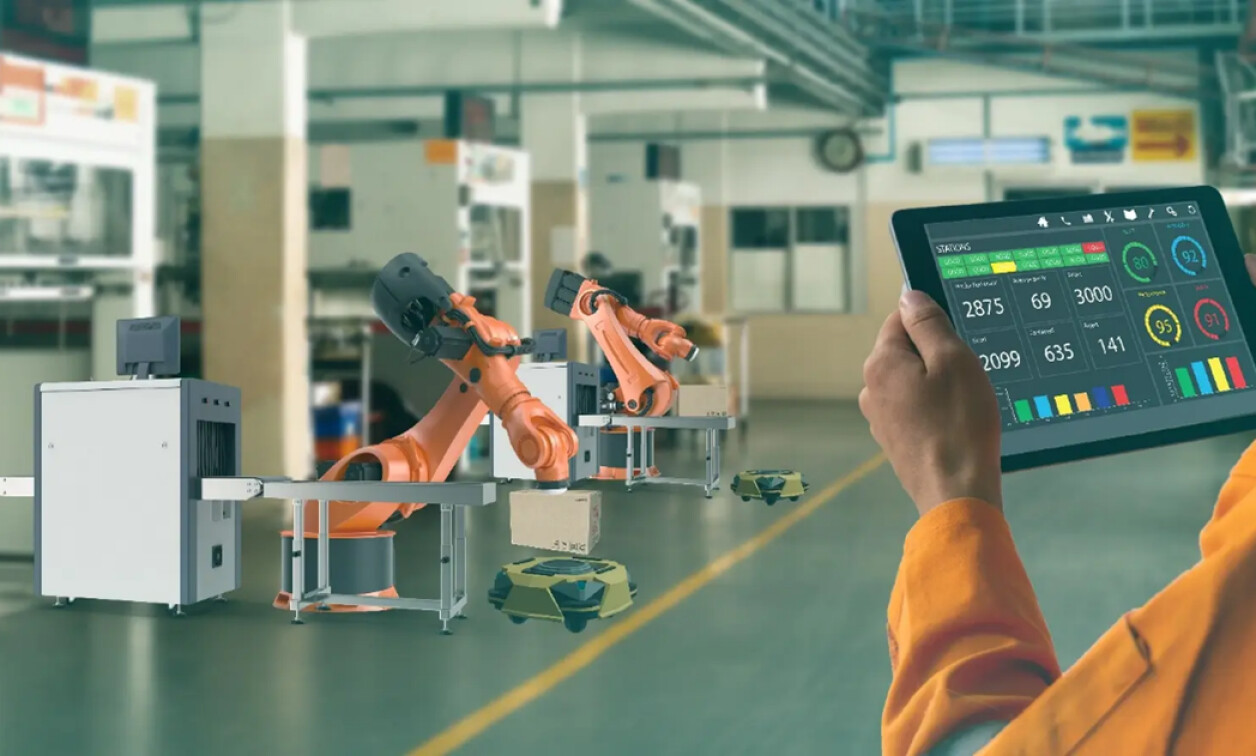
Edge Computing Powering the Next-Gen Factory
The Rise of the Smart Factory
The modern factory is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by the need for increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved product quality. This evolution is fueled by the convergence of several technologies, most notably the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and, increasingly, edge computing. No longer are factories simply places where raw materials are transformed into finished goods; they’re becoming complex, interconnected ecosystems of data-generating machines and processes.
Edge Computing: Bridging the Gap Between Data and Action
Traditional cloud computing, while powerful, often suffers from latency issues when dealing with the massive amounts of real-time data generated by industrial equipment. This delay can be problematic in a factory setting, where quick responses to anomalies are crucial for maintaining productivity and preventing costly downtime. Edge computing addresses this challenge by processing data closer to its source – the factory floor itself. This significantly reduces latency, enabling faster decision-making and immediate action based on real-time insights.

Real-Time Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
One of the most impactful applications of edge computing in factories is predictive maintenance. By analyzing sensor data from machines in real-time, edge devices can identify potential equipment failures before they occur. This allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, minimizing downtime and preventing costly repairs. This predictive capability not only saves time and money but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Quality Control and Improved Product Traceability
Edge computing empowers factories to implement sophisticated quality control systems. Real-time data analysis from various stages of the production process allows for immediate identification of defects or inconsistencies. This allows for quicker intervention, reducing waste and improving the overall quality of finished goods. Furthermore, edge computing facilitates improved product traceability, allowing for easy tracking of products throughout their lifecycle, from raw material sourcing to final delivery.
Optimizing Production Processes through Data-Driven Insights
The wealth of data generated by a smart factory can be overwhelming without effective analysis. Edge computing provides the computational power to process this data locally, providing real-time insights into production processes. This allows for identification of bottlenecks, optimization of workflows, and adjustments to improve efficiency and throughput. This data-driven approach leads to continuous improvement and helps factories stay ahead of the competition.
Enhancing Workforce Safety and Collaboration
Beyond optimizing production, edge computing enhances workforce safety and collaboration. Real-time monitoring of equipment and worker activity allows for immediate identification of potential hazards. This proactive approach minimizes workplace accidents and ensures a safer working environment. Furthermore, edge computing facilitates seamless communication and collaboration between workers, engineers, and management, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Security Considerations in the Edge Environment
With the increased reliance on interconnected devices and data processing at the edge, security becomes paramount. Robust security measures are essential to protect against cyber threats and data breaches. This includes implementing strong access controls, encryption protocols, and regular security audits. A well-defined security strategy is vital for the successful deployment of edge computing in a factory setting.
The Future of Edge Computing in Manufacturing
The integration of edge computing in manufacturing is still in its early stages, yet its potential is vast. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated applications of edge computing in factories. This will lead to even greater efficiency, improved product quality, enhanced safety, and a more sustainable and resilient manufacturing industry. The smart factory powered by edge computing is not just the future; it’s the present, and it’s rapidly transforming the way goods are produced globally. Click here to learn about edge software for smart factories.
AI Revolutionizing Legal Research in 2025
AI-Powered Legal Research Platforms: A Game Changer
The legal profession, traditionally known for its meticulous research methods, is experiencing a seismic shift. 2025 marks a point where AI-powered legal research platforms are no longer a futuristic dream but a practical reality for many firms and solo practitioners. These platforms go far beyond simple keyword searches; they leverage sophisticated algorithms to analyze vast datasets of legal documents, case law, statutes, and regulations, delivering highly targeted and relevant results with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Beyond Keyword Searches: Understanding Context and Nuance
The limitations of traditional keyword searches in legal research are well-documented. A simple keyword might yield thousands of irrelevant results, while crucial information buried within complex documents could easily be missed. AI-powered platforms overcome these limitations by employing natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML). They can understand the context and nuances of legal language, identifying relevant cases even when the precise keywords aren’t present. This allows lawyers to spend less time sifting through irrelevant information and more time analyzing the material that truly matters.
Predictive Analytics: Anticipating Case Outcomes
One of the most exciting developments in AI-driven legal research is the emergence of predictive analytics. These tools analyze vast quantities of past case data to predict the likely outcome of current cases. By identifying patterns and trends in judicial decisions, these platforms can help lawyers assess the strengths and weaknesses of their cases, and potentially inform settlement negotiations. While not a guarantee of success, this predictive capability provides invaluable insights that can significantly impact litigation strategies.
Enhanced Due Diligence and Contract Analysis
Beyond litigation, AI is transforming other aspects of legal practice. Due diligence, a process typically involving painstaking manual review of vast amounts of documentation, is becoming significantly faster and more efficient. AI can automatically scan and analyze contracts, identifying potential risks and clauses that may require further attention. This not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of overlooking crucial details that could have significant legal ramifications.
Accessibility and Democratization of Legal Services
The increasing accessibility of AI-powered legal research tools is democratizing access to legal services. Smaller firms and solo practitioners, who may not have the resources for extensive manual research, can now compete with larger firms by leveraging the power of AI. This level playing field is fostering greater competition and potentially leading to more affordable legal services for clients.
Addressing Ethical Concerns and Data Privacy
The rapid advancement of AI in legal research also raises ethical concerns. Issues of bias in algorithms, data privacy, and the potential displacement of legal professionals need careful consideration. The legal community is actively engaging in discussions to develop responsible guidelines and regulations to ensure that AI is used ethically and transparently. This includes ensuring that AI tools are properly vetted for bias and that data privacy is protected throughout the research process.
The Future of Legal Research: Collaboration Between Humans and AI
The future of legal research is not about humans versus AI, but rather humans and AI working together. AI tools are proving to be invaluable assistants, augmenting the capabilities of legal professionals, not replacing them. While AI can automate tedious tasks and identify patterns, human judgment and legal expertise remain crucial for interpreting complex legal issues and providing nuanced strategic advice. The most successful legal professionals in 2025 and beyond will be those who can effectively leverage the power of AI to enhance their own skills and knowledge.
Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
The bottom line is that AI is significantly improving the efficiency and reducing the costs associated with legal research. Lawyers can spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time on higher-value work, such as client communication, strategy development, and case preparation. This translates to cost savings for both law firms and clients, making legal services more accessible and affordable. Click here to learn about AI in legal research in 2025.
AI-Driven Insights for Legal Professionals
Streamlining Legal Research with AI
The sheer volume of legal documents, case laws, and statutes can be overwhelming for even the most seasoned legal professional. AI-powered research tools are changing this landscape by offering significantly faster and more comprehensive searches. These tools can sift through massive datasets, identifying relevant precedents, statutes, and regulatory information in a fraction of the time it would take a human. They can also analyze the language used in these documents, identifying key themes and patterns that might be missed by human eyes, leading to more thorough and effective legal research.
Predictive Analytics for Case Outcomes
Predicting the outcome of a case is a crucial aspect of legal strategy. AI algorithms, trained on vast amounts of historical case data, can analyze various factors such as jurisdiction, judge, type of claim, and evidence presented to predict the likelihood of success or failure. While not a guarantee, this predictive analytics capability enables lawyers to make more informed decisions about settlement negotiations, resource allocation, and overall case strategy. This improved foresight allows for better client counseling and more realistic expectations.
Enhanced Due Diligence and Contract Review
Due diligence and contract review are notoriously time-consuming processes. AI can significantly accelerate these tasks by automatically identifying key clauses, risks, and potential liabilities within contracts. Sophisticated AI tools can analyze language for ambiguities, inconsistencies, and hidden obligations, alerting legal teams to potentially problematic areas that might otherwise be overlooked. This meticulous analysis reduces the risk of costly errors and allows legal teams to focus their efforts on more complex, nuanced issues.
Automating Routine Tasks and Increasing Efficiency
Many legal tasks are repetitive and mundane, such as document review, summarization, and data entry. AI-powered automation tools can handle these tasks efficiently, freeing up lawyers to focus on more complex and strategically important work. This not only increases efficiency but also reduces the risk of human error associated with repetitive tasks. By automating these processes, law firms can improve their overall productivity and profitability.
Improving Accessibility to Legal Services
AI has the potential to democratize access to legal services, particularly for individuals and small businesses who may not have the resources to hire expensive legal counsel. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide basic legal information and guidance, answering frequently asked questions and providing initial assessments of legal issues. While not a replacement for human lawyers, these tools can act as a crucial first point of contact, ensuring that individuals receive the necessary information and support to navigate legal challenges.
Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy
The use of AI in the legal profession raises significant ethical concerns. Issues such as bias in algorithms, data privacy, and the potential displacement of human lawyers require careful consideration. It’s vital that legal professionals understand the limitations of AI and use it responsibly, ensuring that it enhances, rather than replaces, human judgment and expertise. Strict adherence to data protection regulations and transparency in the use of AI are paramount to maintaining public trust and upholding ethical standards within the legal field.
Integration of AI into Existing Legal Workflows
Successfully integrating AI into existing legal workflows requires careful planning and execution. It’s not simply a matter of adopting new technology; it necessitates a thorough assessment of current processes, identifying areas where AI can add value, and training legal teams on the effective use of new tools. This gradual integration, coupled with ongoing monitoring and evaluation, ensures a smooth transition and maximizes the benefits of AI without disrupting established practices.
The Future of AI in Law
The application of AI in the legal field is still evolving, with new tools and applications constantly emerging. As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and powerful tools that transform the way legal professionals work. This continuous innovation holds the promise of increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and enhanced access to justice for everyone. Please click here to learn about AI innovations in legal research.
Edge Computing Smart Factories’ New Powerhouse
The Rise of Edge Computing in Smart Factories
Smart factories are rapidly evolving, driven by the need for increased efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness. Centralized cloud computing, while powerful, often struggles to keep up with the real-time demands of a modern manufacturing environment. This is where edge computing steps in, offering a powerful solution by processing data closer to the source – the factory floor itself. This shift is transforming how manufacturers collect, analyze, and act upon data, leading to significant improvements across the board.
Real-Time Data Processing: The Key Advantage
One of the biggest benefits of edge computing in smart factories is the ability to process data in real-time. Traditional cloud-based systems often experience latency, meaning there’s a delay between data generation and analysis. In a manufacturing setting, this delay can be costly, leading to production bottlenecks, quality issues, and missed opportunities for optimization. Edge computing eliminates this latency, allowing for immediate responses to changing conditions. This allows for quicker adjustments to machinery, preventing downtime and maximizing output.
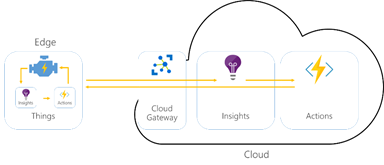
Enhanced Machine-to-Machine Communication (M2M)
Smart factories rely heavily on seamless communication between machines. Edge computing facilitates this by providing a localized network for data exchange. This improved M2M communication allows for better coordination between different parts of the production process, leading to smoother workflows and reduced errors. The localized nature of the data processing also improves security, as sensitive data doesn’t need to travel across a wider network, reducing the risk of breaches.
Improved Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
Predictive maintenance is crucial for maximizing uptime in a manufacturing setting. By analyzing sensor data from machines in real-time, edge computing allows for early detection of potential problems. This allows maintenance teams to address issues before they escalate into major breakdowns, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs. The ability to predict and prevent equipment failures is a significant advantage, leading to substantial cost savings and increased productivity.
Boosting Operational Efficiency and Flexibility
Edge computing contributes to a more efficient and flexible factory environment. By automating tasks and processes, factories can operate more smoothly. Real-time data analysis allows for dynamic adjustments to production schedules based on current demand and resource availability. This flexibility is essential in today’s dynamic market, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in customer orders and market conditions. This agility is a major competitive advantage in a fast-paced global market.
Strengthened Cybersecurity Measures
While connected systems offer significant benefits, they also introduce cybersecurity risks. Edge computing mitigates these risks by keeping sensitive data localized. By processing and analyzing data at the edge, the amount of data needing to travel across a potentially vulnerable network is reduced, thus minimizing the exposure to cyber threats. This layered security approach provides a more robust defense against potential attacks.
Enabling Advanced Analytics and AI at the Edge
Edge computing enables the deployment of sophisticated analytics and artificial intelligence algorithms directly within the factory. This allows for faster insights and more immediate actions based on the analyzed data. AI-powered systems can be used for anomaly detection, quality control, and process optimization, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and product quality. The on-site processing also reduces the reliance on cloud resources for complex computations, further accelerating the decision-making process.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Smart Factories
The modular nature of edge computing allows for easy scalability as factory needs evolve. As production expands or new technologies are integrated, the edge computing infrastructure can be easily adapted to meet the growing demands. This adaptability is crucial for future-proofing smart factories and ensuring their continued competitiveness in a rapidly changing technological landscape. It allows for a smooth and efficient transition to even more advanced technologies in the future.
Challenges and Considerations
While edge computing presents numerous advantages, some challenges need to be considered. Managing and maintaining a distributed edge computing infrastructure can be complex, requiring specialized skills and expertise. Ensuring data consistency and security across multiple edge nodes also demands careful planning and implementation. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach and investment in the right technologies and personnel. Please click here to learn about edge computing for smart factories.
Smart Factories AI’s Revolution in Manufacturing
The Dawn of Intelligent Automation
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into factories. This isn’t just about automating individual tasks; it’s about creating truly smart factories, where AI orchestrates and optimizes the entire production process, from design to delivery. This intelligent automation is leading to unprecedented levels of efficiency, flexibility, and quality, reshaping the future of manufacturing.
Predictive Maintenance: Preventing Downtime Before it Happens
One of the most impactful applications of AI in smart factories is predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from various sensors embedded in machinery, AI algorithms can predict potential equipment failures before they occur. This allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime, reducing repair costs, and ultimately improving overall productivity. Instead of relying on scheduled maintenance, manufacturers can address issues only when necessary, optimizing resource allocation and maximizing uptime.

Quality Control: Ensuring Perfection Through AI-Powered Inspection
Maintaining consistent product quality is crucial in today’s competitive market. AI-powered vision systems are revolutionizing quality control by automating the inspection process with incredible accuracy. These systems can identify even the slightest defects that might be missed by human inspectors, leading to higher quality products and reduced waste. This real-time feedback loop allows for immediate adjustments to the production process, preventing further defects and ensuring consistent quality.
Optimizing Supply Chains: From Raw Materials to Finished Goods
Smart factories leverage AI to optimize the entire supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished goods. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, including market trends, supplier performance, and transportation logistics, to predict demand, optimize inventory levels, and streamline the entire supply chain process. This leads to reduced lead times, improved inventory management, and lower costs.
Enhanced Production Planning and Scheduling: Maximizing Efficiency
AI is also transforming production planning and scheduling. By analyzing real-time data on machine availability, material inventory, and order demands, AI algorithms can create optimal production schedules that minimize lead times, maximize resource utilization, and improve overall factory efficiency. This dynamic scheduling capability allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands and unforeseen events, ensuring that production remains efficient and responsive.
Robotics and Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Human-Machine Collaboration
The integration of robotics and collaborative robots (cobots) is another key element of smart factories. While traditional industrial robots perform repetitive tasks in isolation, cobots work alongside human workers, enhancing their capabilities and improving safety. AI empowers these robots with advanced capabilities like object recognition, path planning, and human-robot interaction, allowing for flexible and collaborative automation.
Data Analytics and Decision Making: The Power of Insights
The heart of a smart factory is its ability to collect, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of data. AI-powered analytics tools can uncover valuable insights that can inform strategic decisions, improve processes, and drive continuous improvement. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions based on real-time information, leading to a more efficient and profitable operation.
The Human Element in the Age of AI
While AI is transforming manufacturing, the human element remains crucial. The focus isn’t on replacing human workers but on augmenting their capabilities. Smart factory technologies empower workers with intelligent tools, enabling them to focus on higher-level tasks such as problem-solving, innovation, and managing complex systems. Reskilling and upskilling initiatives are essential to ensure that the workforce can adapt and thrive in this evolving environment.
The Future of Smart Factories: A Vision of Continuous Improvement
The journey towards truly smart factories is ongoing, with ongoing technological advancements pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As AI continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated applications in manufacturing, leading to greater efficiency, flexibility, sustainability, and competitiveness. The future of manufacturing is intelligent, adaptive, and human-centered. Read also about AI-enabled smart factories.




