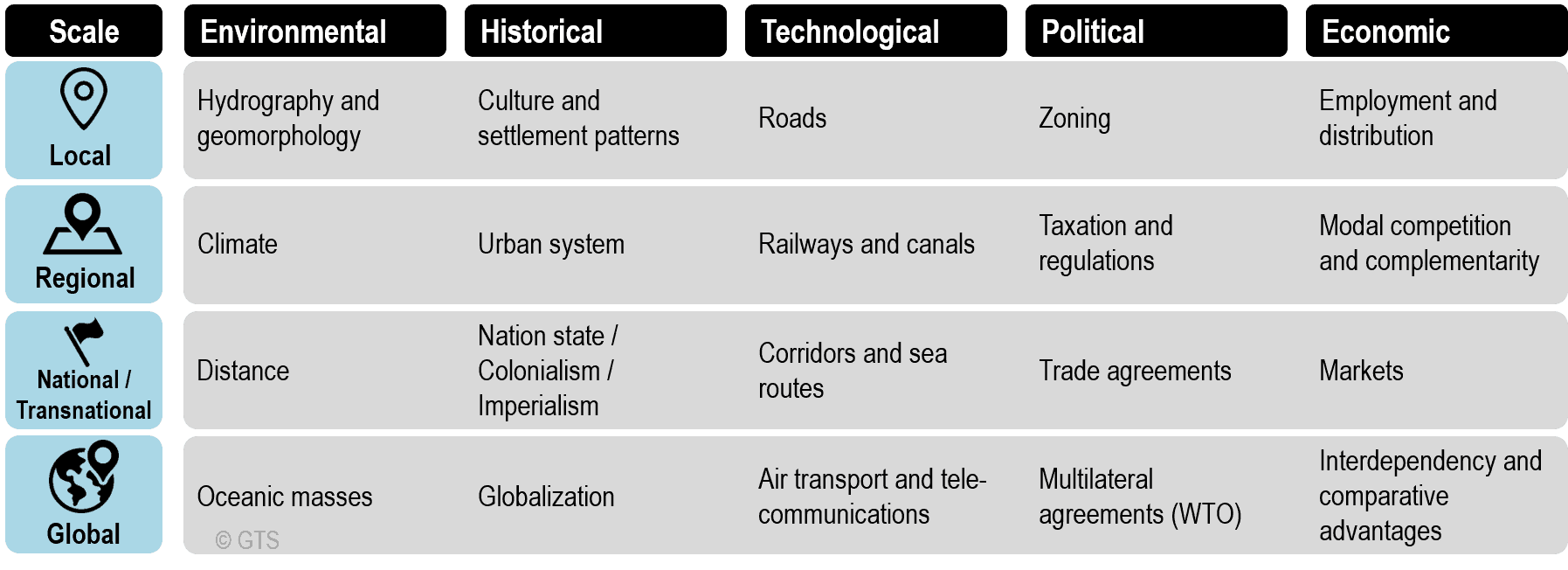
Global Economic Shifts: Changes in Transportation Regulations
Revolutionizing Connectivity: Examining Global Economic Effects of Changes in Transportation Regulations
The evolution of transportation regulations is a catalyst for profound changes in the global economic landscape. This article explores the far-reaching effects of adjustments in transportation regulations, dissecting how these shifts influence economies on a worldwide scale.
Efficiency Gains and Supply Chain Dynamics
Changes in transportation regulations often aim to enhance efficiency in the movement of goods and people. Reforms may address aspects such as logistics, shipping, and air travel, optimizing supply chain dynamics. Streamlining transportation processes results in cost savings for businesses, positively impacting their competitiveness and contributing to economic efficiency.
Impact on Trade and Global Commerce
Transportation regulations are intricately linked with international trade. Alterations in these regulations can facilitate or hinder the flow of goods across borders. Efficient transportation systems foster global commerce, enabling businesses to reach broader markets. Conversely, restrictive regulations may impede trade, affecting industries and potentially leading to shifts in economic balances.
Infrastructure Investment and Economic Stimulus
Changes in transportation regulations often coincide with increased infrastructure investment. Governments may implement reforms to encourage private sector participation in transportation projects, stimulating economic activity. Investment in roads, ports, and other transportation infrastructure creates jobs, boosts local industries, and acts as a powerful economic stimulus.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Transport
Modern transportation regulations increasingly prioritize environmental sustainability. Revisions may target fuel efficiency standards, emissions reductions, and the promotion of sustainable transport modes. These changes not only contribute to environmental conservation but also align with the growing global emphasis on sustainable practices, shaping economic activities in harmony with ecological goals.
Technological Integration and Smart Mobility
The intersection of transportation regulations and technology is reshaping mobility. Regulations may encourage the integration of smart technologies, such as autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management systems. These innovations improve transportation efficiency, reduce congestion, and lay the foundation for smart cities, influencing economic activities in urban centers.
Logistics and the E-Commerce Revolution
E-commerce relies heavily on efficient logistics and transportation systems. Changes in regulations impact how goods are transported and delivered, influencing the logistics landscape. Easier access to global markets and faster delivery times can spur the growth of e-commerce, contributing to the expansion of online businesses and shaping the digital economy.
Global Connectivity and Tourism Impact
Transportation regulations play a vital role in shaping global connectivity and tourism. Policies that facilitate easier movement of people between countries contribute to the growth of the tourism industry. Conversely, restrictive regulations may deter international travel. The tourism sector, closely tied to transportation, significantly influences economies worldwide.
Challenges in Regulatory Alignment and Standardization
Harmonizing transportation regulations across borders is a complex challenge. Divergent regulations can create inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs for international transport. Achieving regulatory alignment and standardization becomes essential for smooth cross-border transportation, fostering international trade and economic cooperation.
Job Creation in Transportation Industries
The transportation sector is a significant source of employment globally. Changes in regulations, especially those promoting infrastructure projects and technological advancements, contribute to job creation. Jobs in logistics, shipping, aviation, and related industries play a crucial role in shaping local and national economies.
Resilience and Adaptation in a Changing Landscape
As transportation regulations evolve, businesses and industries must adapt to new realities. Resilience in the face of change becomes a key factor for economic success. Businesses that can navigate and capitalize on the evolving transportation landscape are better positioned to thrive in the global economy.
For an in-depth exploration of the global economic effects of changes in transportation regulations, refer to this comprehensive study here. The study offers detailed analyses of case studies, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of global economies responding to evolving transportation regulations.
World Economic Resilience Amid Natural Disasters
Introduction:
Natural disasters pose significant challenges to societies worldwide, and their impact on the global economy cannot be overstated. This article delves into the remarkable capacity of the world economy to rebound and adapt in the face of natural disasters, showcasing resilience as a key factor in mitigating the economic fallout.
Historical Perspectives:
The historical record is punctuated with instances where natural disasters have disrupted economic activities. From earthquakes to hurricanes, each event has left an indelible mark on affected regions. However, history also reveals the world’s ability to rebuild, showing an inherent resilience that transcends adversity.
Infrastructure and Economic Foundations:
The resilience of the world economy in the aftermath of natural disasters is closely tied to robust infrastructure. Nations with well-developed and adaptable infrastructure are better equipped to absorb shocks, facilitating a faster recovery process. Investments in resilient structures contribute significantly to economic continuity.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics:
Natural disasters have the potential to disrupt global supply chains, impacting industries and businesses across borders. Understanding and addressing vulnerabilities in the supply chain is crucial for maintaining economic resilience. Diversification and contingency planning play pivotal roles in minimizing disruptions.
Insurance and Risk Management:
The world economy navigates the challenges of natural disasters with the support of insurance and risk management mechanisms. Businesses and nations alike invest in comprehensive risk mitigation strategies to minimize financial losses, ensuring a more prompt recovery and sustained economic stability.
Technological Advancements:
Technological innovations contribute substantially to enhancing economic resilience. From early warning systems to advanced construction materials, technology plays a vital role in minimizing the impact of natural disasters. Continuous advancements empower societies to respond more effectively, safeguarding economic interests.
Government Policies and Preparedness:
Effective government policies and disaster preparedness initiatives are instrumental in fostering economic resilience. Nations that prioritize proactive measures, such as early warning systems, evacuation plans, and post-disaster recovery strategies, demonstrate a greater ability to bounce back from the economic aftermath of natural disasters.
Community and Social Resilience:
The resilience of local communities is intertwined with economic recovery. The ability of communities to support each other, rebuild social structures, and collaborate in the face of adversity contributes significantly to overall economic resilience. Social cohesion is a powerful force in the post-disaster recovery process.
Environmental Sustainability Amid Challenges:
As the world faces an increasing frequency of natural disasters, there is a growing recognition of the importance of environmental sustainability. Balancing economic activities with ecological preservation is essential for long-term resilience, fostering a harmonious coexistence with the natural world.
Global Cooperation and Solidarity:
In an interconnected world, global cooperation is paramount for addressing the economic impacts of natural disasters. Solidarity among nations, sharing resources, expertise, and support, enhances the collective ability to withstand and recover from these challenges, reinforcing the world’s economic resilience.
For more insights into world economic resilience in the face of natural disasters, visit World economic resilience in the face of natural disasters.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the world’s economic resilience in the face of natural disasters is a testament to human ingenuity, technological progress, and collaborative efforts. While challenges persist, the ability of nations to learn from the past, invest in resilience, and foster global cooperation showcases a remarkable capacity to adapt and thrive amid adversity. The journey toward a more resilient world economy continues, guided by the lessons of the past and a commitment to building a sustainable and adaptable future.
Global Economic Resilience: Responding to Public Health Challenges
Navigating Challenges: Global Economic Resilience in Public Health Crisis
In the face of unprecedented public health challenges, the global community is compelled to respond with resilience and agility. The interplay between the health and economic sectors becomes a critical focal point, requiring coordinated efforts, innovative solutions, and adaptive strategies to safeguard both public well-being and economic stability.
Economic Impact of Public Health Crises: A Dual Challenge
Public health crises, such as pandemics, exert profound economic impacts that reverberate across industries and nations. The dual challenge of mitigating the spread of diseases and stabilizing economies becomes apparent. The economic repercussions manifest in disrupted supply chains, decreased consumer spending, and financial market volatility, posing a complex challenge that demands multifaceted solutions.
Fiscal Stimulus Measures: Bolstering Economic Resilience
Governments worldwide deploy fiscal stimulus measures to counteract the economic fallout of public health crises. These measures include financial aid packages, tax relief, and infrastructure spending aimed at supporting businesses, individuals, and sectors heavily affected by disruptions. Fiscal stimulus becomes a key tool in stabilizing economies, fostering recovery, and preventing long-term damage.
Monetary Policy Responses: Navigating Economic Uncertainties
Central banks play a pivotal role in the global economic response to public health challenges. Monetary policy responses involve interest rate adjustments, liquidity injections, and unconventional measures to ensure financial stability. The goal is to ease financial conditions, provide support to credit markets, and bolster confidence in the face of economic uncertainties triggered by health crises.
Adapting Business Models: Innovation Amidst Disruptions
Businesses face the imperative of adapting their models to thrive amidst disruptions. From embracing digital transformations to reevaluating supply chains, companies navigate a new landscape shaped by public health challenges. Innovative solutions, such as remote work arrangements and e-commerce strategies, become integral to sustaining operations and ensuring resilience in the face of uncertainties.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics: A Balancing Act
Public health crises expose vulnerabilities in global supply chains, necessitating a reassessment of dynamics. While there is a trend towards regionalization to mitigate risks, maintaining a delicate balance between efficiency and resilience becomes paramount. Governments and businesses collaborate to enhance supply chain robustness without compromising the benefits of globalization.
Economic Diplomacy in Crisis Management
International cooperation and economic diplomacy assume heightened significance in crisis management. Nations collaborate to share resources, information, and expertise. Economic diplomacy plays a role in trade negotiations, investment collaborations, and collective efforts to stabilize global markets. The shared goal is to foster a coordinated response that transcends borders and addresses the collective challenges posed by public health crises.
Healthcare Investment and Research Collaboration
Public health challenges underscore the importance of healthcare investments and global research collaboration. Governments and private entities direct resources towards strengthening healthcare infrastructure, vaccine development, and pandemic preparedness. The collaboration between the public and private sectors becomes a linchpin in advancing medical solutions and enhancing global health resilience.
Digital Health Innovations: Transforming Healthcare Systems
The intersection of technology and healthcare gains prominence in the global response to public health challenges. Digital health innovations, including telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and data analytics, contribute to more effective healthcare delivery. Governments and businesses invest in these technological advancements to improve healthcare accessibility and responsiveness during crises.
Social Safety Nets and Inclusive Policies
Building resilient societies requires a focus on social safety nets and inclusive policies. Governments design programs to support vulnerable populations, ensure access to healthcare, and address socioeconomic disparities exacerbated by public health challenges. Inclusive policies become a cornerstone for fostering societal resilience and mitigating the long-term economic impact on marginalized communities.
Towards a Resilient Future: Lessons Learned
As the global economic response to public health challenges unfolds, lessons learned become guideposts for a more resilient future. The importance of preparedness, collaboration, and innovation is evident. Governments, businesses, and communities recognize the need for adaptable strategies that can navigate the complexities of interconnected health and economic landscapes.
Explore more about the Global Economic Response to Public Health Challenges and the strategies shaping resilience amidst unprecedented crises.

