-driven global economy.
Demographic Shifts and Future Workforce Planning
Demographic changes influence the demand for education and workforce planning. Changes in education regulations may respond to shifting demographics, such as an aging population or an influx of young professionals. Addressing these demographic considerations ensures that the education system aligns with the future needs of the workforce, impacting economic sustainability.
Global Collaboration in Education Policies
In an interconnected world, global collaboration in education policies is gaining significance. Changes in education regulations often involve sharing best practices, learning from successful models, and collaborating on research initiatives. This international cooperation contributes to a shared pool of knowledge, positively influencing the quality of education and, consequently, the global economic landscape.
For an in-depth exploration of the world economic consequences of changes in education regulations, refer to this comprehensive study here. The study offers detailed analyses of case studies, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of global economies responding to evolving education regulations.



