Fostering Global Economic Sustainability: A Path to Prosperity

Paving the Way for Prosperity: Global Economic Sustainability
In an era where the interconnectedness of nations is more evident than ever, the concept of global economic sustainability takes center stage. This article embarks on a journey to explore the imperative of fostering sustainability on a global scale, examining the challenges, outlining key components, and advocating for collaborative efforts to secure a prosperous future for all.
To delve into the intricacies of global economic sustainability, visit Global Economic Sustainability.
The Challenge of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development on a global scale poses a formidable challenge. As nations strive for economic growth, they must concurrently address environmental concerns, social equity, and resource management. Achieving this delicate balance requires a paradigm shift in economic thinking, where sustainability is not a secondary consideration but an integral part of development strategies.
Environmental Stewardship in Economic Policies
One of the pillars of global economic sustainability is environmental stewardship. Nations and businesses must align economic policies with environmental conservation goals. This involves transitioning to renewable energy sources, adopting sustainable practices in industries, and integrating circular economy principles to minimize waste and resource depletion.
Social Inclusion and Equitable Growth
Economic sustainability goes hand in hand with social inclusion. Sustainable development must prioritize equitable growth, ensuring that the benefits of economic progress are shared across diverse segments of society. This includes addressing income inequality, promoting fair labor practices, and investing in education and healthcare to uplift communities globally.
Resilient Infrastructure for Future Challenges
Building resilient infrastructure is a key component of global economic sustainability. As the world faces challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and technological disruptions, infrastructure must be designed to withstand and adapt to these shocks. This includes investing in sustainable urban development, resilient transportation networks, and digital infrastructure for a connected world.
Innovation and Technology for Sustainable Solutions
Embracing innovation and technology is crucial for achieving global economic sustainability. From green technologies to digital solutions, innovation plays a pivotal role in crafting sustainable solutions. Governments, businesses, and international collaborations should incentivize research and development that fosters sustainable practices and addresses pressing global challenges.
Global Collaboration in Addressing Challenges
The complexity of global economic sustainability necessitates collaboration on an international scale. Nations must come together to set common goals, share best practices, and coordinate efforts to address transboundary issues. Initiatives like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for such collaborative endeavors, emphasizing a shared responsibility for a sustainable future.
Circular Economy: Minimizing Waste, Maximizing Resources
Adopting a circular economy model is paramount for global economic sustainability. This approach aims to minimize waste by promoting recycling, reusing materials, and designing products with a focus on longevity. Shifting from a linear “take, make, dispose” model to a circular one contributes to resource efficiency and reduces the environmental impact of economic activities.
Green Finance and Investment in Sustainability
Global economic sustainability requires a significant shift in financial practices. Green finance, which involves investing in environmentally sustainable projects, is gaining prominence. Governments and financial institutions should incentivize investments in renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and environmentally responsible businesses to redirect capital towards sustainability-focused initiatives.
Educating for Sustainability Awareness
Creating a sustainable future necessitates an informed and engaged global citizenry. Education plays a pivotal role in fostering sustainability awareness. Nations should integrate sustainability education into school curricula, promoting understanding of environmental, social, and economic interdependencies. An educated populace is more likely to support and drive sustainable practices.
Measuring Progress with Sustainable Metrics
To gauge the success of global economic sustainability efforts, there is a need for comprehensive metrics that go beyond traditional economic indicators. Sustainable Development Indicators should encompass environmental health, social well-being, and economic resilience. These metrics provide a holistic view of progress and guide nations in refining their strategies for a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: A Shared Vision for Tomorrow
In conclusion, fostering global economic sustainability is not a choice but a necessity for the well-being of current and future generations. It requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide. By embracing environmental stewardship, social inclusion, resilient infrastructure, innovation, and global collaboration, nations can pave the way for a sustainable future where prosperity is shared by all.
World Economic Governance: Navigating Global Dynamics

Navigating the Global Landscape: World Economic Governance
The intricate dance of global economic dynamics necessitates effective governance to ensure stability and sustainable growth. This article delves into the realm of world economic governance, examining the challenges and complexities it addresses, exploring the institutions and mechanisms in play, and highlighting the imperative for collaborative efforts in steering the course of the global economy.
Challenges in a Globalized World
In an increasingly interconnected world, economic challenges transcend borders. From financial crises to trade disputes and pandemics, the complexities faced by nations require a coordinated response. World economic governance emerges as the linchpin in addressing these challenges, providing a framework for collaboration and collective decision-making on a global scale.
To explore the nuances of world economic governance, visit World Economic Governance.
Institutions Shaping Global Economic Policies
Central to world economic governance are the institutions that shape and implement global economic policies. International organizations like the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and World Trade Organization (WTO) play pivotal roles in coordinating monetary policy, providing development assistance, and facilitating international trade agreements. These institutions serve as forums for dialogue and decision-making among nations.
Policy Coordination for Macroeconomic Stability
Macroeconomic stability is a shared goal, and world economic governance involves policy coordination among nations. This coordination aims to prevent global economic imbalances, currency fluctuations, and trade distortions. Through forums such as the G7 and G20, nations engage in dialogues to align policies, harmonize regulations, and promote stability in the face of economic uncertainties.
Trade Governance and Multilateral Agreements
Trade governance is a critical facet of world economic governance, shaping the rules and norms that govern international trade. Multilateral agreements, such as the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and its successor, the WTO, provide frameworks for negotiations, dispute resolution, and the establishment of a rules-based global trading system. These agreements foster open markets and contribute to global economic integration.
Financial Regulation and Stability
In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, the importance of robust financial regulation became evident. World economic governance addresses the need for coordinated efforts to regulate financial institutions, prevent systemic risks, and enhance the resilience of the global financial system. Bodies like the Financial Stability Board (FSB) work towards developing and implementing international financial regulations.
Addressing Global Inequalities and Sustainable Development
World economic governance extends beyond financial and trade considerations to address global inequalities and promote sustainable development. The United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) serve as a framework for collective action on issues ranging from poverty and inequality to climate change. Governance mechanisms aim to align national policies with these broader global objectives.
Technology Governance in the Digital Age
In the digital age, technology governance has become a crucial dimension of world economic governance. As technological advancements reshape industries and societies, governance mechanisms must adapt to address issues like data privacy, cybersecurity, and the ethical use of emerging technologies. International collaboration on technology governance ensures that standards and norms align with global interests.
Environmental Governance for a Sustainable Future
Environmental sustainability is a pressing global concern, and world economic governance recognizes the need for coordinated efforts to address climate change and environmental degradation. Agreements like the Paris Agreement bring nations together to set emission reduction targets and promote sustainable practices. Environmental governance intertwines with economic policies to build a resilient and sustainable global future.
Emerging Challenges and Adaptive Governance
The landscape of global challenges is ever-evolving, with new complexities emerging over time. World economic governance must be adaptive, anticipating and addressing emerging challenges such as public health crises, geopolitical shifts, and technological disruptions. The ability of governance mechanisms to evolve ensures their relevance in steering the global economy through uncertain terrains.
Collaborative Leadership for Global Prosperity
In conclusion, world economic governance is a complex tapestry of institutions, policies, and collaborative efforts aimed at steering the global economy towards prosperity. As nations grapple with shared challenges, from economic uncertainties to environmental threats, collaborative leadership becomes imperative. By fostering dialogue, aligning policies, and embracing shared responsibilities, world economic governance charts a course for a more stable, inclusive, and sustainable global economy.
Balancing Acts: International Debt and Economic Sustainability

Navigating the Tightrope: International Debt and Economic Sustainability
International debt is a complex facet of the global economic landscape, often requiring a delicate balancing act to ensure economic sustainability. This article delves into the intricate relationship between international debt and a nation’s ability to sustain economic growth, exploring the challenges, implications, and strategies for achieving equilibrium.
Understanding International Debt: A Double-Edged Sword
International debt, accrued by nations through borrowing from foreign creditors, can be both a catalyst for development and a potential threat to economic stability. While it facilitates infrastructure projects, stimulates economic growth, and fills budgetary gaps, excessive debt levels can lead to vulnerabilities, hindering a nation’s capacity to meet financial obligations and sustain economic health.
Implications for Economic Sustainability: The Weight of Debt
The implications of international debt on economic sustainability are profound. High debt levels can strain national budgets, diverting significant portions of revenue towards debt servicing. This leaves fewer resources for crucial investments in education, healthcare, and social welfare – essential components of sustained economic development.
The Role of Debt in Economic Growth: Fueling Progress
On the flip side, judiciously managed international debt can serve as a catalyst for economic growth. Borrowed funds can finance critical infrastructure projects, stimulate job creation, and foster innovation. When debt is deployed strategically, it becomes an investment in the nation’s future prosperity, contributing to sustainable economic development.
Challenges of Excessive Debt: A Precarious Balancing Act
Excessive international debt poses a precarious balancing act for nations. The burden of repaying loans, especially when denominated in foreign currencies, can escalate during economic downturns or currency depreciations. This vulnerability exposes nations to financial crises, making the delicate balancing act between debt accumulation and economic sustainability even more challenging.
Debt Sustainability and Fiscal Responsibility
Maintaining debt sustainability requires a commitment to fiscal responsibility. Nations must craft prudent fiscal policies, ensuring that borrowing aligns with the capacity to repay. Transparent financial management, effective debt monitoring systems, and adherence to responsible lending and borrowing practices are essential for mitigating the risks associated with international debt.
The Role of International Organizations: A Supportive Net
International organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, play a crucial role in supporting nations in managing their international debt. These organizations provide financial assistance, offer guidance on debt restructuring, and promote sound economic policies that enhance a nation’s capacity for sustainable debt management.
Debt Restructuring and Negotiations: Charting a Sustainable Path
When faced with the challenges of unsustainable debt levels, nations often resort to debt restructuring and negotiations. Restructuring agreements may involve extending repayment periods, reducing interest rates, or even partial debt forgiveness. These measures aim to alleviate the immediate financial burden, allowing nations to regain economic stability and chart a sustainable path forward.
Global Economic Interconnectedness: The Domino Effect
The global economic landscape is inherently interconnected, and the implications of international debt resonate globally. Economic challenges in one nation can trigger a domino effect, impacting creditors, trading partners, and international financial markets. This interdependence underscores the importance of collaborative efforts to address debt-related challenges and foster global economic stability.
Strategies for Sustainable Debt Management: A Roadmap Forward
Striking a balance between international debt and economic sustainability requires a comprehensive approach. Nations must prioritize economic diversification, revenue generation, and sound fiscal policies. Investing in education, healthcare, and social welfare creates a foundation for inclusive economic growth, reducing the reliance on debt for immediate budgetary needs.
Fostering a Future of Economic Resilience
In conclusion, the relationship between international debt and economic sustainability is intricate and demands thoughtful navigation. As nations grapple with the challenges posed by debt, the focus should be on fostering a future of economic resilience. This involves strategic debt management, fiscal responsibility, and a commitment to investments that lay the groundwork for sustained, inclusive economic growth.
To explore more about International debt and economic sustainability, visit tankionlineaz.com.
Navigating Economic Shifts Amid Global Demographic Changes

Navigating Economic Shifts Amid Global Demographic Changes
The world is undergoing significant demographic shifts, and these changes are reverberating through the economic landscape. This article explores the multifaceted economic consequences of global demographic changes, examining their impact on various sectors and the strategies needed to navigate this evolving terrain.
Demographic Trends and Economic Dynamics
Demographic changes, such as aging populations and shifts in birth rates, have profound implications for economic structures. As populations age, the labor force composition evolves, influencing productivity, consumption patterns, and overall economic growth. Understanding these demographic trends is essential for policymakers and businesses to formulate effective strategies.
Labor Market Challenges and Opportunities
One of the immediate economic consequences of demographic changes is the transformation of the labor market. Aging populations often lead to a shrinking workforce, posing challenges for industries that rely heavily on labor. However, this shift also presents opportunities for innovation and automation to fill the gaps and enhance productivity.
Pension Systems Under Strain
As populations age, pension systems come under increasing strain. A larger retired demographic, coupled with longer life expectancies, places a burden on pension funds. Governments and businesses must reassess and adapt pension systems to ensure sustainability and to support the financial well-being of the aging population.
Consumer Behavior and Market Demands
Demographic changes influence consumer behavior and market demands. Aging populations tend to prioritize different products and services, creating new opportunities for businesses while challenging traditional market norms. Adapting to evolving consumer preferences becomes crucial for sustained economic success.
Healthcare and Social Services Challenges
The aging demographic also places stress on healthcare and social services. Increased demand for healthcare facilities, long-term care, and other related services necessitates adjustments in public policy and healthcare infrastructure. Addressing these challenges is vital for maintaining a healthy and productive society.
Global Migration Patterns and Economic Impact
Demographic changes often drive global migration patterns. Economic consequences arise as countries experience shifts in their population composition due to immigration and emigration. Understanding and managing these migration patterns is crucial for maintaining a skilled and diverse workforce.
To delve deeper into the economic consequences of global demographic changes, visit Economic Consequences of Global Demographic Changes.
Innovation and Economic Resilience
Amidst demographic changes, fostering innovation becomes a linchpin for economic resilience. Businesses that adapt to demographic shifts by embracing technological advancements and innovative practices position themselves for success. Governments play a pivotal role in creating an environment conducive to innovation through supportive policies and investment in research and development.
Educational Systems for the Future Workforce
The evolving workforce requires a corresponding evolution in educational systems. Investing in education that aligns with the skills needed in the modern economy is crucial. Adaptable educational systems help prepare the workforce for the challenges and opportunities presented by global demographic changes.
Balancing Dependency Ratios for Economic Stability
Dependency ratios, comparing the working-age population to dependent populations (children and elderly), play a crucial role in economic stability. Understanding and managing these ratios are essential for policymakers to ensure sustainable economic growth. Strategies that promote a healthy balance contribute to the overall well-being of societies.
Sustainable Development Goals and Demographic Changes
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) take into account the demographic changes shaping the world. Addressing issues such as poverty, healthcare, education, and gender equality becomes even more critical in the context of evolving global demographics. Aligning economic policies with these goals contributes to a more sustainable and inclusive future.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future
In conclusion, the economic consequences of global demographic changes are intricate and far-reaching. Navigating this future requires a holistic approach, involving governments, businesses, and individuals. Adapting to shifting demographics with innovative solutions, robust education systems, and a focus on sustainable development will be key in building resilient economies that thrive amidst demographic transformations.
Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment: Building Global Prosperity
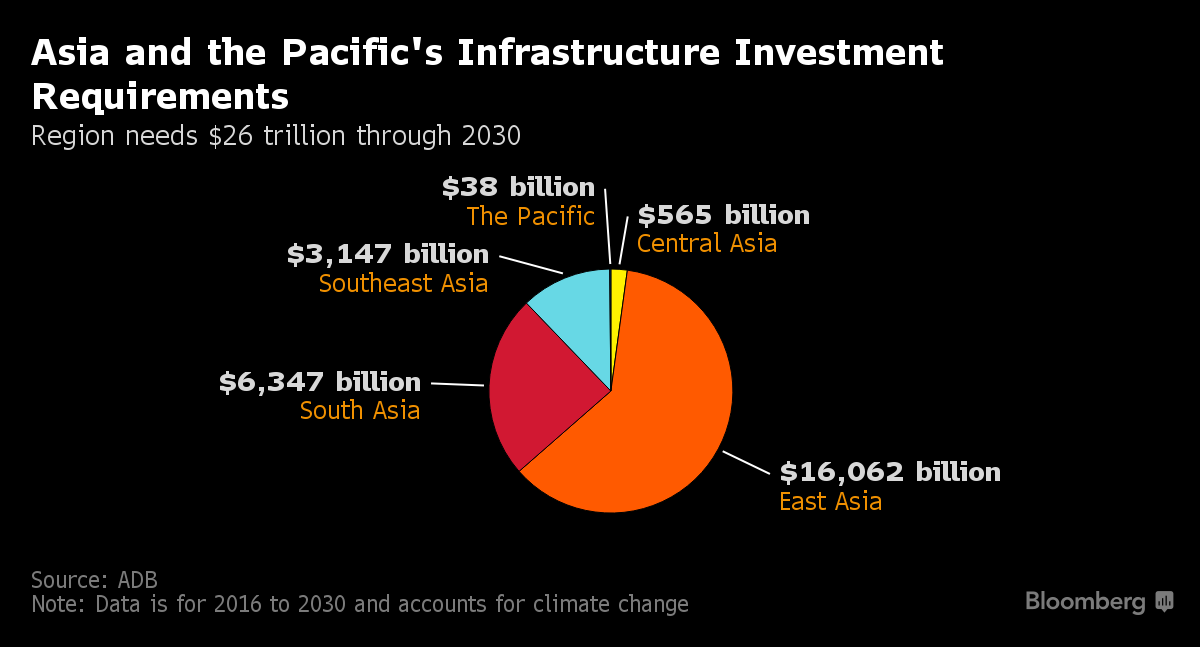
Building Global Prosperity through Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the role of economic infrastructure investment takes center stage. Governments and businesses globally are recognizing the importance of building and maintaining robust infrastructure to foster economic growth and ensure long-term prosperity.
The Foundation of Economic Development
Investment in economic infrastructure forms the bedrock for sustainable development. Roads, bridges, airports, and other essential facilities are critical components that facilitate the movement of goods and people. This physical connectivity is vital for fostering trade, attracting investments, and creating a conducive environment for economic activities to flourish.
Enhancing Connectivity for Trade
One of the primary objectives of worldwide economic infrastructure investment is to enhance connectivity for international trade. Efficient transportation networks and modern logistics systems reduce transit times and costs, making it more attractive for businesses to engage in cross-border trade. This connectivity also opens up new markets and opportunities for global economic integration.
Strategic Importance of Energy Infrastructure
Energy infrastructure plays a strategic role in powering economic activities. Investments in reliable and sustainable energy sources contribute to economic stability and growth. Countries that prioritize diverse and resilient energy infrastructures are better positioned to weather fluctuations in energy markets, ensuring a stable and affordable energy supply for businesses and households.
Digital Infrastructure for the Modern Economy
In the digital age, robust information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure are indispensable for economic competitiveness. High-speed internet, data centers, and advanced communication networks support the growth of digital economies. Nations that invest in cutting-edge digital infrastructure foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of new industries.
Job Creation and Economic Stimulus
Beyond the tangible benefits of improved connectivity and efficiency, worldwide economic infrastructure investment serves as a powerful tool for job creation and economic stimulus. Infrastructure projects, whether they involve construction, maintenance, or upgrades, create employment opportunities, injecting funds directly into local economies. This, in turn, stimulates consumer spending and overall economic activity.
Sustainable Infrastructure for Environmental Resilience
In the era of climate change, there is a growing emphasis on incorporating sustainability into infrastructure projects. Worldwide economic infrastructure investment can align with environmental goals by prioritizing sustainable practices. Green infrastructure, renewable energy projects, and eco-friendly transportation solutions contribute to environmental resilience and long-term economic viability.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Collaborative Approach
Many countries are turning to public-private partnerships (PPPs) to fund and implement large-scale infrastructure projects. This collaborative approach allows governments to leverage private sector expertise and financing, sharing both risks and rewards. PPPs can accelerate the delivery of infrastructure solutions, addressing critical needs more efficiently.
Challenges in Infrastructure Investment
While the benefits of worldwide economic infrastructure investment are evident, challenges persist. Funding constraints, regulatory hurdles, and geopolitical considerations can impede progress. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, transparent governance, and international cooperation to ensure that infrastructure projects meet the needs of diverse communities.
Resilience in the Face of Global Challenges
Investing in resilient infrastructure is essential for mitigating the impact of global challenges, such as pandemics and natural disasters. Resilient infrastructure can withstand shocks and disruptions, enabling communities to recover quickly and continue their economic activities. This resilience is a key component of building a more secure and prosperous future.
Navigating the Future: Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment
As we navigate the complex landscape of a rapidly changing world, worldwide economic infrastructure investment emerges as a critical driver of global prosperity. The interconnectedness of economies demands a concerted effort to build infrastructure that not only meets current needs but also anticipates future challenges. By prioritizing strategic investments and embracing innovative solutions, nations can lay the foundation for sustained economic growth and shared prosperity.
To explore more about the transformative impact of Worldwide Economic Infrastructure Investment, visit our comprehensive guide.
Revitalizing Economies: Global Plans for Economic Recovery

Revitalizing Economies: Navigating Global Economic Recovery Plans
The aftermath of global disruptions, whether caused by pandemics or economic downturns, necessitates robust and strategic responses. This article delves into the diverse array of global economic recovery plans, exploring the overarching strategies, regional variations, and the collaborative efforts aimed at reinvigorating economies worldwide.
To explore the world of global economic recovery plans, visit Global Economic Recovery Plans.
Unveiling Comprehensive Strategies for Recovery
Global economic recovery plans emerge as comprehensive strategies designed to address the multifaceted challenges posed by economic crises. These plans typically encompass fiscal, monetary, and structural measures aimed at restoring confidence, stimulating demand, and fostering sustainable growth. Nations worldwide deploy a mix of policies tailored to their unique circumstances, reflecting a shared goal of revitalizing economic activity.
Fiscal Measures: Injecting Stimulus into Economies
Fiscal measures play a pivotal role in global economic recovery plans. Governments deploy stimulus packages that involve increased public spending, tax incentives, and financial support to individuals and businesses. The objective is to inject liquidity into the economy, spur consumption, and provide a financial safety net for those affected by economic downturns. The scale and nature of fiscal interventions vary, reflecting the diverse economic landscapes.
Monetary Policy: Navigating Interest Rates and Liquidity
Central banks take center stage in global recovery efforts through monetary policy tools. Adjusting interest rates, implementing quantitative easing, and ensuring ample liquidity are key components. These measures aim to stabilize financial markets, encourage borrowing and investment, and manage inflationary pressures. Central banks collaborate to maintain monetary stability globally, recognizing the interconnected nature of the world economy.
Sectoral Focus: Tailoring Recovery to Specific Industries
Global economic recovery plans often adopt a sectoral approach, recognizing the unique challenges faced by different industries. Sectors such as tourism, hospitality, and aviation may require targeted support due to their vulnerability during crises. Governments and international bodies collaborate to devise strategies that provide assistance to sectors disproportionately impacted, ensuring a more balanced recovery.
International Cooperation: Collaborative Efforts for Resilience
The interconnectedness of economies underscores the importance of international cooperation in recovery plans. Nations collaborate through forums, such as the G20 and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), to coordinate policies, share best practices, and provide financial assistance to countries in need. This collaborative approach enhances global economic resilience and fosters a more synchronized recovery.
Green Recovery: Integrating Sustainability into Plans
An emerging trend in global economic recovery plans is the emphasis on a green recovery. Recognizing the urgency of addressing environmental challenges, recovery initiatives increasingly incorporate sustainable practices. Investments in renewable energy, green infrastructure, and eco-friendly technologies contribute not only to economic revitalization but also to long-term environmental sustainability.
Digital Transformation: Accelerating Technological Adoption
The pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of economies, and recovery plans reflect this shift. Investments in digital infrastructure, e-commerce, and technology adoption are prominent features. The goal is not only to recover lost ground but to position economies for future resilience and competitiveness in an increasingly digital world.
Inclusive Growth: Prioritizing Social and Economic Equity
Global economic recovery plans aspire to achieve inclusive growth, recognizing the imperative of addressing social and economic inequities. Policies that prioritize education, healthcare, and social safety nets contribute to a more equitable recovery. The emphasis is on leaving no one behind, ensuring that the benefits of recovery are shared across diverse segments of society.
Challenges and Adaptations: Navigating the Unknown
Despite meticulous planning, global economic recovery is not without challenges. Uncertainties such as evolving pandemic dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and shifts in consumer behavior require continuous adaptation. Flexibility and resilience become watchwords, and recovery plans are dynamic documents that respond to the ever-changing global landscape.
Conclusion: Charting a Collective Path Forward
In conclusion, the journey of global economic recovery is a collective endeavor that transcends borders. The diverse strategies embedded in recovery plans underscore the shared commitment to revitalizing economies and creating a more resilient and sustainable future. As nations navigate the complexities of recovery, collaboration, innovation, and adaptability emerge as crucial elements in charting a collective path forward.
Global Integration Impact: Economic Dynamics Unveiled

Unveiling the Economic Dynamics: Effects of Global Economic Integration
In an era marked by increased interconnectedness, the effects of global economic integration extend far beyond borders, shaping the economic landscape in profound ways. From trade and investment to cultural exchange, the impact of global integration on economies is multifaceted, presenting both opportunities and challenges.
Trade Liberalization and Economic Growth
One of the primary drivers of global economic integration is trade liberalization. Reduced trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, foster increased international trade. This surge in cross-border commerce contributes to economic growth as nations gain access to new markets, diverse products, and a broader consumer base. The reciprocal nature of trade agreements creates a symbiotic relationship, fueling economic expansion.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Flows: A Catalyst for Development
Global economic integration attracts substantial Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows. Companies seek opportunities beyond their domestic markets, establishing operations and investing in foreign countries. This influx of investment acts as a catalyst for economic development, driving innovation, creating jobs, and fostering technology transfer. However, managing the balance between attracting investment and protecting national interests becomes a key challenge for governments.
Supply Chain Interdependence: Efficiency vs. Vulnerability
The integration of global supply chains is a hallmark of economic globalization. While this interconnectedness enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness, it also introduces vulnerabilities. Disruptions in one part of the world can have cascading effects on production and distribution globally. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the fragility of highly interdependent supply chains, prompting a reevaluation of resilience and risk management strategies.
Technological Transfer and Innovation Acceleration
Global economic integration facilitates the transfer of technology and accelerates innovation. Companies operating in diverse markets bring unique perspectives and technological advancements to different regions. This cross-pollination of ideas contributes to global progress and the diffusion of cutting-edge technologies. However, managing the ethical dimensions of technology transfer and ensuring fair competition remain critical considerations.
Cultural Exchange and Market Diversity
Beyond the economic realm, global integration fosters cultural exchange. Consumers gain access to a diverse array of products and services from around the world, enriching their cultural experiences. This diversity in the marketplace encourages innovation and competition, as companies strive to meet the preferences and demands of a global consumer base. Cultural exchange becomes a natural byproduct of economic interconnectedness.
Income Inequality and Social Disparities
While global economic integration generates wealth and opportunities, it also contributes to income inequality and social disparities. The benefits of integration are not evenly distributed, and certain segments of society may face job displacement or wage stagnation. Addressing the social implications of economic integration requires thoughtful policies that promote inclusivity, education, and social safety nets.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainability Challenges
The intensification of global economic activities has environmental ramifications. Increased production and transportation contribute to carbon emissions, deforestation, and resource depletion. Achieving sustainable development amidst global integration necessitates a focus on environmentally responsible practices, renewable energy sources, and international cooperation to address shared environmental challenges.
Financial Market Dynamics: Risks and Opportunities
Financial markets are highly influenced by global economic integration. While integration provides opportunities for diversification and investment, it also exposes markets to contagion risks. Economic events in one part of the world can quickly impact financial markets globally. Effective risk management, international regulatory cooperation, and financial resilience become imperative in navigating the dynamics of integrated financial systems.
Policy Coordination and Governance Challenges
Managing the effects of global economic integration requires effective policy coordination and governance at both national and international levels. Nations must strike a balance between reaping the benefits of integration and safeguarding their domestic interests. Issues such as tax avoidance, regulatory arbitrage, and intellectual property rights necessitate collaborative efforts to establish fair and equitable global economic governance.
Shaping a Balanced Future: Navigating Global Integration
In conclusion, the economic effects of global economic integration are far-reaching and complex. Striking a balance between the opportunities and challenges requires proactive policies, ethical considerations, and a commitment to sustainable development. Navigating the evolving landscape of global integration necessitates adaptability, cooperation, and a shared vision for a more inclusive and balanced economic future.
Explore more about the Economic Effects of Global Economic Integration and the intricate dynamics shaping the global economic landscape.
Adapting Worldwide: Strategies for Economic Resilience

Charting Economic Resilience: Worldwide Adaptation Strategies
In the face of dynamic global challenges, economies worldwide are compelled to embrace adaptive strategies to ensure resilience and sustained growth. This article explores the diverse and innovative worldwide economic adaptation strategies that nations and businesses employ to navigate an ever-evolving landscape.
Agile Policies in Response to Global Shifts
Adaptation begins with responsive policies that can swiftly adjust to global shifts. Governments worldwide are reevaluating and recalibrating economic policies to remain agile. This includes flexible fiscal measures, dynamic trade policies, and responsive regulatory frameworks that foster adaptability in the face of uncertainties.
Diversification of Economic Portfolios
Economic diversification is a key strategy employed globally to mitigate risks associated with dependency on specific industries. Nations are diversifying their economic portfolios, investing in emerging sectors such as technology, renewable energy, and healthcare. This diversification enhances economic resilience by reducing vulnerability to shocks in any single sector.
Digital Transformation for Enhanced Productivity
Digital transformation has become a cornerstone of economic adaptation worldwide. Embracing technological advancements, nations and businesses are integrating digital solutions to enhance productivity, streamline processes, and facilitate remote work. This shift not only ensures operational continuity but also positions economies for growth in the digital era.
Innovation Ecosystems Driving Economic Evolution
Creating innovation ecosystems is a strategy employed by countries to drive economic evolution. By fostering environments that encourage research, development, and entrepreneurship, nations can spur innovation. Robust innovation ecosystems attract investment, talent, and foster the development of cutting-edge technologies, contributing to long-term economic growth.
Sustainable Development as a Core Tenet
Global economic adaptation strategies increasingly prioritize sustainability. Balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility is essential for long-term resilience. Nations are embracing sustainable development goals, investing in green technologies, and adopting eco-friendly practices to ensure economic progress aligns with ecological sustainability.
Global Collaboration for Economic Resilience
In an interconnected world, global collaboration is paramount for economic resilience. Countries are forming partnerships and alliances to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. Collaborative efforts contribute to a more robust response to global challenges, fostering economic stability and ensuring that no nation stands alone in the pursuit of resilience.
Investment in Human Capital and Skills Development
Adaptation strategies extend to investing in human capital and skills development. Nations recognize that a skilled and adaptable workforce is essential for navigating evolving economic landscapes. Educational reforms, vocational training, and upskilling initiatives empower individuals to contribute effectively to a rapidly changing economic environment.
Community-Centric Approaches for Inclusive Growth
Adapting economies for worldwide resilience involves adopting community-centric approaches. Policies that prioritize inclusive growth, address social disparities, and empower local communities contribute to overall economic stability. This approach ensures that the benefits of economic adaptation are shared across diverse segments of society.
Resilient Infrastructure for Economic Continuity
Building resilient infrastructure is a fundamental aspect of economic adaptation worldwide. Nations invest in infrastructure projects that withstand natural disasters, cyber threats, and other disruptions. Robust infrastructure ensures continuity in economic activities, reduces vulnerabilities, and lays the foundation for sustained growth.
Fostering Economic Adaptability in Uncertain Times
In conclusion, worldwide economic adaptation strategies are diverse, reflecting the dynamic nature of the global landscape. Nations and businesses alike recognize the need for flexibility, innovation, and collaboration to navigate uncertainties. By fostering economic adaptability, countries can not only withstand challenges but also position themselves for sustainable and inclusive growth.
Explore more about Worldwide Economic Adaptation Strategies and the dynamic approaches shaping global economic resilience.
Facilitating Global Collaboration: Economic Forums and Summits

Facilitating Global Collaboration: Economic Forums and Summits
International economic forums and summits serve as pivotal platforms for fostering collaboration, shaping economic policies, and addressing global challenges. In this exploration, we delve into the significance of these gatherings, their key objectives, and the impact they have on shaping the future of the global economy.
Setting the Stage for Dialogue and Cooperation
Economic forums and summits bring together leaders, policymakers, business magnates, and experts from around the world. These gatherings provide a unique space for open dialogue, allowing participants to exchange ideas, discuss emerging trends, and explore collaborative solutions to complex economic issues. The diversity of perspectives contributes to well-informed decision-making.
Shaping Economic Policies on a Global Scale
One of the primary objectives of international economic forums is to shape and influence economic policies at the global level. Through discussions, negotiations, and agreements, participating nations can establish common ground on issues such as trade, finance, and development. The outcomes often result in policy frameworks that guide economic practices worldwide.
To delve deeper into the impact of international economic forums and summits, visit International Economic Forums and Summits.
Addressing Global Challenges and Crises
Economic forums play a crucial role in addressing global challenges and crises. Whether it’s responding to financial downturns, pandemics, or environmental concerns, these gatherings provide a platform for swift and coordinated responses. Collaborative efforts, fostered through international summits, contribute to a more resilient global economy.
Promoting Trade and Investment Opportunities
Facilitating trade and investment is a recurring theme in international economic forums. Leaders use these platforms to negotiate trade agreements, discuss investment climates, and explore opportunities for economic collaboration. The outcomes of these discussions can lead to increased international trade, improved investment environments, and economic growth.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
As the world embraces the digital age, international economic forums become hubs for discussions on innovation and technological advancements. Leaders and experts explore ways to leverage technology for economic growth, address digital divides, and ensure that technological progress benefits societies globally. Collaborative initiatives can emerge to drive innovation and competitiveness.
Climate Change and Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainability takes center stage in many international economic forums as leaders grapple with the challenges of climate change and work towards achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These forums provide a space for nations to commit to environmentally responsible policies, explore renewable energy initiatives, and foster global cooperation for a sustainable future.
Crisis Prevention and Economic Stability
International economic summits often focus on crisis prevention and maintaining economic stability. Discussions may revolve around fiscal and monetary policies, financial regulations, and strategies for preventing economic crises. The goal is to create a resilient global financial system that can withstand shocks and uncertainties.
Cultural Exchange and Diplomacy
Beyond economic considerations, these forums facilitate cultural exchange and diplomacy. Leaders engage in bilateral and multilateral discussions that extend beyond economic policies, promoting understanding and cooperation among nations. This cultural diplomacy contributes to fostering peaceful relations and strengthening global partnerships.
Networking and Business Opportunities
For business leaders, international economic forums are invaluable networking opportunities. Executives can engage with counterparts from different countries, explore business partnerships, and gain insights into global market trends. These connections not only benefit individual businesses but also contribute to the overall economic ecosystem.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future Through Collaboration
In conclusion, international economic forums and summits play a crucial role in shaping the future of the global economy. By fostering collaboration, influencing policies, and addressing global challenges, these gatherings contribute to a more interconnected and resilient world. As leaders continue to engage in open dialogue and cooperative efforts, the outcomes of these forums pave the way for a sustainable and prosperous global economy.
Building Global Resilience: Strategies for Economic Stability

Navigating Uncertainties: Strategies for World Economic Resilience
In a world marked by constant change and unpredictability, the need for economic resilience strategies has never been more crucial. Nations, businesses, and individuals must adapt to evolving challenges, employing innovative and robust strategies to foster stability and growth on a global scale.
Diversification of Economies: Beyond Dependency
A key strategy for world economic resilience lies in diversifying economies. Over-reliance on specific industries or trading partners can make economies vulnerable to external shocks. Diversification involves developing multiple sectors, fostering innovation, and seeking new markets to reduce dependency on a single economic driver.
Investment in Technological Infrastructure: Embracing Digitalization
The digital era demands a proactive approach to technological infrastructure. World economic resilience is bolstered by investments in digitalization, smart technologies, and connectivity. These investments not only enhance efficiency and competitiveness but also position economies to thrive in the rapidly evolving landscape of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Sustainable Development: Balancing Growth and Environmental Responsibility
Sustainability is a cornerstone of world economic resilience. Balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility is critical for long-term stability. Nations and businesses must adopt sustainable practices, promote renewable energy sources, and prioritize eco-friendly initiatives to address climate change and ensure a resilient future.
Global Collaboration in Crisis Response
In times of crisis, global collaboration becomes paramount. Shared challenges, such as pandemics or economic downturns, require coordinated responses. World economic resilience strategies involve collaborative efforts among nations, international organizations, and businesses to share resources, expertise, and implement unified solutions to mitigate the impact of crises.
Adaptive Financial Policies: Navigating Economic Fluctuations
Economic fluctuations are inevitable, and world economic resilience hinges on adaptive financial policies. Central banks and financial institutions must implement flexible monetary and fiscal policies to navigate uncertainties. This includes measures like interest rate adjustments, stimulus packages, and liquidity support to maintain economic stability during turbulent times.
Investment in Human Capital: Fostering Education and Skills
Human capital is a vital component of world economic resilience. Investing in education and skills development ensures a workforce equipped to handle evolving job requirements. Nations that prioritize lifelong learning, vocational training, and upskilling initiatives empower their citizens to adapt to changing economic landscapes and drive innovation.
Inclusive Economic Policies: Reducing Disparities
Economic resilience is contingent on inclusive policies that reduce disparities. Addressing income inequality, ensuring access to healthcare and education, and promoting social safety nets contribute to a more resilient and stable society. Inclusive economic policies foster social cohesion and provide a foundation for sustained economic growth.
Strategic Resource Management: Mitigating Resource Risks
Strategic resource management is integral to world economic resilience. Nations must assess and diversify their resource dependencies to mitigate risks associated with shortages or disruptions. Efficient resource utilization, recycling initiatives, and strategic stockpiling contribute to a more resilient response to resource-related challenges.
Crisis Preparedness and Contingency Planning
An essential pillar of world economic resilience is crisis preparedness. Governments, businesses, and organizations must engage in thorough contingency planning to anticipate and respond effectively to potential crises. Preparedness involves scenario analysis, risk assessments, and the development of robust contingency plans to minimize disruptions.
Promotion of Innovation Ecosystems: Adapting to Change
Embracing innovation is key to world economic resilience. Establishing innovation ecosystems that support research and development, entrepreneurship, and technology adoption fosters adaptability. Nations and businesses that prioritize innovation are better positioned to navigate disruptions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Towards a Resilient Future
In conclusion, building world economic resilience requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses economic diversification, technological advancement, sustainability, collaboration, and adaptability. By implementing these strategies, nations can navigate uncertainties, foster stability, and build a resilient foundation for a prosperous future.
Explore more about World Economic Resilience Strategies and the dynamic approaches shaping a resilient global economy.

