Systemic Risk Management Global Market Growth Rise
The global market is a complex web of interconnected financial institutions and activities. When one part of this system experiences distress, it can quickly spread, potentially triggering a widespread financial crisis. This is where Systemic Risk Management comes into play. It’s the proactive process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could destabilize the entire financial system. Understanding its role is crucial for investors, policymakers, and anyone interested in the health of the global economy.
Key Takeaways:
- Systemic Risk Management is essential for maintaining the stability of the global financial system.
- Growth in this area is driven by increased regulatory scrutiny, technological advancements, and a desire for greater financial resilience.
- Effective Systemic Risk Management requires collaboration between institutions, regulators, and international bodies.
Understanding the Growing Importance of Systemic Risk Management
The rise of globalization and the increasing complexity of financial instruments have amplified the potential for systemic risk. Events like the 2008 financial crisis highlighted the devastating consequences when these risks are not adequately managed. As a result, regulators worldwide have implemented stricter rules and guidelines to promote Systemic Risk Management. These regulations often require financial institutions to hold more capital, improve their risk assessment processes, and develop resolution plans to minimize the impact of potential failures.
Furthermore, advancements in technology have both created new avenues for risk and provided new tools for managing it. For example, algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading can amplify market volatility, increasing systemic risk. However, sophisticated data analytics and artificial intelligence can also be used to identify and monitor potential systemic risks more effectively.
The demand for skilled professionals in Systemic Risk Management is also on the rise. Financial institutions, regulatory bodies, and consulting firms are actively seeking individuals with expertise in risk modeling, data analysis, and regulatory compliance. This growing demand reflects the increasing recognition of the importance of proactively managing systemic risk to protect the stability of the financial system and the broader economy. The ongoing pursuit of financial stability and resilience is the core driving force of global market growth in Systemic Risk Management.
Factors Driving Global Market Growth in Systemic Risk Management
Several factors are fueling the growth of the Systemic Risk Management market on a global scale. Let’s examine some of the key drivers:
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: As mentioned earlier, regulators around the world are placing greater emphasis on Systemic Risk Management. New regulations, such as Basel III and Dodd-Frank, require financial institutions to enhance their risk management practices and demonstrate their ability to withstand potential shocks to the system.
- Technological Advancements: The use of technology, particularly data analytics and AI, is transforming Systemic Risk Management. These tools enable institutions to analyze vast amounts of data, identify emerging risks, and develop more effective mitigation strategies. The ability to process complex information more quickly and accurately is essential for managing systemic risk in today’s fast-paced markets.
- Growing Complexity of Financial Instruments: The proliferation of complex financial instruments, such as derivatives and structured products, has made it more difficult to assess and manage systemic risk. These instruments can create hidden interconnections and amplify the impact of market shocks. Effective Systemic Risk Management requires a deep understanding of these instruments and their potential impact on the financial system.
- Globalization of Financial Markets: The increasing integration of financial markets has made them more susceptible to contagion. A crisis in one country can quickly spread to others, potentially triggering a global financial meltdown. Systemic Risk Management must therefore be coordinated across borders, with international cooperation among regulators and institutions.
- The need to protect us from future financial shocks: No one wants another 2008. The memory of the last crisis and the hardship it brought motivates all of us to ensure a stable financial future.
The Role of Technology in Systemic Risk Management
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern Systemic Risk Management. The sheer volume and complexity of data generated by financial markets necessitate the use of advanced tools for analysis and monitoring. Here are some specific ways in which technology is being used:
- Risk Modeling: Sophisticated risk models are used to simulate the impact of various scenarios on the financial system. These models can help institutions identify potential vulnerabilities and develop contingency plans.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics tools are used to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate emerging risks. This includes analyzing transaction data, market data, and news data to identify potential sources of systemic risk.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to automate risk management processes, improve the accuracy of risk assessments, and detect anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity or other forms of misconduct.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Technology enables real-time monitoring of financial markets, allowing regulators and institutions to quickly identify and respond to potential threats. This includes monitoring trading activity,
Capital Requirements Regulation Global Market Growth
The global financial landscape is constantly evolving, and a key driver of this evolution is the implementation and impact of financial regulations. One such regulation with far-reaching consequences is the Capital Requirements Regulation. This regulation plays a vital role in shaping financial stability, influencing investment decisions, and, most importantly, protecting consumers and the overall economy from excessive risk. Understanding the Capital Requirements Regulation and its influence on global market growth is crucial for anyone involved in the financial sector, from investors and bankers to policymakers and even everyday citizens. This article will help us break down the complexities of CRR and illustrate its effects on the global market.
Key Takeaways:
- Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR) aims to strengthen the financial system by setting minimum capital requirements for banks.
- CRR impacts global market growth by influencing lending practices, investment strategies, and overall financial stability.
- Differences in CRR implementation across regions can create both opportunities and challenges for international businesses.
- Ongoing developments and potential future changes to CRR necessitate continuous monitoring and adaptation by financial institutions.
Understanding the Impact of Capital Requirements Regulation
The Capital Requirements Regulation is a set of rules designed to ensure that banks and other financial institutions hold enough capital to absorb potential losses. These regulations are based on the Basel Accords, an international agreement aimed at promoting stability in the global financial system. The core principle is simple: the more risk a bank takes, the more capital it should hold as a buffer. This approach is designed to prevent banks from becoming excessively leveraged and therefore less vulnerable to financial shocks.
The impact of the Capital Requirements Regulation on global market growth is multifaceted. Firstly, by increasing the amount of capital that banks must hold, the CRR can influence their lending practices. Banks with higher capital requirements may be more selective in their lending, potentially leading to reduced credit availability for businesses and consumers. This can impact economic growth, especially for smaller businesses that rely on bank loans for funding.
Secondly, the Capital Requirements Regulation can affect investment strategies. Banks may adjust their investment portfolios to optimize their capital ratios, potentially shifting away from riskier assets toward safer, more liquid investments. This can impact the allocation of capital in the global market and influence asset prices.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, the Capital Requirements Regulation contributes to overall financial stability. By reducing the likelihood of bank failures, the CRR helps to maintain confidence in the financial system and prevent systemic crises. This is crucial for sustained economic growth.
How Does the Capital Requirements Regulation Affect Different Regions?
While the Capital Requirements Regulation is based on international agreements, its implementation can vary across different regions. For example, the European Union has its own version of the CRR, which incorporates the Basel III standards. Other countries and regions may have their own interpretations and implementations of these standards.
These regional differences can create both opportunities and challenges for international businesses. On the one hand, they can allow companies to take advantage of regulatory arbitrage, by choosing to operate in jurisdictions with more favorable capital requirements. On the other hand, they can increase the complexity of doing business across borders, as companies need to comply with different sets of regulations in different countries.
Furthermore, the specific economic conditions and financial systems of different regions can influence the impact of the Capital Requirements Regulation. For example, a region with a highly developed financial market may be better equipped to absorb the costs of higher capital requirements than a region with a less developed market. Therefore, understanding the regional nuances of the Capital Requirements Regulation is essential for assessing its impact on global market growth.
The Role of the Capital Requirements Regulation in Financial Stability
The primary objective of the Capital Requirements Regulation is to promote financial stability. By requiring banks to hold adequate capital, the CRR reduces the risk of bank failures and helps to prevent systemic crises. This is particularly important in today’s interconnected global financial system, where a failure in one institution can quickly spread to others.
The Capital Requirements Regulation also plays a crucial role in protecting consumers. By ensuring that banks are financially sound, the CRR reduces the risk of depositors losing their money. This helps to maintain confidence in the banking system and encourages people to save and invest.
However, it is important to note that the Capital Requirements Regulation is not a silver bullet. It is just one tool in a broader toolkit for managing financial risk. Other important tools include effective supervision, strong corporate governance, and sound macroeconomic policies. A holistic approach is needed to ensure financial stability and promote sustainable economic growth.
Future Trends and Challenges for Capital Requirements Regulation
The Capital Requirements Regulation is not a static set of rules. It
Fostering International Economic Cooperation

Forging Prosperity Through International Economic Cooperation
International economic cooperation stands as a cornerstone for fostering global prosperity, bringing together nations, businesses, and individuals in a collaborative effort to address shared challenges and capitalize on mutual opportunities.
The Imperative of Collaborative Trade Agreements
Trade agreements play a pivotal role in promoting international economic cooperation. By reducing trade barriers, facilitating the flow of goods and services, and establishing a framework for fair competition, nations create an environment conducive to economic growth. Initiatives such as free trade agreements foster a sense of interdependence, promoting stability and prosperity among participating countries.
Addressing Global Challenges Through Multilateral Efforts
Challenges such as climate change, public health crises, and poverty recognize no borders. International economic cooperation provides a platform for nations to pool resources and expertise, tackling these challenges collectively. Multilateral institutions, forums, and agreements enable collaborative problem-solving, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the global community in addressing complex issues.
Financial Cooperation for Stability and Development
In the realm of finance, cooperation among nations is essential for maintaining economic stability and fostering development. International monetary organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, facilitate financial cooperation by providing support during economic crises, promoting fiscal discipline, and financing projects that contribute to sustainable development.
Technology Transfer and Innovation Sharing
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, international economic cooperation plays a crucial role in sharing innovation and technology. Collaborative efforts in research and development, as well as the transfer of technological know-how, enable nations to bridge the digital divide, fostering inclusive economic growth and ensuring that technological benefits are shared globally.
Cultivating Cross-Border Investments
International economic cooperation extends to the realm of investments, as nations seek to attract foreign capital and businesses look for opportunities in global markets. Cross-border investments stimulate economic activity, create employment opportunities, and contribute to the transfer of skills and knowledge. This interconnected flow of investments strengthens economic ties among nations.
Policy Harmonization for Regulatory Consistency
Harmonizing policies and regulations across borders is essential for promoting a seamless and efficient global economic system. International economic cooperation involves aligning standards, regulations, and legal frameworks to reduce barriers to trade and investment. This consistency fosters a conducive environment for businesses to operate across borders, promoting economic integration.
Building Resilient Supply Chains
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains. International economic cooperation is crucial for building resilient and diversified supply chains that can withstand disruptions. Collaborative efforts in supply chain management, risk assessment, and contingency planning contribute to the stability of the global economic system.
Sustainable Development Goals and Global Cooperation
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) serve as a blueprint for a better and more sustainable future. Achieving these goals requires international economic cooperation to address issues such as poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental sustainability. Collaborative efforts are essential to ensure that no country is left behind in the pursuit of a more equitable and sustainable world.
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships
International economic cooperation often involves partnerships between governments and the private sector. Public-private collaborations bring together the strengths of both sectors to address complex challenges and drive economic development. These partnerships can range from infrastructure projects to initiatives promoting social and environmental responsibility.
In conclusion, international economic cooperation is not merely an option but a necessity in an interconnected world. As nations navigate the complexities of the global economy, collaboration becomes the key to unlocking shared prosperity. By fostering trade agreements, addressing global challenges, and promoting financial, technological, and policy cooperation, nations can collectively build a more resilient and sustainable future.
To explore more about International economic cooperation, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Navigating Global Economic Regulations for Stability

Navigating Global Economic Regulations for Stability
In the intricate web of global finance, economic regulations serve as the backbone, providing structure and stability to interconnected markets. This article delves into the world of worldwide economic regulations, exploring their significance, impact, and the challenges inherent in their implementation.
Understanding the Purpose of Economic Regulations
Economic regulations are a set of rules and guidelines established by governments to oversee and manage various aspects of economic activity. These regulations aim to prevent market failures, ensure fair competition, and protect consumers and investors. By providing a framework for ethical business conduct, they foster an environment conducive to sustainable economic growth.
The Global Landscape of Economic Regulations
In a world characterized by cross-border transactions and interdependence, the need for harmonized global economic regulations is evident. International organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Trade Organization (WTO), play a crucial role in facilitating cooperation among nations to develop and implement consistent regulatory standards. This harmonization is essential for maintaining financial stability on a worldwide scale.
Challenges in Implementing Consistent Regulations
While the idea of uniform global economic regulations is compelling, the reality is fraught with challenges. Each country has its unique economic, social, and political landscape, making it difficult to establish one-size-fits-all regulations. Negotiating and reaching consensus on regulatory standards among diverse nations require diplomatic finesse and a nuanced understanding of each country’s priorities.
The Role of Technology in Regulatory Compliance
As technology continues to advance, its impact on economic regulations is substantial. Innovations such as blockchain and artificial intelligence are being leveraged to enhance regulatory compliance and oversight. These technologies provide transparency, security, and efficiency in monitoring financial transactions, contributing to a more robust regulatory framework.
Balancing Regulation and Innovation
One of the perennial challenges in economic governance is striking the right balance between regulation and innovation. Excessive regulations can stifle economic growth and hinder technological advancements, while inadequate oversight may lead to market abuses and financial crises. Achieving equilibrium requires a dynamic approach that adapts to evolving market dynamics without compromising systemic stability.
The Role of Public Policy in Shaping Regulations
Public policy plays a pivotal role in shaping economic regulations. Governments formulate policies to address socio-economic challenges, and these policies often translate into regulatory measures. Policymakers must navigate a complex landscape, considering the needs of diverse stakeholders, economic trends, and the global interconnectedness of markets.
Economic Regulations and Financial Inclusion
A critical aspect of economic regulations is their impact on financial inclusion. Regulations that are too stringent can exclude marginalized populations from accessing financial services. Striking a balance between regulatory oversight and promoting inclusive financial practices is essential for fostering economic development that benefits all segments of society.
Global Cooperation for Effective Regulation
Recognizing the limitations of a purely national approach, global cooperation is essential for effective economic regulation. Collaborative efforts among nations, international organizations, and regulatory bodies can lead to the development of comprehensive frameworks that address the challenges of the modern global economy.
To explore the latest developments in worldwide economic regulations, visit Worldwide Economic Regulations.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Economic Regulations
In conclusion, the landscape of worldwide economic regulations is complex and dynamic. Navigating this terrain requires a delicate balance between international cooperation, technological innovation, and responsive public policy. As we move forward, the challenge lies in creating a regulatory environment that fosters stability, encourages innovation, and ensures the inclusive participation of all stakeholders in the global economy.
Revitalizing Economies: Global Plans for Economic Recovery

Revitalizing Economies: Navigating Global Economic Recovery Plans
The aftermath of global disruptions, whether caused by pandemics or economic downturns, necessitates robust and strategic responses. This article delves into the diverse array of global economic recovery plans, exploring the overarching strategies, regional variations, and the collaborative efforts aimed at reinvigorating economies worldwide.
To explore the world of global economic recovery plans, visit Global Economic Recovery Plans.
Unveiling Comprehensive Strategies for Recovery
Global economic recovery plans emerge as comprehensive strategies designed to address the multifaceted challenges posed by economic crises. These plans typically encompass fiscal, monetary, and structural measures aimed at restoring confidence, stimulating demand, and fostering sustainable growth. Nations worldwide deploy a mix of policies tailored to their unique circumstances, reflecting a shared goal of revitalizing economic activity.
Fiscal Measures: Injecting Stimulus into Economies
Fiscal measures play a pivotal role in global economic recovery plans. Governments deploy stimulus packages that involve increased public spending, tax incentives, and financial support to individuals and businesses. The objective is to inject liquidity into the economy, spur consumption, and provide a financial safety net for those affected by economic downturns. The scale and nature of fiscal interventions vary, reflecting the diverse economic landscapes.
Monetary Policy: Navigating Interest Rates and Liquidity
Central banks take center stage in global recovery efforts through monetary policy tools. Adjusting interest rates, implementing quantitative easing, and ensuring ample liquidity are key components. These measures aim to stabilize financial markets, encourage borrowing and investment, and manage inflationary pressures. Central banks collaborate to maintain monetary stability globally, recognizing the interconnected nature of the world economy.
Sectoral Focus: Tailoring Recovery to Specific Industries
Global economic recovery plans often adopt a sectoral approach, recognizing the unique challenges faced by different industries. Sectors such as tourism, hospitality, and aviation may require targeted support due to their vulnerability during crises. Governments and international bodies collaborate to devise strategies that provide assistance to sectors disproportionately impacted, ensuring a more balanced recovery.
International Cooperation: Collaborative Efforts for Resilience
The interconnectedness of economies underscores the importance of international cooperation in recovery plans. Nations collaborate through forums, such as the G20 and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), to coordinate policies, share best practices, and provide financial assistance to countries in need. This collaborative approach enhances global economic resilience and fosters a more synchronized recovery.
Green Recovery: Integrating Sustainability into Plans
An emerging trend in global economic recovery plans is the emphasis on a green recovery. Recognizing the urgency of addressing environmental challenges, recovery initiatives increasingly incorporate sustainable practices. Investments in renewable energy, green infrastructure, and eco-friendly technologies contribute not only to economic revitalization but also to long-term environmental sustainability.
Digital Transformation: Accelerating Technological Adoption
The pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of economies, and recovery plans reflect this shift. Investments in digital infrastructure, e-commerce, and technology adoption are prominent features. The goal is not only to recover lost ground but to position economies for future resilience and competitiveness in an increasingly digital world.
Inclusive Growth: Prioritizing Social and Economic Equity
Global economic recovery plans aspire to achieve inclusive growth, recognizing the imperative of addressing social and economic inequities. Policies that prioritize education, healthcare, and social safety nets contribute to a more equitable recovery. The emphasis is on leaving no one behind, ensuring that the benefits of recovery are shared across diverse segments of society.
Challenges and Adaptations: Navigating the Unknown
Despite meticulous planning, global economic recovery is not without challenges. Uncertainties such as evolving pandemic dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and shifts in consumer behavior require continuous adaptation. Flexibility and resilience become watchwords, and recovery plans are dynamic documents that respond to the ever-changing global landscape.
Conclusion: Charting a Collective Path Forward
In conclusion, the journey of global economic recovery is a collective endeavor that transcends borders. The diverse strategies embedded in recovery plans underscore the shared commitment to revitalizing economies and creating a more resilient and sustainable future. As nations navigate the complexities of recovery, collaboration, innovation, and adaptability emerge as crucial elements in charting a collective path forward.
Economic Consequences of International Monetary Regulation Changes
Navigating the Economic Landscape: International Changes in Monetary Regulations
The intricate dance of global economics is continually influenced by a multitude of factors. One such pivotal element is the constant evolution of monetary regulations on the international stage. In this article, we delve into the economic consequences of these changes and their far-reaching impacts.
The Ripple Effect on Global Trade and Commerce
Changes in international monetary regulations have a profound impact on global trade and commerce. Alterations in exchange rates, trade agreements, and currency valuations can lead to shifts in the competitive landscape. Exporters and importers must adapt to these changes, affecting supply chains and ultimately influencing the cost of goods and services worldwide.
Investor Sentiment and Financial Markets
Investors are particularly sensitive to changes in monetary regulations as they directly affect financial markets. Currency fluctuations and adjustments in interest rates can significantly impact investment strategies and portfolio performances. The uncertainty stemming from regulatory changes often leads to shifts in investor sentiment, influencing market trends and volatility.
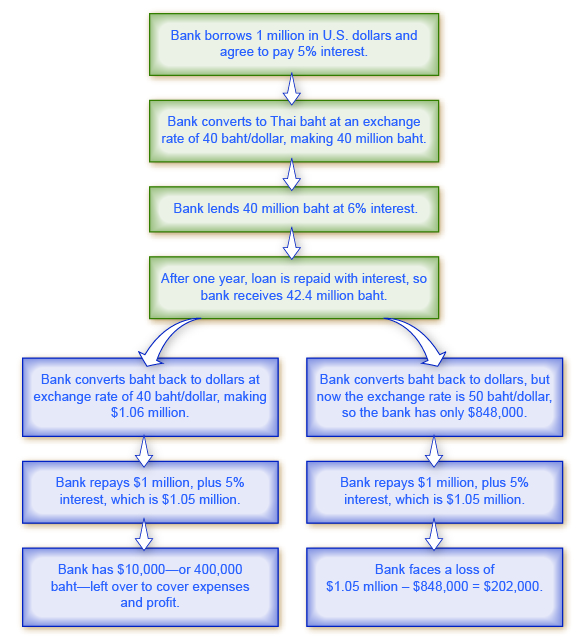
Currency Valuations and Exchange Rate Risks
One of the direct consequences of international monetary changes is the fluctuation in currency valuations. Exchange rates become more volatile, introducing new dimensions of risk for businesses engaged in international transactions. Companies must carefully manage and hedge against these risks to maintain stability in their financial operations.
Inflationary Pressures and Central Bank Policies
Changes in monetary regulations can have direct implications on inflationary pressures within countries. Central banks often adjust interest rates and money supply to achieve economic stability. However, the effectiveness of these policies can vary, leading to challenges in managing inflation and its cascading effects on consumer purchasing power and overall economic health.
Global Financial Stability and Systemic Risks
The interconnectedness of the global financial system means that changes in monetary regulations can introduce systemic risks. Events in one part of the world can quickly transmit shockwaves across borders, affecting financial institutions and markets. Policymakers must carefully balance the need for regulatory adjustments with the potential destabilizing effects on the broader financial ecosystem.
Impacts on Developing Economies and Emerging Markets
Developing economies and emerging markets are often more susceptible to the consequences of international changes in monetary regulations. These regions may face challenges in maintaining economic stability, attracting investments, and managing debt levels. The resulting disparities in economic conditions can exacerbate global inequalities.
Trade Balances and Current Account Deficits
International monetary changes can influence a country’s trade balance and current account deficits. Fluctuations in exchange rates impact the competitiveness of exports and imports, affecting the overall balance of trade. Persistent current account deficits can lead to economic imbalances and vulnerability to external shocks.
Technological Innovations in Financial Services
The landscape of financial services is evolving rapidly, and international monetary changes play a role in shaping this transformation. Innovations such as digital currencies and blockchain technology are gaining prominence, challenging traditional banking systems and providing new avenues for cross-border transactions. These advancements bring both opportunities and challenges for the global economic system.
Looking Ahead: Adaptation and Collaboration
As the world grapples with the economic consequences of international changes in monetary regulations, adaptation and collaboration are key. Policymakers, businesses, and investors must remain vigilant, fostering an environment that supports economic resilience and sustainability. The ability to navigate the complexities of the global economic landscape will be crucial for ensuring a stable and prosperous future.
For a more comprehensive understanding of the economic consequences of international changes in monetary regulations, explore this detailed study here. The study provides insights into case analyses and potential strategies to navigate the evolving global economic landscape in the wake of regulatory shifts.
Global Financial Reforms: Navigating Economic Consequences
Navigating the Economic Landscape: Consequences of Global Financial Reforms
In the aftermath of financial crises and economic downturns, the global community often rallies to implement financial reforms aimed at fostering stability, resilience, and transparency in financial systems. While these reforms are crucial for preventing future crises, they also bring about significant economic consequences that ripple through various sectors.
Foundation of Reforms: Responding to Financial Crises
Global financial reforms typically emerge as responses to systemic failures and crises. The aftermath of events like the 2008 financial crisis witnessed an international commitment to reevaluate and enhance financial regulations. The primary objective was to build a more robust financial system that could withstand shocks and ensure the protection of investors and the broader economy.
Tightening Regulatory Measures: Impact on Financial Institutions
One of the immediate consequences of global financial reforms is the tightening of regulatory measures on financial institutions. Stricter capital requirements, stress testing, and enhanced risk management practices are imposed to mitigate the likelihood of financial institutions engaging in risky behaviors that could lead to systemic failures. While these measures contribute to stability, they can also limit the profitability and flexibility of financial institutions.
Effects on Lending Practices: Balancing Risk and Access to Credit
The reforms often influence lending practices, impacting the balance between risk management and the accessibility of credit. Stringent regulations may lead banks to adopt more conservative lending approaches, affecting businesses and individuals seeking loans. Striking the right balance becomes a delicate task for policymakers, ensuring that financial institutions remain stable without stifling economic growth through restricted credit availability.
Market Liquidity and Trading Dynamics
Global financial reforms can reshape market liquidity and trading dynamics. Regulations like the Volcker Rule, aimed at curbing excessive risk-taking by banks, can affect market-making activities. While the intention is to prevent speculative trading that could lead to financial instability, there’s a need to carefully assess the consequences on market liquidity, particularly during times of stress or crises.
Impact on Cross-Border Financial Activities
In an interconnected global economy, financial reforms have significant implications for cross-border financial activities. The extraterritorial reach of certain regulations can create challenges for multinational corporations and financial institutions operating across jurisdictions. Coordination and harmonization efforts become essential to ensure a consistent and effective regulatory framework globally.
Technological Innovation and Compliance Costs
As financial institutions adapt to new regulatory requirements, there’s a notable impact on technological innovation and compliance costs. The need to implement sophisticated risk management systems and reporting mechanisms can drive investments in technology. Simultaneously, compliance costs can escalate, particularly for smaller financial entities, influencing their competitiveness and ability to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape.
Global Financial Reforms and Emerging Markets
The consequences of global financial reforms are often amplified in emerging markets. While reforms aim to enhance stability, they may inadvertently create challenges for economies with less-developed financial systems. Stricter regulations can limit the flow of capital to these markets, impacting investment and growth. Policymakers in emerging economies must strike a balance between compliance and fostering economic development.
Unintended Consequences and Regulatory Adjustments
Despite meticulous planning, global financial reforms may lead to unintended consequences. Market participants and institutions may find ways to circumvent regulations, leading to new risks or vulnerabilities. Periodic reassessment and adjustments to regulatory frameworks are crucial to address emerging challenges and maintain the effectiveness of the reforms over time.
The Role of International Cooperation
The consequences of global financial reforms highlight the importance of international cooperation. Coordination among regulatory bodies, central banks, and policymakers is vital to address cross-border challenges and ensure a harmonized global financial system. Regular communication and collaboration contribute to a more effective implementation of reforms while minimizing potential conflicts.
Strategies for Navigating the New Financial Landscape
As the global financial landscape evolves under the influence of reforms, businesses, investors, and policymakers need to develop strategies for navigating the changes. This includes staying informed about regulatory developments, adapting risk management practices, and embracing technological innovations that enhance compliance and efficiency.
Explore more about the Economic Consequences of Global Financial Reforms to understand the evolving dynamics and strategies for navigating the reshaped financial landscape.




