Global Economic Shifts: Changes in Transportation Regulations
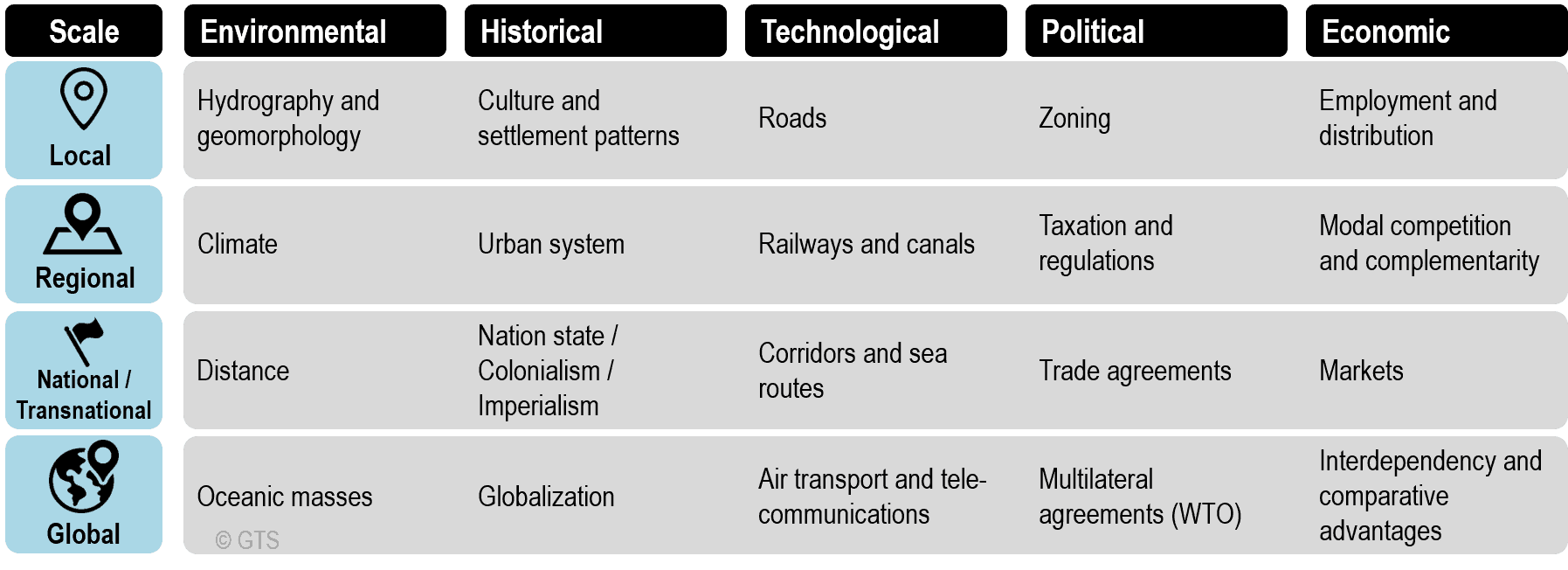
Revolutionizing Connectivity: Examining Global Economic Effects of Changes in Transportation Regulations
The evolution of transportation regulations is a catalyst for profound changes in the global economic landscape. This article explores the far-reaching effects of adjustments in transportation regulations, dissecting how these shifts influence economies on a worldwide scale.
Efficiency Gains and Supply Chain Dynamics
Changes in transportation regulations often aim to enhance efficiency in the movement of goods and people. Reforms may address aspects such as logistics, shipping, and air travel, optimizing supply chain dynamics. Streamlining transportation processes results in cost savings for businesses, positively impacting their competitiveness and contributing to economic efficiency.
Impact on Trade and Global Commerce
Transportation regulations are intricately linked with international trade. Alterations in these regulations can facilitate or hinder the flow of goods across borders. Efficient transportation systems foster global commerce, enabling businesses to reach broader markets. Conversely, restrictive regulations may impede trade, affecting industries and potentially leading to shifts in economic balances.
Infrastructure Investment and Economic Stimulus
Changes in transportation regulations often coincide with increased infrastructure investment. Governments may implement reforms to encourage private sector participation in transportation projects, stimulating economic activity. Investment in roads, ports, and other transportation infrastructure creates jobs, boosts local industries, and acts as a powerful economic stimulus.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Transport
Modern transportation regulations increasingly prioritize environmental sustainability. Revisions may target fuel efficiency standards, emissions reductions, and the promotion of sustainable transport modes. These changes not only contribute to environmental conservation but also align with the growing global emphasis on sustainable practices, shaping economic activities in harmony with ecological goals.
Technological Integration and Smart Mobility
The intersection of transportation regulations and technology is reshaping mobility. Regulations may encourage the integration of smart technologies, such as autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management systems. These innovations improve transportation efficiency, reduce congestion, and lay the foundation for smart cities, influencing economic activities in urban centers.
Logistics and the E-Commerce Revolution
E-commerce relies heavily on efficient logistics and transportation systems. Changes in regulations impact how goods are transported and delivered, influencing the logistics landscape. Easier access to global markets and faster delivery times can spur the growth of e-commerce, contributing to the expansion of online businesses and shaping the digital economy.
Global Connectivity and Tourism Impact
Transportation regulations play a vital role in shaping global connectivity and tourism. Policies that facilitate easier movement of people between countries contribute to the growth of the tourism industry. Conversely, restrictive regulations may deter international travel. The tourism sector, closely tied to transportation, significantly influences economies worldwide.
Challenges in Regulatory Alignment and Standardization
Harmonizing transportation regulations across borders is a complex challenge. Divergent regulations can create inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs for international transport. Achieving regulatory alignment and standardization becomes essential for smooth cross-border transportation, fostering international trade and economic cooperation.
Job Creation in Transportation Industries
The transportation sector is a significant source of employment globally. Changes in regulations, especially those promoting infrastructure projects and technological advancements, contribute to job creation. Jobs in logistics, shipping, aviation, and related industries play a crucial role in shaping local and national economies.
Resilience and Adaptation in a Changing Landscape
As transportation regulations evolve, businesses and industries must adapt to new realities. Resilience in the face of change becomes a key factor for economic success. Businesses that can navigate and capitalize on the evolving transportation landscape are better positioned to thrive in the global economy.
For an in-depth exploration of the global economic effects of changes in transportation regulations, refer to this comprehensive study here. The study offers detailed analyses of case studies, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of global economies responding to evolving transportation regulations.
Economic Implications: Global Changes in Infrastructure Regulations

Shaping the Future: Exploring Economic Implications of International Changes in Infrastructure Regulations
The world is in a constant state of transformation, and one of the key drivers of this change is the evolving landscape of international infrastructure regulations. This article delves into the economic implications of such changes and their far-reaching effects on global economies.
Infrastructure as the Backbone of Economic Development
Infrastructure serves as the backbone of economic development for nations across the globe. Roads, bridges, airports, and telecommunications networks are crucial elements that facilitate trade, transportation, and connectivity. Changes in infrastructure regulations can, therefore, have a profound impact on a country’s economic growth, influencing its competitiveness and attractiveness to investors.
Investment Opportunities and Economic Stimulus
International changes in infrastructure regulations often open up new investment opportunities. Governments may implement policies to encourage private sector participation in infrastructure development, leading to increased investment in construction projects. This surge in infrastructure spending serves as an economic stimulus, creating jobs, boosting local industries, and fostering overall economic growth.
Global Connectivity and Trade Facilitation
Changes in infrastructure regulations can enhance global connectivity and facilitate international trade. Improved transportation networks and efficient logistics systems reduce the costs and time associated with moving goods across borders. This, in turn, promotes trade between nations, encourages foreign direct investment, and contributes to the expansion of global markets.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
International changes in infrastructure regulations often align with the need for innovation and technological advancements. Smart infrastructure, incorporating technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, is becoming increasingly prevalent. These innovations not only enhance the efficiency of infrastructure systems but also contribute to economic development through the growth of technology-related industries.
Environmental Sustainability and Green Infrastructure
As the world grapples with environmental challenges, changes in infrastructure regulations are steering towards sustainability. Green infrastructure initiatives, such as renewable energy projects, eco-friendly transportation, and sustainable urban planning, are becoming integral components of international regulations. This shift not only addresses environmental concerns but also opens up new economic avenues in the growing green sector.
Challenges in Implementation and Regulatory Alignment
While changes in infrastructure regulations bring forth opportunities, they also pose challenges. Implementing large-scale infrastructure projects requires significant financial resources and effective regulatory frameworks. Achieving regulatory alignment between nations becomes crucial for cross-border projects, demanding diplomatic collaboration and international cooperation.
Job Creation and Human Capital Development
Investments in infrastructure have a direct impact on job creation and human capital development. Large-scale projects necessitate skilled and unskilled labor, contributing to employment opportunities within the construction and related industries. Additionally, infrastructure development often involves skill-building initiatives, enhancing the overall human capital of a nation.
Resilience and Infrastructure Security
Changes in infrastructure regulations are increasingly considering the aspect of resilience and security. With the rise of cyber threats and the unpredictability of natural disasters, securing critical infrastructure is paramount. Regulatory changes aim to fortify infrastructure systems against potential disruptions, ensuring economic stability and the uninterrupted functioning of essential services.
Public-Private Partnerships and Collaborative Initiatives
Governments are increasingly turning to public-private partnerships (PPPs) to bridge the infrastructure funding gap. Changes in regulations often promote collaborative initiatives between the public and private sectors. This partnership model not only attracts private investment but also leverages the efficiency and innovation that the private sector brings to infrastructure projects.
For an in-depth exploration of the economic implications of international changes in infrastructure regulations, refer to this comprehensive study here. The study offers detailed analyses of case studies, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of global economies responding to evolving infrastructure regulations.
Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment: Building Global Prosperity
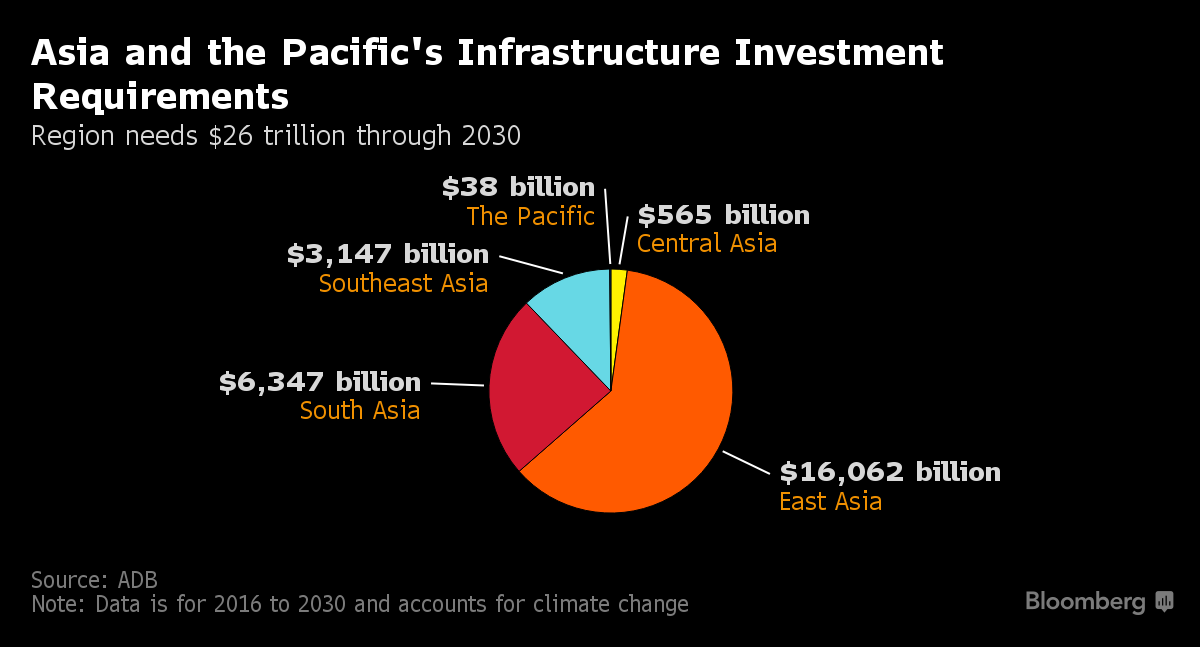
Building Global Prosperity through Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the role of economic infrastructure investment takes center stage. Governments and businesses globally are recognizing the importance of building and maintaining robust infrastructure to foster economic growth and ensure long-term prosperity.
The Foundation of Economic Development
Investment in economic infrastructure forms the bedrock for sustainable development. Roads, bridges, airports, and other essential facilities are critical components that facilitate the movement of goods and people. This physical connectivity is vital for fostering trade, attracting investments, and creating a conducive environment for economic activities to flourish.
Enhancing Connectivity for Trade
One of the primary objectives of worldwide economic infrastructure investment is to enhance connectivity for international trade. Efficient transportation networks and modern logistics systems reduce transit times and costs, making it more attractive for businesses to engage in cross-border trade. This connectivity also opens up new markets and opportunities for global economic integration.
Strategic Importance of Energy Infrastructure
Energy infrastructure plays a strategic role in powering economic activities. Investments in reliable and sustainable energy sources contribute to economic stability and growth. Countries that prioritize diverse and resilient energy infrastructures are better positioned to weather fluctuations in energy markets, ensuring a stable and affordable energy supply for businesses and households.
Digital Infrastructure for the Modern Economy
In the digital age, robust information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure are indispensable for economic competitiveness. High-speed internet, data centers, and advanced communication networks support the growth of digital economies. Nations that invest in cutting-edge digital infrastructure foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of new industries.
Job Creation and Economic Stimulus
Beyond the tangible benefits of improved connectivity and efficiency, worldwide economic infrastructure investment serves as a powerful tool for job creation and economic stimulus. Infrastructure projects, whether they involve construction, maintenance, or upgrades, create employment opportunities, injecting funds directly into local economies. This, in turn, stimulates consumer spending and overall economic activity.
Sustainable Infrastructure for Environmental Resilience
In the era of climate change, there is a growing emphasis on incorporating sustainability into infrastructure projects. Worldwide economic infrastructure investment can align with environmental goals by prioritizing sustainable practices. Green infrastructure, renewable energy projects, and eco-friendly transportation solutions contribute to environmental resilience and long-term economic viability.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Collaborative Approach
Many countries are turning to public-private partnerships (PPPs) to fund and implement large-scale infrastructure projects. This collaborative approach allows governments to leverage private sector expertise and financing, sharing both risks and rewards. PPPs can accelerate the delivery of infrastructure solutions, addressing critical needs more efficiently.
Challenges in Infrastructure Investment
While the benefits of worldwide economic infrastructure investment are evident, challenges persist. Funding constraints, regulatory hurdles, and geopolitical considerations can impede progress. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, transparent governance, and international cooperation to ensure that infrastructure projects meet the needs of diverse communities.
Resilience in the Face of Global Challenges
Investing in resilient infrastructure is essential for mitigating the impact of global challenges, such as pandemics and natural disasters. Resilient infrastructure can withstand shocks and disruptions, enabling communities to recover quickly and continue their economic activities. This resilience is a key component of building a more secure and prosperous future.
Navigating the Future: Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment
As we navigate the complex landscape of a rapidly changing world, worldwide economic infrastructure investment emerges as a critical driver of global prosperity. The interconnectedness of economies demands a concerted effort to build infrastructure that not only meets current needs but also anticipates future challenges. By prioritizing strategic investments and embracing innovative solutions, nations can lay the foundation for sustained economic growth and shared prosperity.
To explore more about the transformative impact of Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment, visit our comprehensive guide.
International Tech Regulation Shifts: Economic Impacts

Introduction:
The intersection of technology and international regulations is a pivotal factor shaping the global economic landscape. This article explores the profound economic effects of international changes in technology regulations, shedding light on how policies influence innovation, trade, and overall economic dynamics.
Innovation and Technology Development:
Changes in technology regulations at the international level have a direct impact on innovation. Policies that encourage a conducive environment for technological advancements, intellectual property protection, and research and development contribute to economic growth. Conversely, stringent regulations may stifle innovation by creating barriers and compliance challenges for technology companies.
Global Trade and Market Access:
International technology regulations play a crucial role in shaping global trade dynamics. Policies related to market access, trade agreements, and cross-border data flow impact the ability of technology companies to expand globally. Open and collaborative regulatory frameworks facilitate the seamless flow of technology-related goods and services, fostering economic interconnectedness.
Digital Economy and E-commerce:
The digital economy is significantly influenced by changes in technology regulations. Policies governing e-commerce, data privacy, and online transactions shape the landscape for digital businesses. Forward-thinking regulations that provide a balance between consumer protection and business innovation contribute to the growth of the digital economy, positively impacting economic indicators.
Cybersecurity and Resilience:
International technology regulations also address cybersecurity concerns. Policies aimed at enhancing cybersecurity measures and protecting critical infrastructure contribute to economic resilience. The economic consequences of cyber threats can be significant, and robust regulations play a vital role in safeguarding businesses, government institutions, and the overall economy from digital risks.
Cross-Border Collaboration and Research Partnerships:
Collaboration across borders is crucial for technology advancements. Regulations that foster international research partnerships and collaboration contribute to the collective growth of the global technology ecosystem. Policies that facilitate the movement of talent, ideas, and resources across borders enhance the capabilities of the technology sector, positively impacting economic innovation.
Data Governance and Privacy Protection:
As data becomes a cornerstone of the digital era, international regulations governing data governance and privacy protection are paramount. Policies that establish clear guidelines for data handling and protection contribute to user trust and confidence. A robust data governance framework is essential for fostering a secure digital environment, supporting economic activities that rely on data-driven insights.
Competition and Market Dynamics:
Regulations in the technology sector also address issues of competition and market dynamics. Policies that prevent anti-competitive practices, promote fair market competition, and ensure a level playing field contribute to economic efficiency. Striking the right balance between fostering innovation and preventing monopolistic behavior is essential for a healthy and competitive technology market.
Consumer Trust and Regulatory Compliance:
Consumer trust is a key factor in the success of technology products and services. Regulations that prioritize consumer rights, ensure transparency, and enforce regulatory compliance contribute to building and maintaining trust. Consumer confidence in the technology sector is a driving force behind economic adoption and growth.
Job Creation and Workforce Development:
The technology sector is a significant contributor to job creation and workforce development. Regulations that support the growth of technology companies also influence employment opportunities. Policies that encourage skills development, workforce training, and inclusivity in the technology workforce contribute to economic prosperity and societal well-being.
Environmental Sustainability in Technology:
As technology continues to advance, concerns about its environmental impact have come to the forefront. International regulations addressing e-waste management, energy efficiency, and sustainable technology practices contribute to economic sustainability. Policies that promote environmentally responsible technology development align with global efforts for a more sustainable and resilient economy.
For more insights into the economic effects of international changes in technology regulations, visit Economic effects of international changes in technology regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic effects of international changes in technology regulations are far-reaching, influencing innovation, trade, and various facets of the digital economy. Striking a balance between fostering technological advancements and addressing societal concerns is crucial. Collaborative efforts on the international stage are essential to create regulatory frameworks that not only support economic growth but also ensure the responsible and ethical development of technology on a global scale.
World Energy Regulation Shifts: Economic Transformations

Introduction:
The world is undergoing transformative changes in energy regulations, and these shifts have far-reaching economic implications. This article explores the profound impact of changes in energy regulations on the global economy, examining how policies shape energy markets, influence investments, and contribute to broader economic trends.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
One of the primary drivers of changes in energy regulations is the global shift towards renewable energy sources. Policies promoting the use of clean and sustainable energy, such as solar and wind power, contribute to the growth of the renewable energy sector. This revolution not only addresses environmental concerns but also stimulates economic activity by creating jobs and fostering innovation in the renewable energy industry.
Investments in Clean Technologies:
Changes in energy regulations often lead to increased investments in clean technologies. Governments worldwide are incentivizing businesses to adopt energy-efficient practices and invest in green technologies. This trend not only aligns with environmental goals but also stimulates economic growth by driving innovation and creating new markets for clean and sustainable technologies.
Energy Independence and Security:
Strategic changes in energy regulations are aimed at achieving energy independence and security. Policies that diversify energy sources, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and enhance energy efficiency contribute to a more secure and resilient energy infrastructure. This, in turn, has positive economic implications by reducing vulnerabilities to energy supply disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Job Creation in the Energy Sector:
The transition to cleaner energy sources creates job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. Policies supporting the growth of clean energy industries lead to job creation in areas such as solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and green construction. The economic impact extends beyond energy production, positively influencing employment rates and local economies.
Impact on Traditional Energy Industries:
While there is a push towards cleaner energy, changes in regulations also impact traditional energy industries. Policies aimed at reducing reliance on fossil fuels may pose challenges for industries like coal and oil. Governments must navigate a delicate balance between promoting clean energy and managing the economic transition for regions heavily dependent on traditional energy sources.
Smart Grids and Technological Innovation:
Advancements in energy regulations often involve the integration of smart grids and innovative technologies. Policies supporting the development of smart grids enhance energy efficiency, enable better management of energy resources, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. These technological innovations contribute to economic efficiency and the modernization of energy infrastructure.
Global Cooperation in Energy Transition:
Energy regulations are increasingly becoming a focal point of global cooperation. International agreements and collaborations aim to address climate change by transitioning to sustainable energy systems. This cooperation not only has environmental benefits but also fosters economic collaboration between nations, creating opportunities for joint investments and technology exchange.
Consumer Empowerment and Energy Choices:
Changes in energy regulations empower consumers to make sustainable energy choices. Policies that promote consumer access to clean energy options, such as rooftop solar panels or community-based renewable projects, contribute to a decentralized energy landscape. This empowerment enhances economic resilience and supports the growth of local and community-driven energy initiatives.
Economic Challenges and Transition Costs:
While the shift towards cleaner energy is promising, there are economic challenges associated with the transition. Changes in energy regulations may entail upfront costs for businesses and industries adapting to new standards. Governments must carefully manage these challenges to ensure a smooth and economically viable transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Innovation Hubs and Economic Hubs:
Cities and regions that embrace changes in energy regulations become innovation hubs and economic centers. Policies that encourage the development of clean energy technologies attract businesses, research institutions, and skilled professionals. These hubs drive economic growth, creating a ripple effect that extends beyond the energy sector to various industries and services.
For more insights into the world economic impact of changes in energy regulations, visit World economic impact of changes in energy regulations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, changes in energy regulations are reshaping the global economic landscape. The transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources presents significant opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation. As nations navigate this energy transition, it is crucial to implement policies that balance environmental stewardship with economic considerations, fostering a resilient and prosperous global economy.
Global Energy Policy Shifts: Economic Implications
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy policies, global shifts have profound implications for the world economy. This article explores the economic impacts of changes in energy policies, shedding light on how nations navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the transition to new energy paradigms.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
As the world grapples with environmental concerns, changes in energy policies drive a revolution in renewable energy. Nations investing in and transitioning to cleaner energy sources contribute not only to environmental sustainability but also stimulate economic growth. The renewable energy sector becomes a key player in job creation, innovation, and economic resilience.
Investments in Sustainable Infrastructure:
Changes in energy policies prompt substantial investments in sustainable infrastructure. Governments and businesses allocate resources to build and upgrade energy-efficient systems, creating a foundation for economic activities. These investments not only reduce environmental impact but also contribute to long-term economic sustainability.
Impact on Energy Markets and Prices:
Shifts in energy policies influence energy markets and prices on a global scale. Policies favoring renewable energy sources can impact the cost and availability of energy. As nations transition, fluctuations in energy markets create challenges and opportunities for businesses, shaping economic dynamics.
Technological Advancements and Innovation:
Energy policy changes drive technological advancements and innovation. Policies supporting research and development in clean energy technologies spur economic innovation. Nations at the forefront of these innovations often experience economic benefits, including the growth of new industries and increased global competitiveness.
Supply Chain Resilience and Energy Security:
Diversification of energy sources, a result of policy changes, enhances supply chain resilience and energy security. Nations less dependent on a single energy source are better equipped to withstand external shocks. This resilience contributes to economic stability and continuity in the face of energy-related challenges.
Environmental Externalities and Economic Considerations:
Energy policies often consider environmental externalities, impacting economic decision-making. Nations weighing the economic costs and benefits of energy policies take into account environmental factors, aiming for a balance that promotes economic growth while addressing environmental concerns.
Job Creation and Economic Opportunities:
The transition to new energy policies generates job opportunities and economic growth. The renewable energy sector, in particular, becomes a significant contributor to employment. Policies that facilitate a just transition for workers in traditional energy sectors to cleaner alternatives mitigate economic challenges associated with job displacement.
Global Cooperation in Energy Transition:
The global nature of energy challenges necessitates international cooperation. Changes in energy policies often spark collaborative efforts to address common issues. International partnerships in research, technology transfer, and policy coordination contribute to a more harmonized and economically viable global energy landscape.
Policy Certainty and Investment Attraction:
Policy certainty is crucial for attracting investments in the energy sector. Nations with clear and consistent energy policies create an attractive environment for investments. A stable policy framework encourages businesses to commit to long-term projects, fostering economic growth and sustainability.
For more insights into the world economic impact of changes in energy policies, visit World economic impact of changes in energy policies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the world economic impact of changes in energy policies is multi-faceted, influencing various aspects of global economies. From renewable energy revolutions and sustainable infrastructure investments to the reshaping of energy markets and supply chain resilience, the economic implications underscore the interconnected relationship between energy policies and global economic well-being. As nations navigate the path toward cleaner and more sustainable energy, the collaborative efforts of policymakers, businesses, and citizens are paramount for ensuring a resilient and prosperous global economic future.

